Navigating the world of cancer treatment can be overwhelming, especially with so many new drugs being developed. This guide will help you understand what it means when a drug is in a clinical trial, the different phases of these trials, and why FDA approval is crucial. We’ll also explain some key terms and list the most promising cancer drugs in 2024.
What Are Clinical Trials?
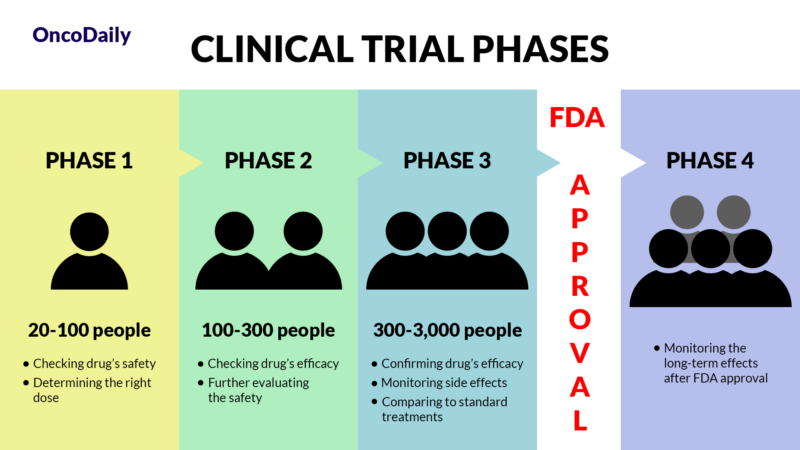
Clinical trials are research studies that test new medical treatments, like drugs, in people. These trials are essential for determining whether new treatments are safe and effective. They follow a strict plan, called a protocol, to ensure reliable results.
Phases of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are divided into phases:
- Phase 1: Tests a new drug on a small group (20-100 people) to determine its safety and the right dose.
- Phase 2: Involves more people (100-300) to see if the drug works and to further evaluate its safety.
- Phase 3: Includes a larger group (300-3,000) to confirm the drug’s effectiveness, monitor side effects, and compare it to standard treatments.
- Phase 4: Happens after FDA approval, monitoring the drug’s long-term effects in a larger population.
What Does FDA Approval Mean?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviews data from clinical trials to decide if a new drug should be approved for public use. FDA approval means the drug is safe and effective for its intended use. This approval is crucial because it ensures that the benefits of the drug outweigh any potential risks.
Key Terms Explained
- Investigational Drug: A drug that is being tested in clinical trials but is not yet approved by the FDA.
- Bispecific Antibody: A type of antibody that can bind to two different targets at the same time, helping to attack cancer cells more effectively.
