Thyroid cancer is one of the most treatable forms of cancer, particularly when diagnosed at an early stage. It is also one of the few cancers with relatively high survival rates, especially for younger patients and those with well-differentiated forms of thyroid cancer. Understanding the cure thyroid cancer cure rate, treatment options, and factors that influence prognosis can empower patients to make informed decisions about their care and improve their chances of successful treatment.
How Common Is Thyroid Cancer?
Thyroid cancer, while not as prevalent as other cancers, is one of the fastest-growing cancers in terms of incidence, particularly in women. The American Cancer Society reports that over 50,000 new cases of thyroid cancer are expected in the United States in 2024, with women being more likely to develop it than men (American Cancer Society, 2024). Early detection through screening and awareness of symptoms are vital in improving outcomes.
Read About Thyroid Cancer on Oncodaily
What Does “Cure” Mean in Thyroid Cancer?
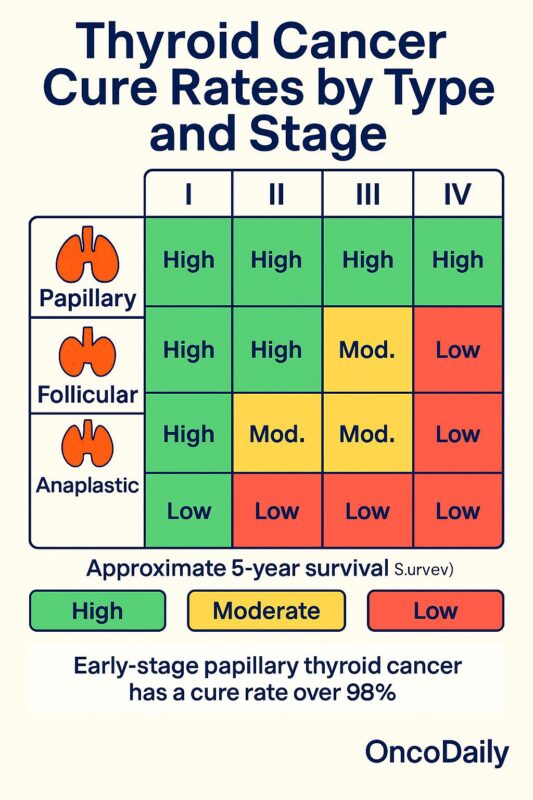
In thyroid cancer, the term “cure” is used when patients achieve long-term remission after treatment, with no recurrence of cancer. For most patients with early-stage disease, thyroid cancer can be considered highly treatable. The 5-year survival rate for patients with localized thyroid cancer is typically over 98% (American Cancer Society, 2024). However, survival rates can vary by cancer type, stage, and response to treatment.
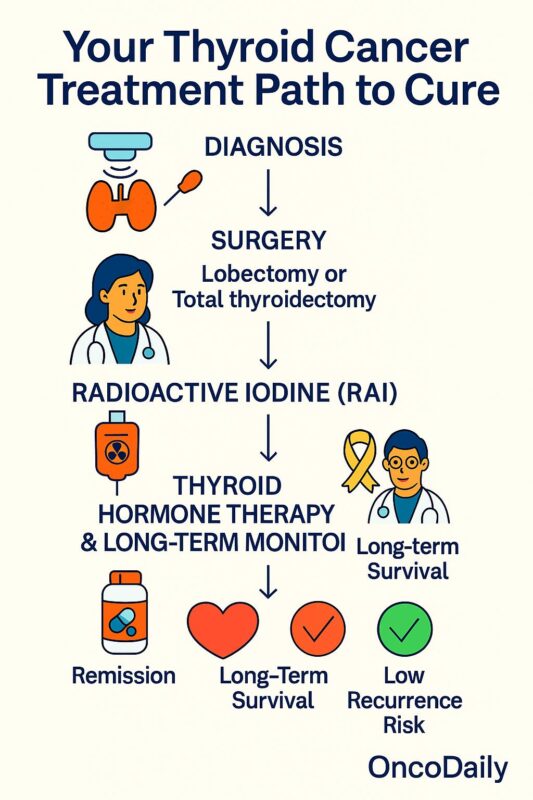
Treatment for thyroid cancer generally involves surgery to remove the thyroid gland, followed by radioactive iodine therapy to eliminate any remaining cancerous tissue. In cases of more advanced disease, additional therapies such as radiation or chemotherapy may be required, but these treatments are less likely to result in a complete cure.
