FDA immunotherapy approvals in the first half of 2025 reflect major progress across gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and head and neck cancers. Multiple landmark phase III trials—KEYNOTE-811, NIAGARA, CHECKMATE-8HW, AK105-304, and POD1UM-303—have established new standards of care by integrating PD-1/PD-L1 or dual checkpoint blockade into frontline and perioperative treatment strategies.
These approvals highlight the expanding role of immune-based therapy across HER2-positive gastric/GEJ cancer, muscle-invasive bladder cancer, MSI-H/dMMR colorectal cancer, recurrent/metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and anal squamous cell carcinoma.
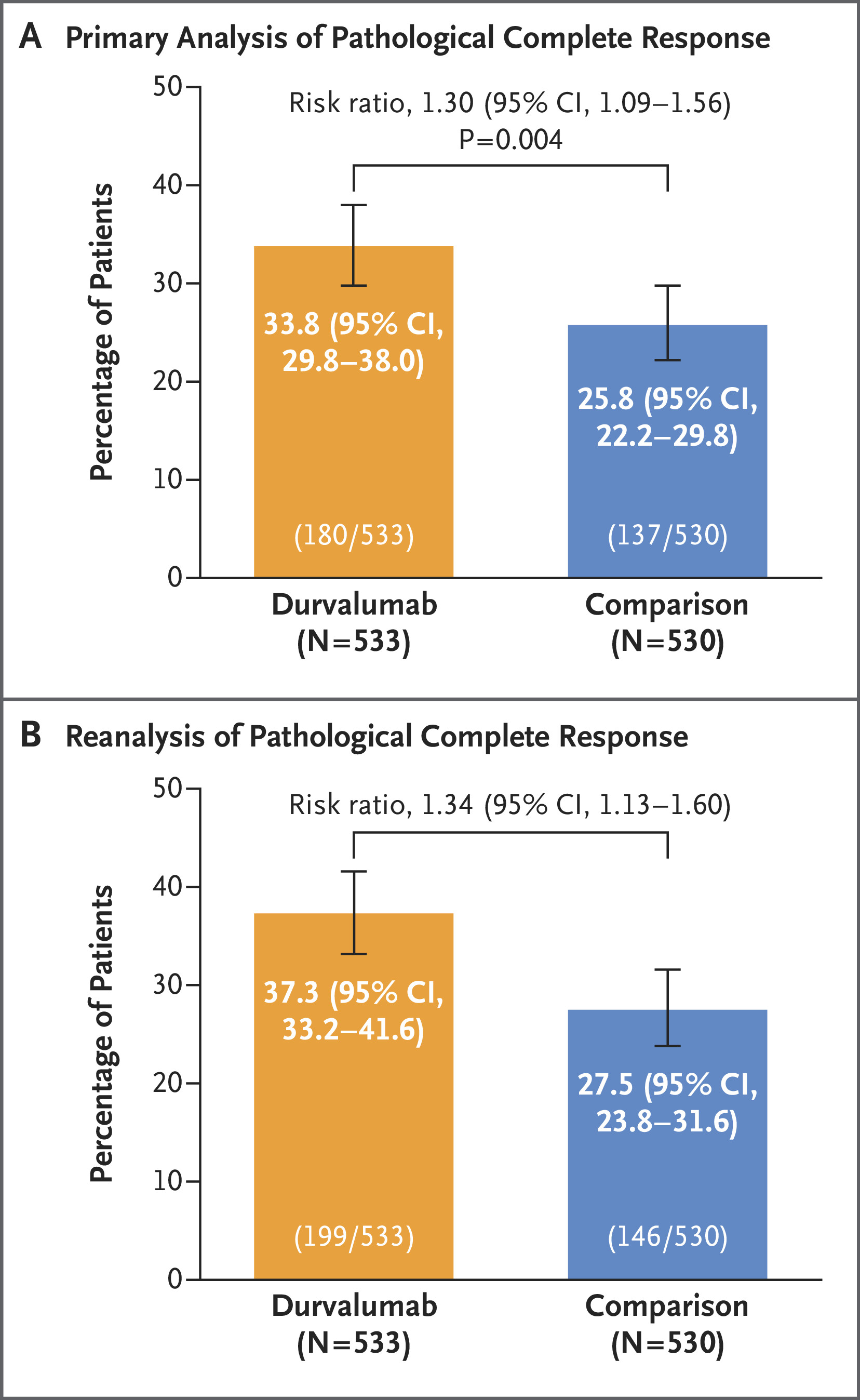
Pembrolizumab + Trastuzumab + Chemotherapy for HER2-Positive Gastric/GEJ Adenocarcinoma
FDA Approval Date: March 19, 2025
The FDA granted full approval to pembrolizumab in combination with trastuzumab and fluoropyrimidine/platinum chemotherapy for first-line treatment of HER2-positive metastatic or unresectable gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma expressing PD-L1 (CPS ≥1). The approval is based on KEYNOTE-811, in which pembrolizumab significantly improved both progression-free and overall survival compared with trastuzumab-chemotherapy alone. Median PFS was 10.9 vs 7.3 months, and median OS was 20.1 vs 15.7 months. This marks a definitive establishment of PD-1 inhibition as part of frontline therapy for HER2-positive, PD-L1-expressing upper GI cancers.