- Breakthrough Therapy Designation: A status given by the FDA to drugs that show substantial improvement over existing treatments for serious conditions. This designation helps speed up the development and review process.
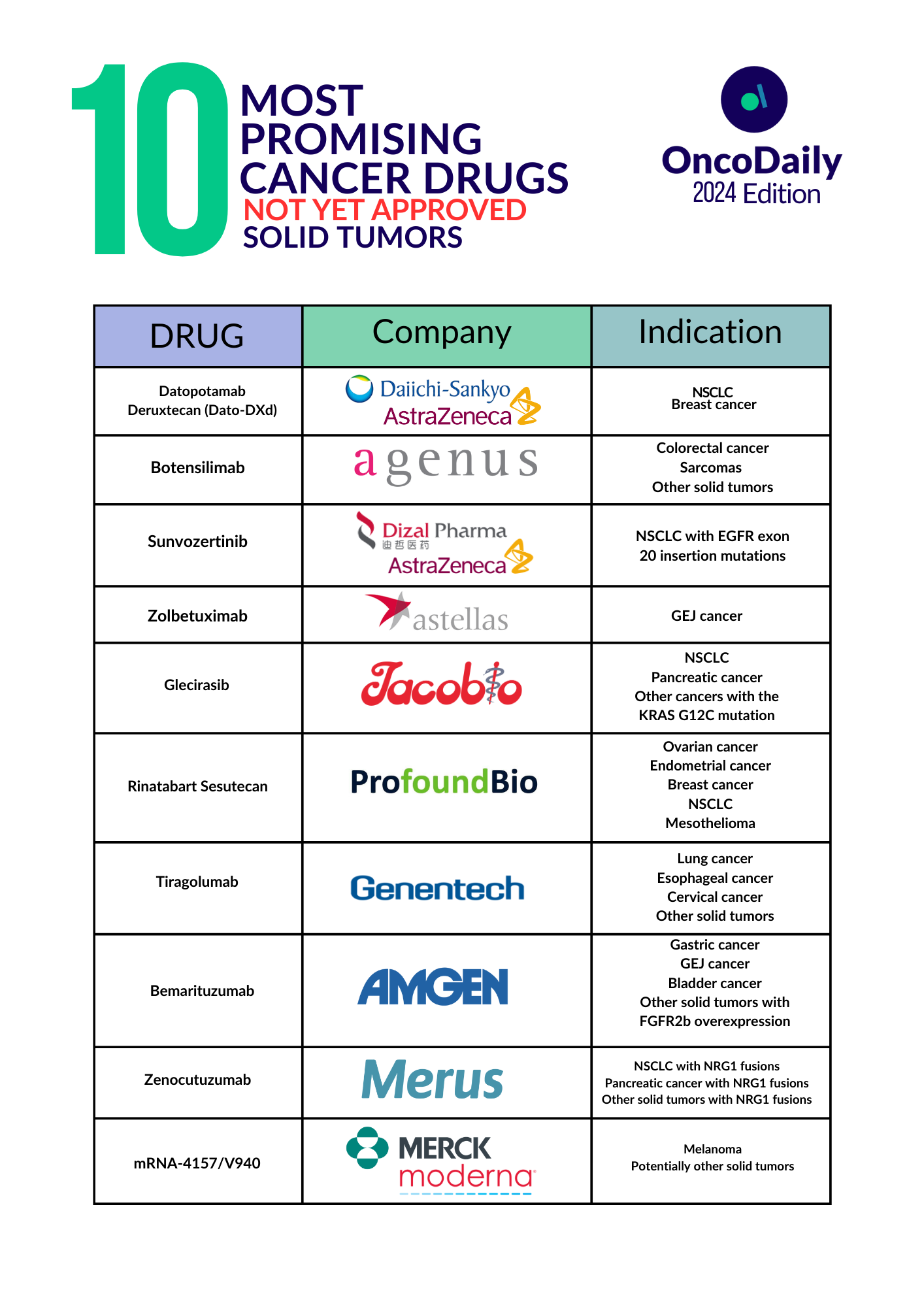
Introduction to 10 Promising New Cancer Drugs in 2024: Not Yet Approved
Cancer treatment is constantly evolving, with researchers working tirelessly to develop new and more effective therapies. In this article, we’ll explore ten of the most promising cancer drugs currently in development. While these medications are not yet FDA-approved, they show great potential in clinical trials and could significantly impact cancer care in the near future.
1. Datopotamab Deruxtecan (Dato-DXd)
Company
What is it?
Datopotamab deruxtecan is a targeted therapy known as an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC). It’s designed to deliver cancer-fighting medication directly to tumor cells.
How does it work?
Datopotamab deruxtecan is like a smart bomb for cancer cells. It has two parts:
- A targeting system that finds cancer cells with a specific protein called TROP2
- A powerful chemotherapy drug attached to it
When the drug reaches a cancer cell, it delivers its chemotherapy payload directly inside, killing the cell while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Breast cancer, including hormone receptor-positive (HR+) and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
What do the studies show?
Clinical trials have shown promising results:
- In lung cancer: It improved survival time without cancer progression compared to standard chemotherapy.
- In breast cancer: About 1 in 4 patients with HR+ breast cancer and 1 in 3 with TNBC saw their tumors shrink.
What’s next?
The FDA is currently reviewing datopotamab deruxtecan for use in certain breast cancer patients.
2. Botensilimab
Company
What is it?
