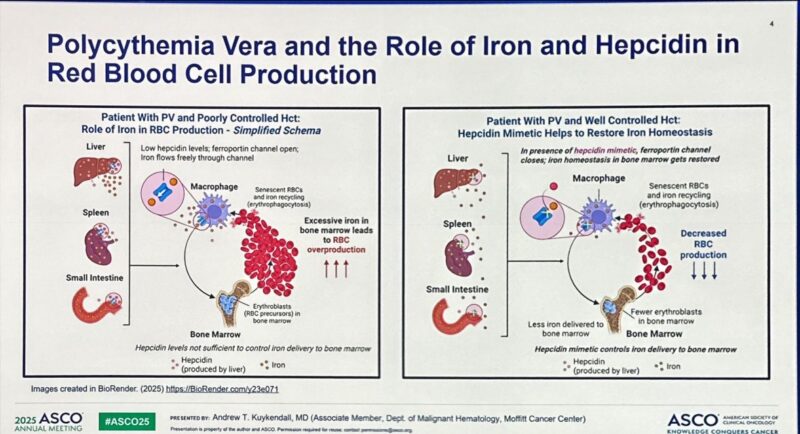
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm marked by excessive production of red blood cells, leading to increased blood viscosity and a heightened risk of thrombotic events. Standard-of-care (SOC) management focuses on controlling hematocrit (Hct) to below 45% using phlebotomy and cytoreductive therapy (CRT), but frequent phlebotomies can be burdensome and negatively impact patient quality of life. Rusfertide, a novel, self-injected, subcutaneous hepcidin mimetic, offers a targeted approach to decrease erythrocytosis by modulating iron metabolism. The ongoing global phase 3 VERIFY trial (NCT05210790) evaluated the efficacy and safety of rusfertide compared to placebo in phlebotomy-dependent PV patients receiving SOC.
Study Design
VERIFY is a multi-part, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. In Part 1a, adults with PV who required frequent phlebotomy, with or without stable CRT, were randomized 1:1 to receive weekly rusfertide or placebo for 32 weeks. Stratification was based on concurrent PV therapy. Patients completing Part 1a could enter an open-label extension (Part 1b) to receive rusfertide through Week 52, with further extension possible for eligible participants.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a clinical response—defined as absence of phlebotomy eligibility and no phlebotomies from Weeks 20-32, with completion of Part 1a. Key secondary endpoints included mean number of phlebotomies during the 32-week period, percentage of patients with Hct maintained below 45%, and changes in patient-reported outcomes (PROs), specifically the PROMIS Fatigue Short Form 8a (SF-8a) total T-score and Myelofibrosis Symptom Assessment Form (MFSAF) v4.0 Total Symptom Score (TSS).
Results
A total of 293 patients (73% male, median age 57 years [range: 27–86]) were enrolled and randomized to rusfertide (n=147) or placebo (n=146). Over half in each arm received concurrent CRT (rusfertide: 56.5%; placebo: 55.5%). The efficacy population was well-matched for baseline characteristics.
Clinical Response and Phlebotomy Outcomes: Between Weeks 20 and 32, 76.9% of rusfertide-treated patients achieved a clinical response compared to 32.9% of placebo patients (p<0.0001), meeting the primary endpoint with high statistical significance. The mean (SE) number of phlebotomies required over 32 weeks was 0.5 (0.2) for rusfertide versus 1.8 (0.2) for placebo (p<0.0001), a substantial reduction in phlebotomy burden.
Hematocrit Control: Maintaining Hct <45% is a critical therapeutic target in PV. 62.6% of rusfertide recipients maintained Hct below this threshold over 32 weeks, compared to only 14.4% of placebo (p<0.0001).

