The HER2CLIMB-02 trial has added another important layer to the evolving treatment landscape of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. The study demonstrates that adding tucatinib to trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) improves progression-free survival (PFS) in patients previously treated for advanced disease, including those with brain metastases. However, overall survival (OS) data remain immature, toxicity is higher with the combination, and the trial arrives at a time when trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) has already reshaped second-line therapy.
As a result, HER2CLIMB-02 clearly shows clinical activity, but its exact role in treatment sequencing remains uncertain.

Background: The Evolution of HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Therapy
HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer historically carried an aggressive prognosis. The introduction of trastuzumab transformed outcomes, followed by pertuzumab in the CLEOPATRA trial, which established dual HER2 blockade with trastuzumab, pertuzumab, and chemotherapy as first-line standard of care (Swain et al., 2015, N Engl J Med).
In the second-line setting, the EMILIA trial demonstrated that T-DM1 significantly improved survival compared with lapatinib plus capecitabine (Verma et al., 2012, N Engl J Med). T-DM1 subsequently became the standard after trastuzumab-based progression.
More recently, trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) has redefined expectations. In the DESTINY-Breast03 trial, T-DXd significantly improved PFS compared with T-DM1, with a hazard ratio of 0.28 and unprecedented response rates (Cortés et al., 2022, N Engl J Med). Updated analyses also demonstrated an overall survival benefit (Cortés et al., 2023, Lancet).
In parallel, tucatinib, an oral HER2-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor, demonstrated improved PFS and OS in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine in the original HER2CLIMB trial, including in patients with active brain metastases (Murthy et al., 2020, N Engl J Med).
Against this backdrop, the HER2CLIMB-02 trial explores a logical question: does combining tucatinib with T-DM1 enhance outcomes compared with T-DM1 alone?
HER2CLIMB-02 Trial Design
The HER2CLIMB-02 trial is a randomized phase III study evaluating tucatinib plus T-DM1 versus T-DM1 plus placebo in patients with previously treated HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.
Importantly, the trial includes patients with brain metastases, a population historically underrepresented in clinical trials. Central nervous system (CNS) involvement remains a major clinical challenge in HER2-positive disease, affecting up to 50% of patients over the disease course.
The primary endpoint of HER2CLIMB-02 was progression-free survival, with overall survival as a key secondary endpoint.
Progression-Free Survival Benefit
HER2CLIMB-02 demonstrates that adding tucatinib to T-DM1 significantly improves progression-free survival compared with T-DM1 alone.
The benefit extends to patients with brain metastases, reinforcing tucatinib’s known CNS activity. This finding aligns with results from the original HER2CLIMB trial, which showed meaningful CNS efficacy and survival benefit in patients with active brain metastases (Murthy et al., 2020).
The HER2CLIMB-02 PFS improvement confirms biological synergy between tucatinib and T-DM1. Tucatinib inhibits HER2 signaling intracellularly, while T-DM1 delivers cytotoxic payload via HER2-directed antibody targeting. The dual approach enhances pathway suppression while maintaining targeted delivery.
From a mechanistic perspective, the results are coherent and expected.
Overall Survival: Still Immature
While the PFS signal is clear, overall survival data remain immature. This is a critical limitation in interpreting HER2CLIMB-02.
In modern HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer, treatment sequencing is complex. Many patients receive multiple subsequent lines of effective therapy, including T-DXd, tucatinib-based regimens, and newer antibody-drug conjugates. Post-progression crossover and subsequent therapy exposure can dilute overall survival differences.
Without mature OS data, it is difficult to determine whether earlier tucatinib intensification meaningfully alters long-term outcomes.
Given the precedent set by DESTINY-Breast03, where T-DXd showed both PFS and OS superiority over T-DM1 the survival benchmark for second-line therapy is now higher than ever.
Toxicity Considerations
HER2CLIMB-02 also reports increased toxicity with the combination.
Tucatinib adds gastrointestinal toxicity, particularly diarrhea, as well as transaminase elevations and other adverse events consistent with HER2-targeted TKIs. T-DM1 carries risks of thrombocytopenia, hepatotoxicity, and neuropathy. Combining the two increases the cumulative toxicity burden.
In a metastatic setting where quality of life and treatment tolerability are central, this matters. The incremental PFS gain must be weighed against higher rates of adverse events and treatment discontinuation. This becomes especially relevant when comparing against T-DXd, which carries its own risk profile, most notably interstitial lung disease, but has demonstrated profound efficacy.
The T-DXd Question
The most pressing issue raised by HER2CLIMB-02 is not whether tucatinib plus T-DM1 works. It does.
The real question is how it compares with T-DXd.