Botensilimab is an immunotherapy drug that helps the body’s immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
How does it work?
It targets a protein called CTLA-4, which normally helps prevent the immune system from becoming overactive. By blocking CTLA-4, botensilimab allows the immune system to mount a stronger attack against cancer cells.
It works by:
- Removing a “brake” that cancer cells put on your immune system
- Allowing your immune cells to recognize and attack cancer more effectively
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Colorectal cancer
- Sarcomas (cancers of connective tissues)
- Various other solid tumors
What do the studies show?
According to clinical trials:
- In colorectal cancer: About 1 in 5 patients with a hard-to-treat form of the disease saw their tumors shrink.
- In sarcomas: More than 1 in 4 patients responded to the treatment, with many experiencing long-lasting benefits.
What’s next?
Botensilimab is being studied in combination with other immunotherapy drugs to potentially enhance its effectiveness.
3. Sunvozertinib
Company
What is it?
Sunvozertinib is a targeted therapy designed for a specific type of lung cancer with a particular genetic mutation.
How does it work?
This drug blocks a mutated form of the EGFR protein, which is found in some lung cancers and helps them grow. By targeting this specific mutation, sunvozertinib can slow or stop cancer growth while potentially causing fewer side effects than older treatments.
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations
What do the studies show?
In clinical trials, about 6 out of 10 patients saw their tumors shrink, and nearly 9 out of 10 had their disease controlled.
What’s next?
Sunvozertinib has received a Breakthrough Therapy Designation from the FDA, which may help speed up its development and review process.
4. Zolbetuximab
Company
What is it?
Zolbetuximab is an antibody therapy that targets a specific protein found on some stomach cancer cells.
How does it work?
Zolbetuximab is an antibody that acts like a bright flag on stomach cancer cells. It attaches to a protein called claudin-18.2 found on some stomach cancers. This does two things:
- Makes the cancer cells more visible to your immune system
- Triggers your immune cells to attack the flagged cancer
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Gastric (stomach) cancer
- Gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer
What do the studies show?
When combined with chemotherapy, zolbetuximab helped patients live longer compared to chemotherapy alone.
What’s next?
While not yet approved in the U.S., zolbetuximab has been approved in Japan for treating gastric cancer.
5. Glecirasib
Company
What is it?
Glecirasib is a targeted therapy that works against cancers with a specific genetic mutation called KRAS G12C.
How it works?
Glecirasib targets a specific genetic mutation called KRAS G12C, which is like an “on switch” that keeps some cancer cells growing. This drug:
- Finds cells with this mutation
- Blocks the mutated protein, turning off the cancer growth signal
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Pancreatic cancer
- Other cancers with the KRAS G12C mutation
What do the studies show?
According to clinical trials:
- In lung cancer: About half of the patients saw their tumors shrink.
- In pancreatic cancer: More than 4 out of 10 patients responded to the treatment.
What’s next?
Glecirasib has received special designations from the FDA and Chinese regulators to help speed up its development for pancreatic cancer treatment.
6. Rinatabart Sesutecan
Company
What is it?
Rinatabart sesutecan is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) that combines a targeted antibody with a powerful cancer-fighting drug.
How does it work?
This drug targets a protein called folate receptor alpha (FRα), which is found in high levels on some cancer cells. By attaching to FRα, rinatabart sesutecan can deliver a potent cancer-killing agent directly to tumor cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Ovarian cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Breast cancer
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Mesothelioma
What do the studies show?
Early clinical trials have shown promising results, with about 2 out of 3 patients with ovarian and endometrial cancers responding to the treatment.
What’s next?
The FDA has granted Fast Track Designation to rinatabart sesutecan for certain types of ovarian cancer, which may speed up its development and review process.
7. Tiragolumab
Company
What is it?
Tiragolumab is an immunotherapy drug designed to boost the body’s natural defenses against cancer.
How does it work?
This drug blocks a protein called TIGIT, which:
- Normally helps prevent your immune system from overreacting
- Can be exploited by cancer to hide from immune cells
By blocking TIGIT, tiragolumab helps your immune cells stay active and fight cancer more effectively.