Patient-Reported Outcomes
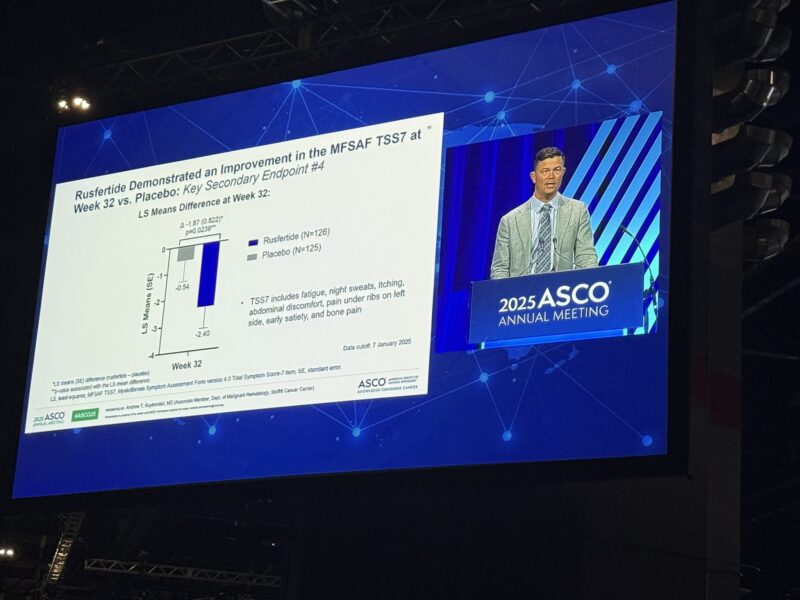
Rusfertide treatment led to significant improvements in fatigue and symptom burden. Statistically significant changes were observed in the PROMIS Fatigue SF-8a total T-score and MFSAF TSS (p<0.03), reflecting meaningful benefits in patient quality of life.
Safety and Tolerability
The safety profile of rusfertide was manageable and in line with previous studies. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) were injection site reactions (rusfertide: 55.9%; placebo: 32.9%), anemia (15.9% vs. 4.1%), and fatigue (15.2% vs. 15.8%). Serious AEs were infrequent (3.4% rusfertide; 4.8% placebo) and none were deemed related to rusfertide. New malignancies occurred in one patient on rusfertide and seven on placebo. No new safety signals emerged.
Conclusions
The phase 3 VERIFY trial demonstrates that rusfertide, added to SOC in PV, significantly reduces the need for phlebotomy, improves hematocrit control, and alleviates fatigue and symptom burden compared to placebo. Rusfertide’s safety and tolerability were consistent with prior studies, and the agent did not increase serious adverse events or treatment-emergent malignancies.
Rusfertide is the first investigational therapy to prospectively show a significant improvement in both disease control and patient-reported outcomes for polycythemia vera. These findings position rusfertide as a potentially practice-changing addition to PV management, particularly for patients struggling with phlebotomy dependence or inadequate hematocrit control on existing therapies.

Clinical Implications
The introduction of rusfertide offers a promising advance for PV patients, targeting the hepcidin pathway to address a critical pathophysiological mechanism in erythrocytosis. Its self-injectable format, substantial reduction in phlebotomy frequency, and positive impact on fatigue and symptom scores may significantly enhance both disease control and quality of life for individuals with PV.
Key Takeaway Messages from VERIFY Trial Trial
The VERIFY trial showed that rusfertide, a self-injected hepcidin mimetic, significantly reduced the need for phlebotomy in phlebotomy-dependent PV patients compared to placebo. More than three-quarters of patients on rusfertide achieved the primary efficacy endpoint (76.9% vs. 32.9% for placebo), and patients required far fewer phlebotomies over 32 weeks. Rusfertide also enabled more patients to maintain target hematocrit levels below 45% and led to statistically significant improvements in fatigue and symptom burden based on validated patient-reported outcomes.
The safety profile was consistent with previous experience, with the most common side effects being injection site reactions and anemia. No new safety concerns or increase in serious adverse events were observed. Overall, rusfertide represents the first investigational agent in PV to prospectively demonstrate improvements in both disease control and quality of life, marking a potential new standard for managing phlebotomy-dependent polycythemia vera.
What They’re Saying: Reactions to VERIFY Trial at ASCO 2025
Ruben A. Mesa, MD, Clinical Leader, Advocate Health Cancer National Service Line & Exec Director AH Wake Forest Baptist Comprehensive Cancer Center shared on X
Amazing day at ASCO25 plenary session! First an MPN abstract in the plenary! Second, amazing job by KuykendallMd
for presenting VERIFY PhIII trial demonstrating Rusferatide impact on phlebotomy and PV symptoms in PV
Valentin Garcia, Hematologo en Hospital Universitario Ramon y Cajal , Profesor asociado Universidad de Alcalá. Granaino, marido y padre en Madrid shared on X
Proud to be a co-author of the VERIFY study, presented as a Plenary Session at ASCO25. These results represent a major advance toward a new therapeutic option for patients with polycythemia vera.
You Can Watch More on OncoDaily Youtube TV
Written by Armen Gevorgyan, MD


