Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B): What patients should know about
What Is Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B)?
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) is a rare but serious genetic condition that causes certain glands in the body to develop tumors and produce too many hormones. The main glands affected are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands.
In this article, we will cover what MEN2B is, what causes it, common symptoms, how it is diagnosed, treatment options, genetic testing for family members, and how to manage life with MEN2B. Understanding this condition can help patients and families take control of their health and make informed decisions.
What Causes MEN2B?
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) is caused by a change (mutation) in a specific gene called the RET gene. This gene normally helps control how certain cells grow and develop. When the RET gene is mutated, it causes the cells in hormone-producing glands, like the thyroid and adrenal glands, to grow abnormally and form tumors.
In most cases, this gene mutation happens by chance, meaning it is not inherited from a parent but develops in the person before birth. However, once a person has the RET mutation, they can pass it on to their children, with each child having a 50% chance of inheriting the condition. Because MEN2B is genetic, doctors often recommend genetic testing for family members to check if they carry the same RET gene mutation. Early testing helps with early diagnosis, so treatment can start before serious problems develop.
Common Symptoms and Early Signs of MEN2B
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) has several signs and symptoms that usually start in childhood or early adulthood. Recognizing these early signs is important for diagnosis and treatment.
One of the most common signs is the development of thyroid nodules or lumps in the thyroid gland. These nodules are often cancerous and can grow quickly if not treated. Another key feature of MEN2B is the presence of mucosal neuromas, which are small, painless bumps on the lips, tongue, and inside the mouth. Sometimes, these neuromas can also appear on the eyelids or inside the digestive tract.
Many people with MEN2B also have a distinct body appearance known as a Marfanoid body type. This means they tend to be tall and slender, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. Their joints may be more flexible than usual. Some other symptoms include digestive problems, like constipation or diarrhea, and enlarged lips due to the mucosal neuromas. Because MEN2B often causes tumors in the adrenal glands (called pheochromocytomas), people may also experience high blood pressure, headaches, or sweating.
Noticing these signs early and seeing a doctor can help catch the condition before serious problems develop. Regular check-ups and monitoring are important for managing MEN2B effectively.
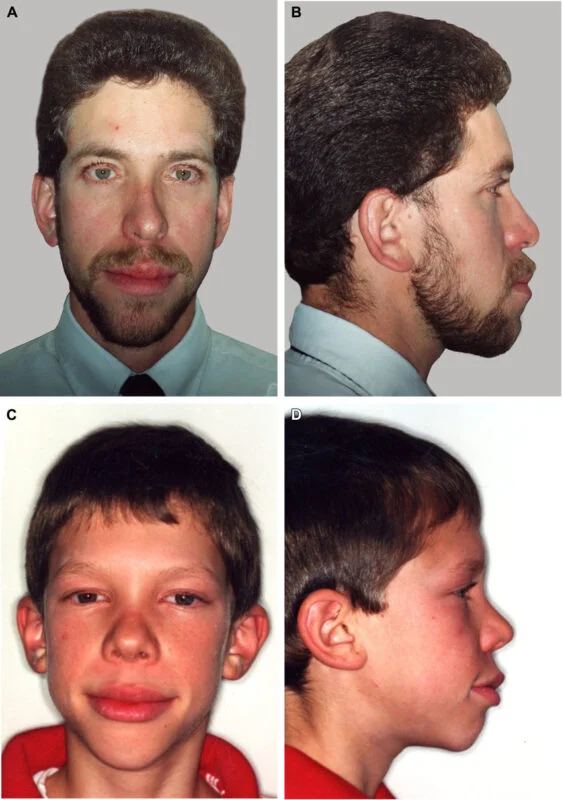
This image is taken from “Researchgate”, which shows the characteristic facial physiognomy of patients with MEN2B.
How Is MEN2B Diagnosed?
Doctors use several tests to diagnose Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) and check for any tumors or hormone problems.