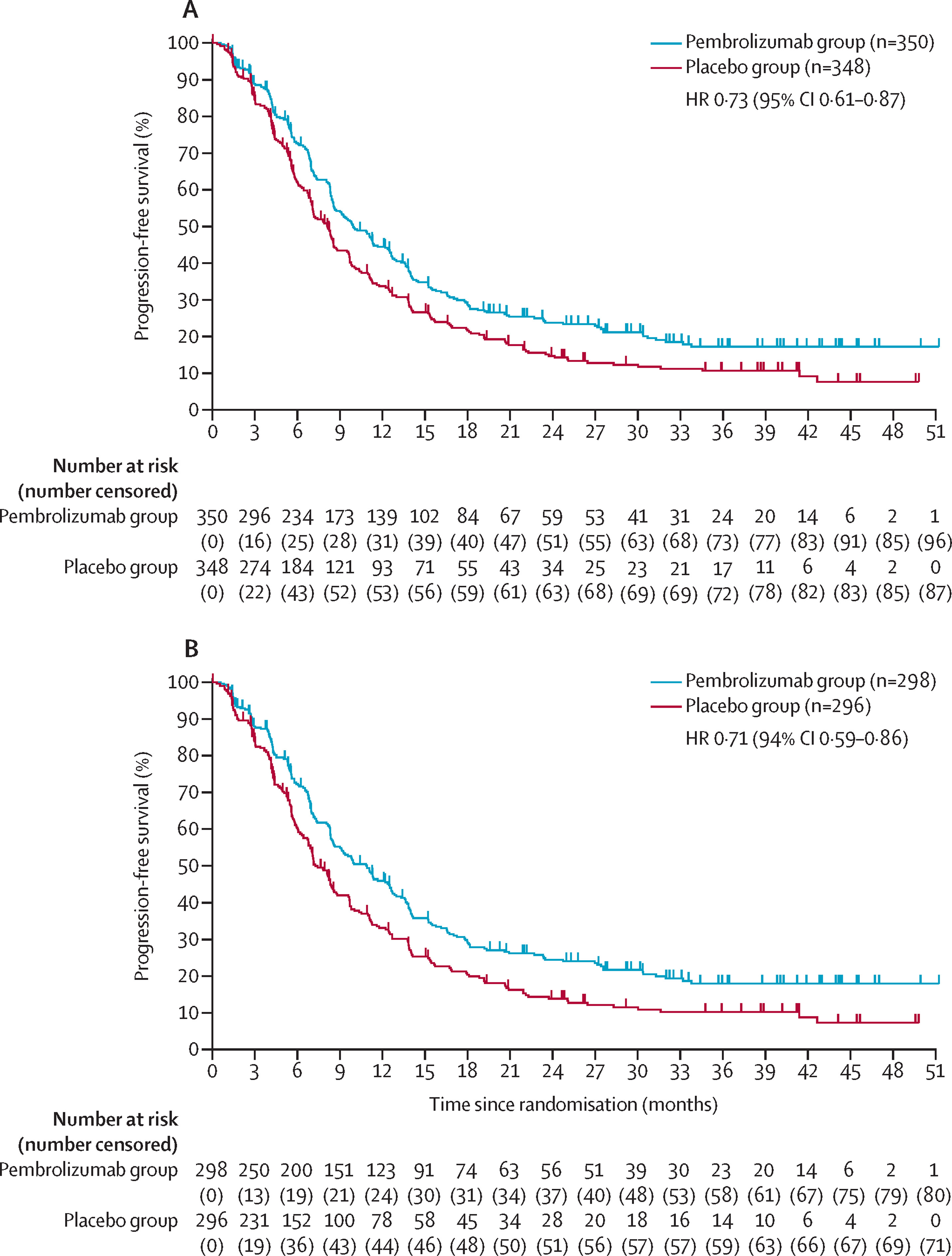
Durvalumab for Neoadjuvant + Adjuvant Treatment of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC)
FDA Approval Date: March 28, 2025
Durvalumab received approval for perioperative use in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy. The NIAGARA trial demonstrated significant improvements in event-free survival and overall survival when durvalumab was added to neoadjuvant gemcitabine/cisplatin and continued as adjuvant monotherapy. Median EFS was not reached in the durvalumab arm versus 46.1 months in the chemotherapy-only arm (HR 0.68), establishing the first major perioperative immunotherapy advance in MIBC and reinforcing PD-L1 blockade as a cornerstone of multimodal bladder cancer management.
