Oncomarkers Awareness Day, celebrated for the first time on November 13, 2025, is a landmark occasion dedicated to recognizing the critical role that biomarkers play in cancer care. The day aims to raise both public and professional awareness about how biomarker testing guides personalized treatment strategies and improves outcomes for people with cancer.
Biomarkers are measurable biological indicators in the form of genes, proteins, or other molecular characteristics that reveal important insights about a patient’s specific cancer, beyond just its type. This detailed molecular information enables precision oncology, allowing treatments to be tailored to the unique biology of each tumor.

Photo: Depositphotos
Despite their growing importance, many patients still do not receive biomarker testing or may be unaware of its significance. Oncomarkers Awareness Day serves to empower patients, caregivers, healthcare providers, and researchers to advocate for broad access to biomarker testing, which is key to transforming cancer diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis.
By highlighting the value of biomarkers, this day underscores their revolutionary impact on cancer care and the ongoing need for education, research, and equitable testing availability nationwide.
Role of Oncomarkers in Cancer Management
Cancer biomarkers, or oncomarkers, are measurable molecular indicators associated with the presence, progression, or response to treatment of cancer. They include a wide range of biomolecules such as genetic mutations, proteins, metabolites, and changes in gene expression. Cancer biomarkers hold both molecular and clinical significance as they can be detected in tumor tissues or more conveniently through non-invasive sampling like blood, saliva, or urine.
There are several types of cancer biomarkers distinguished by their clinical roles:
- Diagnostic biomarkers help detect and confirm the presence of cancer.
- Prognostic biomarkers provide information about the likely course or outcome of the disease.
- Predictive biomarkers indicate how a patient will respond to a particular treatment.
- Monitoring biomarkers track the response to therapy and detect minimal residual disease or recurrence.
Emerging classes of biomarkers include circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), which are fragments of tumor-derived genetic material found in the blood, and extracellular vesicles such as exosomes, which carry proteins and nucleic acids involved in tumor progression and immune modulation. These novel biomarkers enable non-invasive liquid biopsies that offer promising avenues for earlier diagnosis and dynamic treatment monitoring in precision oncology.
About 30-40% of HCC patients have normal AFP at diagnosis, emphasizing the need for additional biomarkers and surveillance tools.
Role of Oncomarkers in Cancer Management
Oncomarkers play a pivotal role in cancer management by significantly enhancing early detection, guiding personalized treatment decisions, and monitoring therapy response and recurrence.
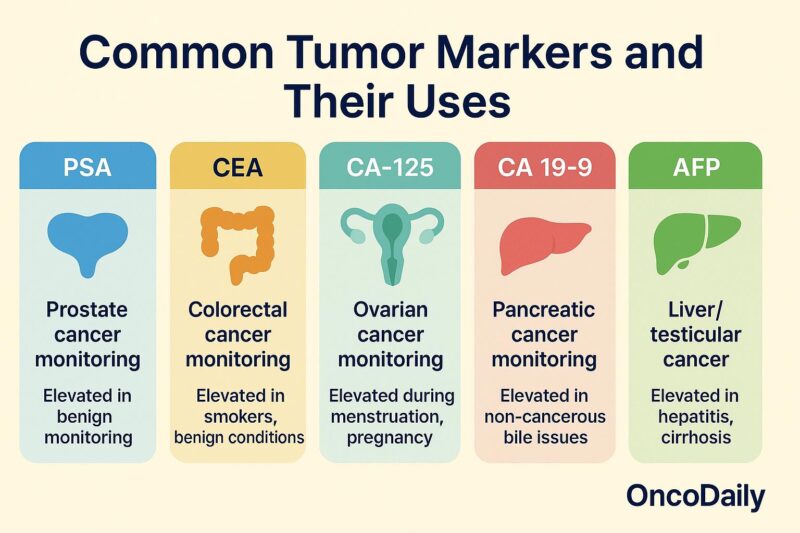
- Early Cancer Detection: Oncomarkers enable the identification of cancer at its earliest stages, often before clinical symptoms appear. Biomarkers such as PSA, CA19-9, CEA, and novel markers like circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and exosomes provide non-invasive means to detect malignancies early, leading to improved survival and better treatment outcomes. Early detection allows less invasive interventions and reduces treatment-related side effects.
- Personalized Treatment Decisions: Biomarkers characterize the molecular profile of tumors, helping clinicians select therapies best suited to an individual’s cancer biology. Predictive biomarkers indicate responsiveness to targeted therapies or immunotherapies, optimizing treatment efficacy while minimizing unnecessary toxicity.
- Monitoring Treatment Response and Detecting Recurrence: Oncomarkers are used to assess how well a patient responds to therapy in real time. Rising biomarker levels during or after treatment may signal recurrence or resistance, prompting timely modifications in management. Regular monitoring improves disease control and long-term prognosis.
Up to approximately 76-80% of CA 19-9 elevations can be due to benign conditions, especially in inflammatory or obstructive states.
Recent Advances and Challenges
Recent advances in cancer biomarker research include significant technological innovations such as liquid biopsies and multi-omics integration. Liquid biopsies enable non-invasive sampling of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), extracellular vesicles, and other biomolecules from blood, facilitating early cancer detection, real-time monitoring, and assessment of tumor evolution without the need for tissue biopsy. Multi-omics approaches combine genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data to provide holistic insights into tumor biology, enabling the discovery of novel biomarkers and personalized treatment strategies.
However, several challenges remain. Tumor heterogeneity the presence of diverse cancer cell populations within a tumor or between primary and metastatic sites creates variability in biomarker expression, complicating validation and clinical application. This heterogeneity necessitates multi-sample and longitudinal analysis to accurately capture tumor dynamics. Additionally, robust validation of biomarkers is difficult due to biological complexity, technical variability, and the need for large, well-characterized patient cohorts.
There is a growing need for reliable predictive biomarkers to guide immunotherapy, as not all patients respond equally to immune checkpoint inhibitors or other immunomodulatory treatments. The identification and validation of such biomarkers remain an ongoing frontier, requiring sophisticated assays and integrative data analysis.
In sum, while advances like liquid biopsies and multi-omics offer promising avenues, tumor heterogeneity and rigorous validation processes represent critical hurdles in translating biomarker discoveries into routine clinical practice.
ctDNA can detect relapse earlier than imaging in some cancers, typically 8-12 months prior.
Impact of Biomarker Awareness on Patients and Healthcare
Biomarker awareness significantly benefits patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency by enabling more precise, personalized cancer care. Awareness promotes timely biomarker testing, which helps clinicians select therapies tailored to a patient’s molecular tumor profile. This targeted approach improves treatment effectiveness, reduces adverse drug reactions, and enhances quality of life. Studies show that biomarker-guided therapies contribute to increased survival rates and decreased premature mortality among cancer patients.
Moreover, awareness drives healthcare system efficiency by minimizing unnecessary interventions and avoiding ineffective treatments, reducing costs and resource use. Enhanced knowledge among providers improves clinical workflows and decision-making, fostering a precision medicine approach that benefits patients and optimizes care delivery.
You Can Also Read Tumor Markers: What They Are, How They Help and Their Role in Cancer Care by OncoDaily

Written by Aharon Tsaturyan, MD, Editor at OncoDaily Intelligence Unit