One of the most important steps is genetic testing. A simple blood test can check for a change (mutation) in the RET gene, which causes MEN2B. If this mutation is found, it confirms the diagnosis. Family members may also be tested to see if they have the same gene change. During a physical exam, the doctor will look for common signs of MEN2B, like bumps on the lips or tongue (mucosal neuromas), a lump in the neck (which could be a thyroid tumor), or a tall, slender body shape (Marfanoid body type).
Doctors will also do blood tests to check for high levels of certain hormones, such as calcitonin and catecholamines. These hormones can be higher if there are tumors in the thyroid or adrenal glands. Finally, imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI, help doctors see if there are any tumors in the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, or other areas.
Types of Tumors in MEN2B
People with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) often develop three main types of tumors. Knowing about these tumors helps understand how MEN2B affects the body.
The most common tumor is medullary thyroid cancer. This cancer starts in the thyroid gland, which is in the neck. It can grow quickly if not treated, so doctors often recommend removing the thyroid gland early, even before symptoms appear. Another tumor seen in MEN2B is called a pheochromocytoma. These tumors grow in the adrenal glands, which sit above the kidneys. Pheochromocytomas can cause the body to make too much adrenaline, leading to high blood pressure, headaches, sweating, and a fast heartbeat.
People with MEN2B also often have mucosal neuromas. These are small, non-cancerous bumps that appear on the lips, tongue, and inside the mouth. They may also be found on the eyelids or in the digestive tract. Though they are harmless, they are a key sign of MEN2B and help doctors recognize the condition early.
Finding these tumors early through regular check-ups and tests can help doctors manage MEN2B and keep patients healthy.
Treatment Options for MEN2B
Treatment for Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) focuses on removing tumors, managing hormone levels, and closely monitoring the patient’s health over time.
The most common treatment is surgery. Many people with MEN2B have surgery to remove the thyroid gland, called a thyroidectomy, often at a young age. This is done to prevent or treat medullary thyroid cancer before it spreads. If tumors develop in the adrenal glands (called pheochromocytomas), doctors may recommend an adrenalectomy, which is surgery to remove one or both adrenal glands. After surgery, patients may need to take medications to replace the hormones that the thyroid or adrenal glands used to make. These medications help keep hormone levels balanced and prevent symptoms like fatigue or high blood pressure.
Regular monitoring is very important for people with MEN2B. This includes routine blood tests, imaging scans, and check-ups to watch for new tumors or hormone changes. By staying on top of their care, patients with MEN2B can live healthier lives and catch any issues early.
Living with MEN2B: What to Expect
Living with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) means staying proactive about your health. Regular check-ups are very important. Your doctor will schedule routine blood tests and scans to watch for any new tumors and check hormone levels. This helps catch any changes early, before they cause problems.
If you’ve had surgery to remove your thyroid or adrenal glands, you will need to take daily medications to replace the hormones your body no longer makes. These medicines help keep your energy, metabolism, and blood pressure stable.
Emotional and mental support is also key. Talking to a genetic counselor, support group, or therapist can help you and your family cope with the challenges of living with MEN2B. With regular care, monitoring, and support, many people with MEN2B can lead active and fulfilling lives.
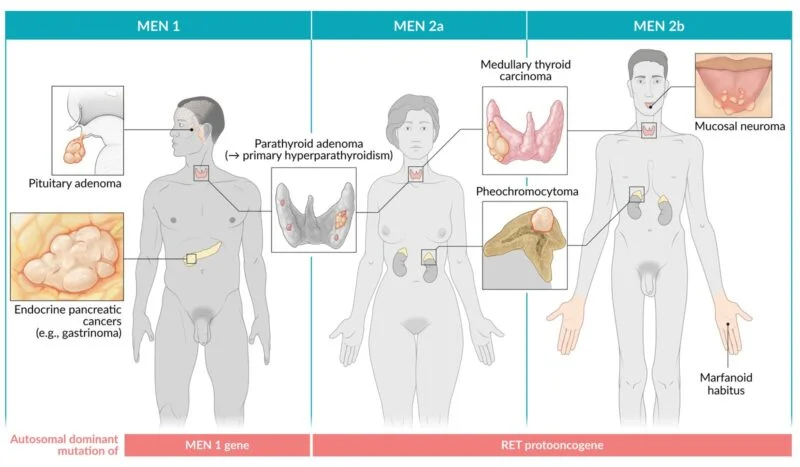
This image is taken from “Amboss”, which shows the main symptoms and affected organs in MEN syndromes.
