On September 3, 2025, Boehringer Ingelheim announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation to Zongertinib as a potential first-line treatment for adult patients with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) carrying HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations.
Commenting on the designation, Vicky Brown, Senior Vice President and Head of Immunology, Oncology, and Eye Health at Boehringer Ingelheim, emphasized the company’s commitment to advancing innovation in oncology.
“Exploring accelerated review pathways is part of Boehringer’s strategy to have an unprecedented and generational impact on people facing cancer. We are incredibly pleased that HERNEXEOS has received Breakthrough Therapy Designation for first-line use in patients living with HER2-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. This pathway was designed to expedite the development and review of promising medicines for serious diseases, and clearly highlights the potential of HERNEXEOS.”

LinkedIn photo of Vicky Brown
What Are the Other Global Approvals for Zongertinib?
Zongertinib has recently reached important regulatory milestones for the treatment of HER2-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In the United States, the FDA granted accelerated approval for adults with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC whose tumors carry HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain mutations and who have previously received systemic therapy on August 8, 2025. This approval was based on objective response rate and duration of response, with full approval contingent on confirmatory trials.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) conditionally approved zongertinib as a monotherapy for adults with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC harboring activating HER2 mutations after at least one prior systemic therapy. The therapy also recently received Breakthrough Therapy Designation from the NMPA’s Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) for first-line use in patients with HER2 tyrosine kinase domain mutations.
Additionally, HERNEXEOS has been granted Orphan Drug Designation in Japan, highlighting its potential to address unmet needs in rare cancer populations. These global regulatory milestones underscore zongertinib’s emerging role as a targeted therapy for HER2-mutant NSCLC.
Find more information in Boehringer Ingelheim Official Website.
What research is behind the approval?
The FDA’s approval of Zongertinib was supported by results from Beamion LUNG-1 (NCT04886804), an open-label, multi-center trial assessing the safety and efficacy of zongertinib in patients with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC harboring HER2 TKD mutations who had previously received systemic therapy.

Read More About FDA’s Accelerated Approval of Zongertinib for HER2 TKD–Mutated Non-Squamous NSCLC on OncoDaily.
Results of Beamion LUNG-1 trial
The pivotal results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2025. Results from the Beamion LUNG-1 trial, recently published in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM, April 2025), highlight the efficacy and safety of zongertinib (HERNEXEOS) in patients with previously treated HER2-mutant non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
The study evaluated zongertinib across three key cohorts:
- Cohort 1: Patients with HER2 tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) mutations, no prior HER2-targeted therapy
- Cohort 5: Patients with HER2 TKD mutations who had received prior HER2-directed antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs)
- Cohort 3: Patients with non-TKD HER2 mutations
The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR), with duration of response (DOR) and progression-free survival (PFS) as secondary endpoints.
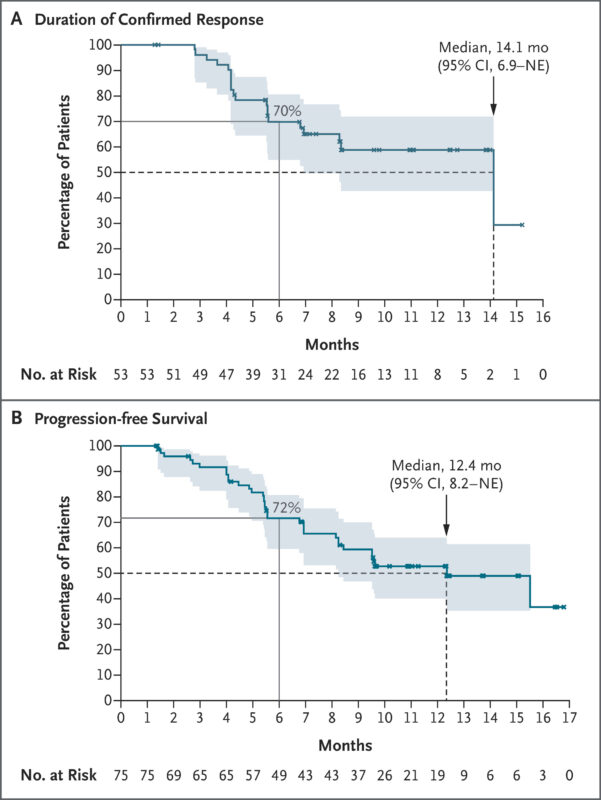
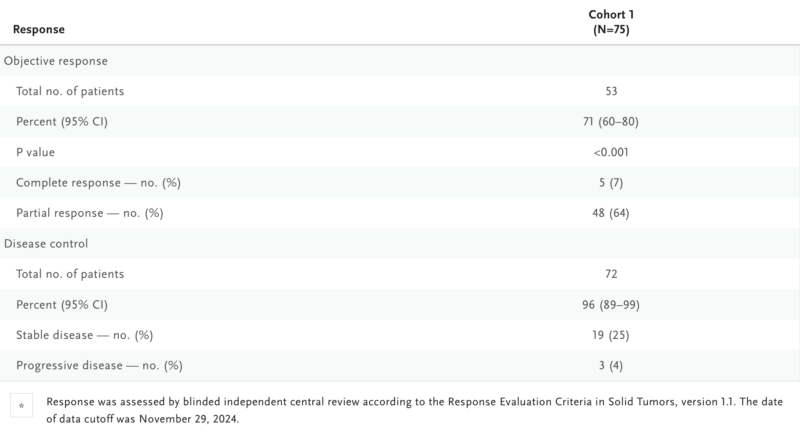
In Cohort 1 (75 patients, 120 mg daily), 71% achieved an objective response, including 5 complete responses. Responses were durable, with a median DOR of 14.1 months and PFS of 12.4 months. Importantly, patients with brain metastases also showed systemic and intracranial responses.