The two strategies have not been directly compared in a head-to-head trial. T-DXd, evaluated in DESTINY-Breast03, achieved median PFS exceeding 25 months in updated analyses and showed overall survival superiority over T-DM1 (Cortés et al., 2023). Response rates exceeded 75%, with durable control even in patients with brain metastases.
Given these results, T-DXd has become the preferred second-line standard in many treatment guidelines, including those from NCCN and ESMO. HER2CLIMB-02, by contrast, compares tucatinib plus T-DM1 against T-DM1 alone, not against T-DXd.
Therefore, we do not know whether tucatinib intensification offers superior, inferior, or equivalent efficacy compared with T-DXd in the post-trastuzumab setting. Until such comparative data exist, positioning HER2CLIMB-02 within sequencing algorithms remains speculative.
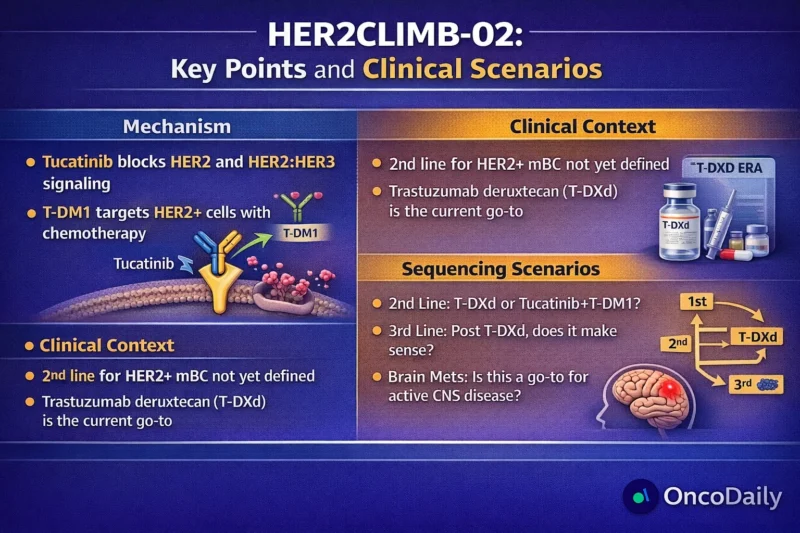
Brain Metastases: A Key Differentiator
One area where HER2CLIMB-02 is particularly compelling is CNS disease.
Brain metastases remain a major cause of morbidity and mortality in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Tucatinib has demonstrated CNS penetration and activity in both stable and active brain metastases. In HER2CLIMB-02, the PFS benefit extended to patients with brain metastases, reinforcing tucatinib’s role as a CNS-active agent.
While T-DXd has also shown promising intracranial activity in subgroup analyses, tucatinib’s CNS efficacy is supported by robust prospective data from HER2CLIMB.
For patients with progressive brain metastases after T-DXd, or in settings where CNS control is prioritized tucatinib-based strategies may retain particular relevance.
Sequencing Remains the Central Question
The HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer treatment landscape is no longer linear.
First-line therapy: trastuzumab, pertuzumab, and chemotherapy.
Second-line: increasingly T-DXd.
Third-line and beyond: tucatinib-based regimens, T-DM1 (where not previously used), and emerging ADCs.
Where does tucatinib plus T-DM1 fit?
If T-DXd is used second-line, many patients will no longer be T-DM1 naïve. This limits applicability of HER2CLIMB-02 data in current real-world practice. Alternatively, tucatinib plus T-DM1 could theoretically serve as an option when T-DXd is contraindicated, such as in patients with pre-existing interstitial lung disease risk.
However, without direct comparative evidence, the optimal sequence remains undefined.
What Does HER2CLIMB-02 Ultimately Show?
HER2CLIMB-02 shows that intensifying HER2 blockade with tucatinib plus T-DM1 improves progression-free survival, including in patients with brain metastases. It confirms biological activity and provides another effective option in a disease where therapeutic depth matters.
But it does not answer:
- Whether this combination is superior to T-DXd
- Whether earlier use improves overall survival
- How best to sequence therapies after modern standards
In short, HER2CLIMB-02 demonstrates clinical activity, but not definitive positioning.

Read About CLEOPATRA Trial on OncoDaily
Final Perspective
The HER2CLIMB-02 trial reinforces that HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer remains one of the most dynamic areas in oncology. Innovation continues, combinations expand, and CNS-directed strategies evolve.
Yet progress now creates complexity.
Without head-to-head comparisons against T-DXd, the precise role of tucatinib plus T-DM1 remains uncertain. Toxicity considerations further complicate adoption. As overall survival data mature and sequencing strategies are refined, HER2CLIMB-02 may ultimately find a defined niche, particularly in CNS-focused management.
For now, the results signal activity, not paradigm shift.
Written by Armen Gevorgyan, MD