Genetic Testing and Family Screening
Since Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) is caused by a change in the RET gene, it can sometimes be passed from parents to their children. Even though many cases happen randomly, once someone is diagnosed with MEN2B, their close family members might still be at risk.
This is why genetic testing is important for family members. A simple blood test can check if they carry the same gene change. If the mutation is found early, doctors can start monitoring and treatment right away, often before symptoms appear. Genetic counseling is also helpful. A genetic counselor will explain what the test results mean and guide family members through their options. This helps families make informed decisions about their health and future.
Early testing and counseling give families the chance to catch MEN2B early and manage it effectively, keeping everyone healthier and more prepared.
Myths and Misconceptions About MEN2B
There are a few common misunderstandings about Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B (MEN2B) that can cause confusion or worry. Let’s clear them up:
- MEN2B is always inherited: While MEN2B is a genetic condition, most cases happen because of a new gene change (mutation) that occurs by chance. It’s not always passed down from a parent.
- MEN2B only affects the thyroid: MEN2B affects more than just the thyroid. It can also cause tumors in the adrenal glands and non-cancerous growths (neuromas) in the mouth and digestive tract. It’s important to monitor the whole body.
- Surgery means you’re cured forever: Surgery, like removing the thyroid, is very important, but people with MEN2B still need lifelong check-ups. Tumors or hormone problems can develop later, so ongoing care is essential.
- You’ll have symptoms right away: Some people with MEN2B may not feel sick at first. That’s why regular screening and genetic testing are so important — even if you feel fine, doctors can catch issues early.
To learn more, including common myths and misconceptions, visit the OncoDaily YouTube TV
FAQ
What is MEN2B?
MEN2B is a rare genetic disorder that causes tumors in hormone-producing glands, especially the thyroid and adrenal glands.
What causes MEN2B?
MEN2B is caused by a mutation in the RET gene, which leads to abnormal cell growth in certain glands.
Is MEN2B inherited?
Most MEN2B cases are caused by new (spontaneous) mutations, but it can be inherited and passed on to children.
What are the early symptoms of MEN2B?
Early signs include mucosal neuromas, enlarged lips, thyroid lumps, and digestive problems like constipation or diarrhea.
What is a mucosal neuroma?
It’s a small, painless bump found on the lips, tongue, or inside the mouth—common in MEN2B patients.
What tumors are common in MEN2B?
Common tumors include medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytomas (adrenal tumors), and mucosal neuromas.
How is MEN2B diagnosed?
Diagnosis includes genetic testing, blood hormone tests, and imaging scans like CT or MRI.
What is the treatment for MEN2B?
Treatment includes thyroidectomy, adrenal surgery, and hormone replacement medications.
Can family members be tested?
Yes. Genetic testing is recommended for close relatives to detect the RET gene mutation early.
Can you live a normal life with MEN2B?
Yes. With early diagnosis, regular monitoring, and proper treatment, many people live full and active lives.
-
Challenging the Status Quo in Colorectal Cancer 2024
December 6-8, 2024
-
ESMO 2024 Congress
September 13-17, 2024
-
ASCO Annual Meeting
May 30 - June 4, 2024
-
Yvonne Award 2024
May 31, 2024
-
OncoThon 2024, Online
Feb. 15, 2024
-
Global Summit on War & Cancer 2023, Online
Dec. 14-16, 2023