In Cohort 5 (31 patients previously treated with HER2 ADCs), 48% had a confirmed response, with a median DOR of 5.3 months and median duration of follow-up – 6.8 months.
In Cohort 3 (20 patients with non-TKD mutations), the ORR was 30%, with responses seen across different mutation types.
Overall, zongertinib demonstrated meaningful and durable antitumor activity in heavily pretreated HER2-mutant NSCLC, with a manageable safety profile.
Safety of Beamion LUNG-1 trial
Zongertinib was generally well tolerated in the Beamion LUNG-1 trial, with most patients experiencing mild to moderate side effects. In the primary cohort receiving 120 mg daily, nearly all patients (97%) reported drug-related adverse events, though only 17% experienced grade 3 or higher events. The most common severe effects involved liver enzyme elevations, while one patient experienced a grade 4 liver-related reaction. No drug-related interstitial lung disease was observed.
Gastrointestinal effects, particularly diarrhea, were frequent but mostly mild, and skin rashes were generally low grade. Dose reductions were necessary in a small number of patients, and only a few discontinued treatment due to side effects. Higher doses of 240 mg showed a slightly increased risk of severe adverse events and diarrhea. Cohorts 5 and 3 demonstrated similar tolerability, with grade 3 or higher events occurring in 3% and 25% of patients, respectively, confirming zongertinib’s manageable safety profile across HER2-mutant NSCLC populations.
How Zongertinib Stops Tumor Growth in HER2-Mutant NSCLC?
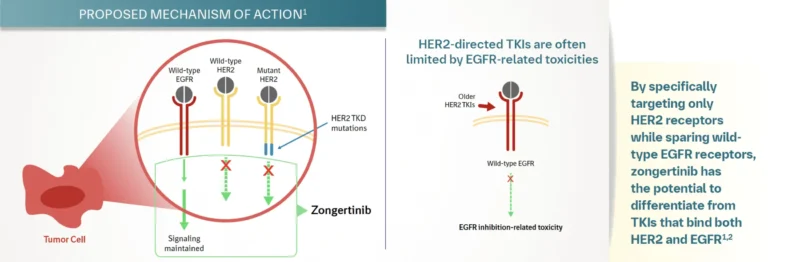
HERNEXEOS is an oral, targeted therapy developed by Boehringer Ingelheim for patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors harbor HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations. These mutations keep the HER2 protein continuously active, driving unchecked cancer cell growth.
Zongertinib works by selectively binding to the mutated HER2 kinase, blocking its activity and interrupting the downstream signaling that fuels tumor progression. This precision-targeted approach helps stop tumor growth while minimizing effects on healthy cells. As a precision medicine, zongertinib offers a valuable treatment option for patients with HER2-mutant NSCLC, particularly when previous therapies have failed.
Source: Boehringer Ingelheim Official Website
Ongoing Clinical Trials with Zongertinib
Ongoing clinical trials are a critical step in expanding the understanding of HERNEXEOS and its potential across HER2-altered cancers.
Beamion LUNG-2 is a Phase 3, randomized, open-label study designed to compare zongertinib with standard-of-care therapies in patients with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC carrying HER2 TKD mutations. Key objectives of this trial include progression-free survival, overall survival, and objective response rate. Results from LUNG-2 are expected to provide critical confirmatory data for first-line use and further establish zongertinib’s role in the treatment paradigm.
Beyond NSCLC, the Beamion PANTUMOR-1 trial (NCT06581432) investigates HERNEXEOS in adults with advanced solid tumors exhibiting HER2 alterations, including mutations, amplifications, or overexpression. Participants are assigned to one of thirteen cohorts based on tumor type and HER2 profile, receiving daily oral doses of zongertinib. The study continues as long as patients derive clinical benefit and can tolerate the therapy. Tumor assessments, disease progression monitoring, and safety evaluations are conducted regularly, providing insight into zongertinib’s broader anti-tumor potential across multiple cancer types.