Survival Rates by Stage
The prognosis for thyroid cancer is heavily influenced by the stage at diagnosis. Stage I thyroid cancer, where the tumor is confined to the thyroid and has not spread, is associated with a >98% 5-year survival rate (American Cancer Society, 2024). For patients diagnosed at this stage, treatment typically involves a thyroidectomy, or partial removal of the thyroid, which can often be curative.
For Stage II disease, where the tumor has grown beyond the thyroid but not yet spread to distant lymph nodes or organs, the survival rate is still high, typically around 95% (American Cancer Society, 2024). Treatment typically involves surgery followed by radioactive iodine therapy. Stage III disease, which involves regional lymph node spread, has a 5-year survival rate of around 90%. In these cases, aggressive surgery, followed by radioactive iodine therapy, can provide long-term remission.
However, Stage IV thyroid cancer, in which the tumor has spread to distant organs such as the lungs or bones, presents a much more challenging prognosis. The survival rate for Stage IV thyroid cancer can vary, but the 5-year survival rate is generally lower, around 50-60% (Van Cutsem et al., 2020). Even at this stage, newer treatments such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy are helping improve survival, with some patients achieving long-term remission.
Factors Affecting the Thyroid Cancer Cure Rate
Several factors play a role in determining the likelihood of cure for thyroid cancer patients. Age is a significant factor, as younger patients tend to have better outcomes due to the tumor’s slower progression and their better tolerance to aggressive treatments (Van Cutsem et al., 2020). The type of thyroid cancer is another crucial factor: papillary thyroid cancer, which accounts for most cases, has a very high cure rate, while anaplastic thyroid cancer, which is rare and aggressive, has a much poorer prognosis.
The genetic profile of the cancer, such as the presence of RET mutations in medullary thyroid cancer, can affect treatment choices and outcomes (American Cancer Society, 2024). Response to treatment is also a critical factor. For example, patients who achieve complete resection of the thyroid tumor and respond well to radioactive iodine have a significantly better prognosis.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Cancer
The first line of treatment for thyroid cancer is surgery. A total thyroidectomy (complete removal of the thyroid) is the most common procedure, especially for patients with larger or more aggressive tumors. In some cases, a partial thyroidectomy may be sufficient, especially if the tumor is small and localized.
After surgery, many patients undergo radioactive iodine therapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells. This treatment is particularly effective for papillary and follicular thyroid cancers, as these types typically absorb the iodine. In some cases, additional treatments such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be used, particularly if the cancer is aggressive or has recurred.
For advanced or metastatic thyroid cancer, targeted therapy with drugs like lenvatinib and sorafenib can help slow tumor growth and prolong survival. Immunotherapy is an emerging option for advanced thyroid cancer, and ongoing clinical trials are exploring its effectiveness.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is paramount in thyroid cancer, as it significantly improves the chances of a cure. Patients who undergo routine screening or who notice early symptoms—such as a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, or hoarseness—are more likely to catch the disease before it spreads. Regular follow-up care after treatment, including blood tests and neck ultrasounds, is also crucial for detecting any recurrence of the cancer.
Final Thoughts: Optimism for the Future
Thyroid cancer is one of the most treatable cancers, with the potential for cure, especially when diagnosed at an early stage. Through advances in surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and newer treatments like targeted therapies and immunotherapy, many thyroid cancer patients can expect long-term survival and a good quality of life. Personalized treatment plans based on the type of cancer, stage of disease, and patient health are the key to optimizing outcomes.
Thyroid cancer may be challenging, but with early detection and the right treatment, many patients go on to live fulfilling lives.
You Can Watch More on OncoDaily Youtube TV
Written by Armen Gevorgyan, MD