At the ESMO Congress 2025 in Berlin, Dr. Scott Kopetz (Houston, USA) presented new translational findings from the phase III BREAKWATER study (NCT04607421), the pivotal trial that established encorafenib + cetuximab + mFOLFOX6 (EC + mFOLFOX6) as the new first-line standard of care for patients with BRAF V600E–mutant metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC).
These results provide a detailed look at how circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) reflects treatment response and resistance evolution, linking molecular dynamics to clinical outcomes.
Background
The BRAF V600E mutation defines a biologically aggressive mCRC subset with historically poor outcomes under standard chemotherapy. The BREAKWATER trial demonstrated that combining encorafenib (a BRAF inhibitor) with cetuximab (anti-EGFR) and mFOLFOX6 yields statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in objective response rate (ORR) compared with chemotherapy ± bevacizumab.
Following these results, EC + mFOLFOX6 received FDA accelerated approval as the first molecularly targeted regimen for untreated BRAF V600E-mutant mCRC. The present ctDNA analysis aimed to understand how early molecular changes correlate with clinical benefit and how resistance mutations emerge under therapy.
Study Design
In this randomized, three-arm phase III trial, patients with previously untreated BRAF V600E-mutant mCRC were assigned to:
- EC + mFOLFOX6,
- EC alone
- Control chemotherapy ± bevacizumab.
Plasma samples were collected at baseline (BL), Cycle 2 Day 15 (C2D15), and end of treatment (EOT) for ctDNA sequencing with the Guardant Infinity assay. Concordance between tissue and plasma BRAF V600E detection was assessed with the QIAGEN Therascreen® PCR kit.
Associations between BRAF V600E variant-allele frequency (VAF) and clinical outcomes (ORR, overall survival [OS]) were analyzed, and acquired resistance alterations (KRAS, NRAS, MAP2K1) were compared across arms. Data cut-off dates for the ctDNA analysis were January 6 and May 1, 2025, ensuring alignment between molecular and clinical datasets.

Key Results
Baseline plasma samples were available for 494 of 514 patients (96 %).
BRAF V600E ctDNA was detected in 425 of 494 (86 %), with a high concordance (87.4 %) between ctDNA and tumor tissue testing, reinforcing the validity of ctDNA as a tool for molecular profiling and real-time disease monitoring.
Clinical benefit with EC + mFOLFOX6 was consistent across VAF-high (≥ median) and VAF-low (< median) groups:
BRAF V600E VAF-high cohort
- ORR: 75 % (95 % CI 65–83) for EC + mFOLFOX6 vs 49 % (36–62) for EC and 42 % (32–53) for control.
- OS HR (95 % CI): 0.50 (0.35–0.73) for EC + mFOLFOX6 vs 0.76 (0.52–1.13) for EC.
BRAF V600E VAF-low cohort
- ORR: 63 % (52–72) for EC + mFOLFOX6 vs 40 % (28–54) for EC and 40 % (30–51) for control.
- OS HR (95 % CI): 0.39 (0.24–0.64) for EC + mFOLFOX6 vs 0.66 (0.41–1.06) for EC.
Thus, adding mFOLFOX6 to targeted therapy improved outcomes regardless of baseline ctDNA burden, supporting its integration into frontline management.
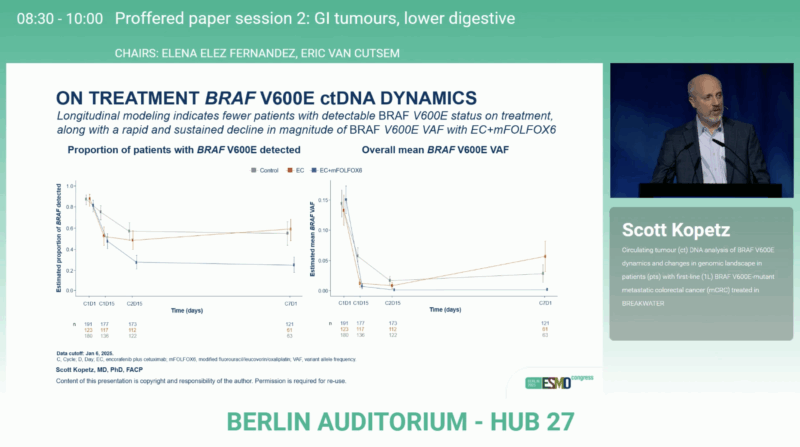
ctDNA Clearance and Survival
Patients whose BRAF V600E mutation became undetectable in ctDNA at Cycle 2 Day 15 experienced notably longer OS compared with those with persistent detection.
Hazard ratios for OS (D/ND vs detectable): 0.30 for EC + mFOLFOX6, 0.36 for EC, and 0.50 for control.
The proportion achieving ctDNA clearance was highest with EC + mFOLFOX6 (67 %), compared with 45 % for EC and 38 % for control.
This early ctDNA negativity emerged as a powerful on-treatment biomarker, reflecting deep molecular responses and superior survival.
Resistance Landscape
Among 241 paired baseline → EOT samples, emerging resistance mutations were evaluated.
NRAS, KRAS, and MAP2K1 mutations — previously linked to MAPK pathway reactivation — were more frequent with EC monotherapy (37.9 % at C7D1) than with EC + mFOLFOX6 (6.6 %).
In addition, MET amplifications and BRAF exon deletions occurred less often in the combination arm (≈ 9–14 %) than in EC alone (≈ 14–17 %), underscoring that the addition of chemotherapy not only enhances tumor regression but also suppresses clonal evolution and delays acquired resistance.
You can read the full abstract here.
Conclusion
The BREAKWATER ctDNA analysis reinforces EC + mFOLFOX6 as the standard first-line regimen for BRAF V600E-mutant mCRC.
Across molecular subgroups, it achieved higher response rates (63–75 %) and favorable OS hazard ratios (0.39–0.50) versus control, while demonstrating enhanced ctDNA clearance and fewer acquired MAPK pathway mutations.
These results underscore the dual advantage of deep early molecular responses and resistance suppression, positioning EC + mFOLFOX6 as a comprehensive, biomarker-driven therapy for this high-risk patient population.
Read more about CITRIC Trial Results at ESMO 2025: ctDNA-Guided Anti-EGFR Rechallenge in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer on OncoDaily.


