Approval Date: November 13, 2025
The FDA granted full approval to ziftomenib (Komzifti, Kura Oncology/Kyowa Kirin) for adults with R/R AML harboring an NPM1 mutation. This marks the first approved targeted therapy specifically for NPM1-mutated AML, addressing a critical population with historically poor outcomes and limited therapeutic choices.
Approval was based on the pivotal KOMET-001 (KO-MEN-001) trial (NCT04067336), which enrolled 112 adults with R/R NPM1-mutated AML.
Efficacy
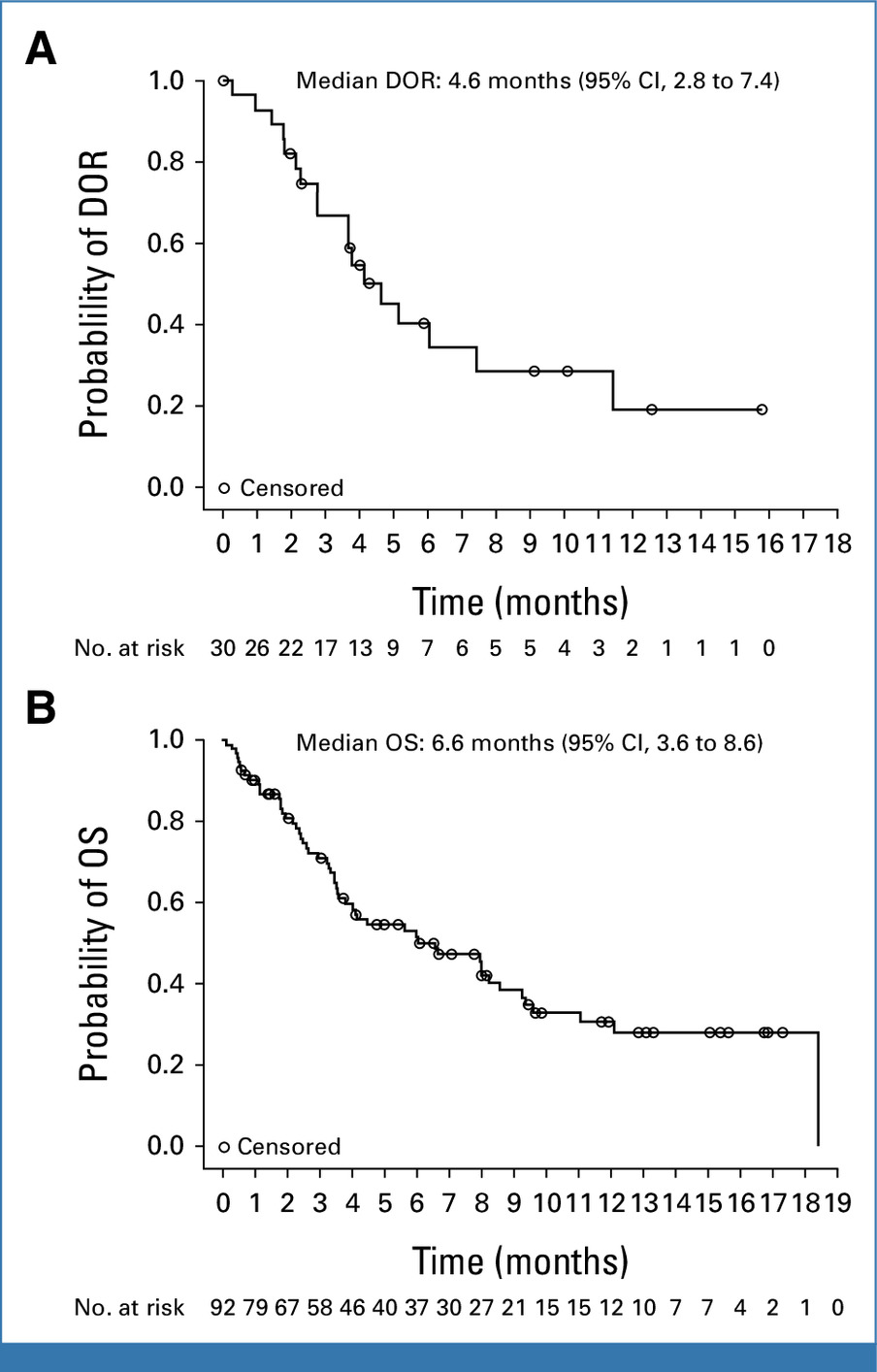
In the KOMET-001 trial, ziftomenib demonstrated clinically meaningful activity in a difficult-to-treat population of adults with relapsed or refractory NPM1-mutated AML. The combined complete remission (CR) plus CR with partial hematologic recovery (CRh) rate was 21.4%, with 17% of patients achieving a full CR and 4.5% achieving CRh. Responses occurred relatively quickly—the median time to first response was 2.7 months—and, importantly, they were durable, with a median CR/CRh duration of 5 months.
Ziftomenib also showed benefits in transfusion requirements. Among patients who were transfusion-dependent at baseline, 21.2% became transfusion-independent, while 26.1% of those who began the trial transfusion-independent maintained that status.
Altogether, these findings highlight that ziftomenib can induce deep, durable remissions and meaningful clinical improvement, even in heavily pretreated patients with limited therapeutic options.
Safety
The prescribing information includes warnings for:
- Differentiation syndrome (Boxed Warning)
- QTc prolongation
- Embryo–fetal toxicity
Most common adverse reactions (≥20%) included increased liver enzymes, infections, electrolyte abnormalities, hemorrhage, diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, edema, musculoskeletal pain, bilirubin elevation, differentiation syndrome, pruritus, and febrile neutropenia.
Notably, Komzifti does not carry a boxed warning for QTc prolongation, and no clinically meaningful drug–drug interactions were identified—important for older AML patients receiving multiple supportive medications
Recommended Dosage
- 600 mg orally once daily
- Continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Administration considerations:
- Avoid PPIs, H2 blockers, and antacids (timing adjustments required).
- Avoid strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers.
- Monitor ECGs regularly due to QTc prolongation risk.
Clinical Significance
NPM1 mutations occur in ~30% of AML cases and represent a major unmet need, with most patients relapsing within 12–36 months after frontline therapy. Ziftomenib provides:
- A first-in-class oral targeted option
- Manageable safety profile
- Potential integration into future combination regimens
- Once-daily dosing favorable for treatment adherence
This approval marks a milestone in precision therapy for AML, expanding the treatment landscape for NPM1-mutated disease.