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Lung cancer
- Esophageal cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Various other solid tumors
What do the studies show?
When combined with other immunotherapy drugs and chemotherapy:
- In lung cancer: It improved response rates and survival times.
- In esophageal cancer: About 6 out of 10 patients saw their tumors shrink, with improved survival rates.
What’s next?
Tiragolumab has received Breakthrough Therapy Designation from the FDA for certain types of lung cancer, potentially accelerating its development.
8. Bemarituzumab
Company
What is it?
Bemarituzumab is a targeted therapy that focuses on a specific protein found on some cancer cells.
How does it work?
Bemarituzumab targets a protein called FGFR2b that some cancer cells use to receive growth signals. The drug:
- Attaches to FGFR2b on cancer cells
- Blocks growth signals from reaching the cancer
- May also flag the cancer cells for destruction by your immune system
- can slow or stop cancer growth in tumors that have high levels of this protein.
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Gastric (stomach) cancer
- Gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer
- Bladder cancer
- Other solid tumors with FGFR2b overexpression
What do the studies show?
In clinical trials for stomach and GEJ cancers, adding bemarituzumab to chemotherapy improved survival times and slowed cancer progression.
What’s next?
Bemarituzumab has received Breakthrough Therapy Designation from the FDA for certain types of stomach and GEJ cancers, which may help speed up its development and approval process.
9. Zenocutuzumab
Company
What is it?
Zenocutuzumab is a bispecific antibody, meaning it can target two different proteins at once.
How does it work?
Zenocutuzumab is like a bridge between your immune system and cancer cells. It connects to two different proteins:
- One found on your immune cells
- Another found on some cancer cells with rare NRG1 gene fusions
By linking these together, it helps your immune system find and attack the cancer more effectively.
What types of cancer might it treat?
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with NRG1 fusions
- Pancreatic cancer with NRG1 fusions
- Other solid tumors with NRG1 fusions
What do the studies show?
According to clinical trials:
- About 1 in 3 lung cancer patients and 2 in 5 pancreatic cancer patients with NRG1 fusions saw their tumors shrink.
- Responses were often long-lasting, with many patients benefiting for a year or more.
What’s next?
Zenocutuzumab has received Breakthrough Therapy Designation and Priority Review from the FDA for NRG1 fusion-positive lung and pancreatic cancers.
10. mRNA-4157/V940
Company
What is it?
mRNA-4157/V940 is a personalized cancer vaccine that uses mRNA technology (similar to some COVID-19 vaccines) to train the immune system to fight cancer.
How does it work?
This personalized cancer vaccine uses mRNA technology (similar to some COVID-19 vaccines) to teach your immune system about your specific cancer. Here’s how:
- A small sample of your tumor is analyzed
- A custom vaccine is created based on the unique features of your cancer
- The vaccine trains your immune cells to recognize and attack your cancer
What types of cancer might it treat?
Currently being studied in:
- Melanoma (skin cancer)
- Potentially other types of solid tumors in the future
What do the studies show?
According to clinical trials for high-risk melanoma:
- Patients who received the vaccine plus immunotherapy had a lower risk of cancer recurrence compared to those who received immunotherapy alone.
- At 18 months, 79% of patients on the combination treatment were cancer-free, compared to 62% on immunotherapy alone.
What’s next?
A larger phase III trial is currently underway to further evaluate this personalized vaccine approach in melanoma patients.
Conclusion
These ten innovative cancer therapies represent the cutting edge of cancer research, offering new hope for more effective and personalized treatments. While they’re still in development, the promising results from clinical trials suggest a future where cancer care may be more targeted, effective, and potentially less toxic.
As always, patients need to discuss their individual situations and treatment options with their healthcare team. The field of cancer research is dynamic, with discoveries and advancements happening regularly.
Remember, while these drugs show promise, they are still under investigation. Approved treatments and clinical trials are available for many cancer types, and your oncologist can provide the most up-to-date and personalized advice for your specific situation.
Healthcare professionals and researchers interested in more detailed analysis of these promising cancer drugs can refer to the Professional version of the article