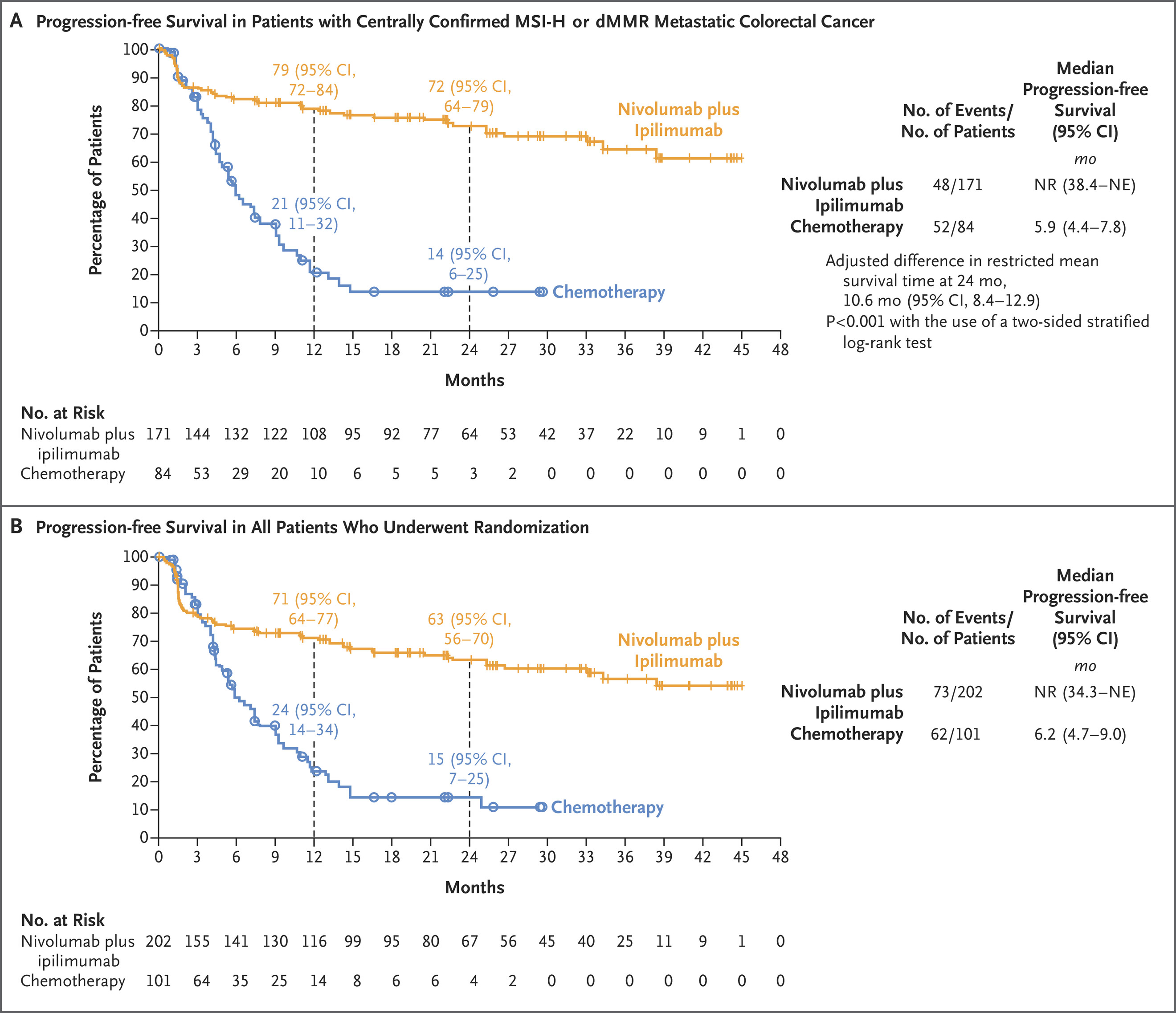
Nivolumab + Ipilimumab for MSI-H/dMMR Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
FDA Approval Date: April 8, 2025
The FDA approved nivolumab plus ipilimumab for adults and adolescents (≥12 years) with unresectable or metastatic MSI-H/dMMR colorectal cancer, converting nivolumab monotherapy from accelerated to regular approval. CHECKMATE-8HW showed that dual checkpoint blockade produced markedly superior progression-free survival compared with chemotherapy in the first-line setting (median PFS not reached vs 5.8 months; HR 0.21). Versus nivolumab alone, the combination also achieved longer PFS and higher response rates (ORR 71% vs 58%). This solidifies PD-1 + CTLA-4 inhibition as a high-efficacy regimen for immunotherapy-sensitive CRC.
Penpulimab (Anti–PD-1) for Recurrent or Metastatic Non-Keratinizing Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
FDA Approval Date: April 23, 2025
Penpulimab, an Fc-engineered PD-1 inhibitor, was approved with platinum-gemcitabine chemotherapy for first-line treatment of recurrent or metastatic non-keratinizing NPC, and as monotherapy after platinum-based therapy. In the AK105-304 study, penpulimab + chemotherapy significantly prolonged PFS compared with chemotherapy alone (median 9.6 vs 7.0 months; HR 0.45). In previously treated patients, single-agent penpulimab achieved an ORR of 28% with durable responses. The antibody’s stabilized Fc region minimizes Fc-mediated effector function, contributing to a distinct safety profile in EBV-associated NPC.
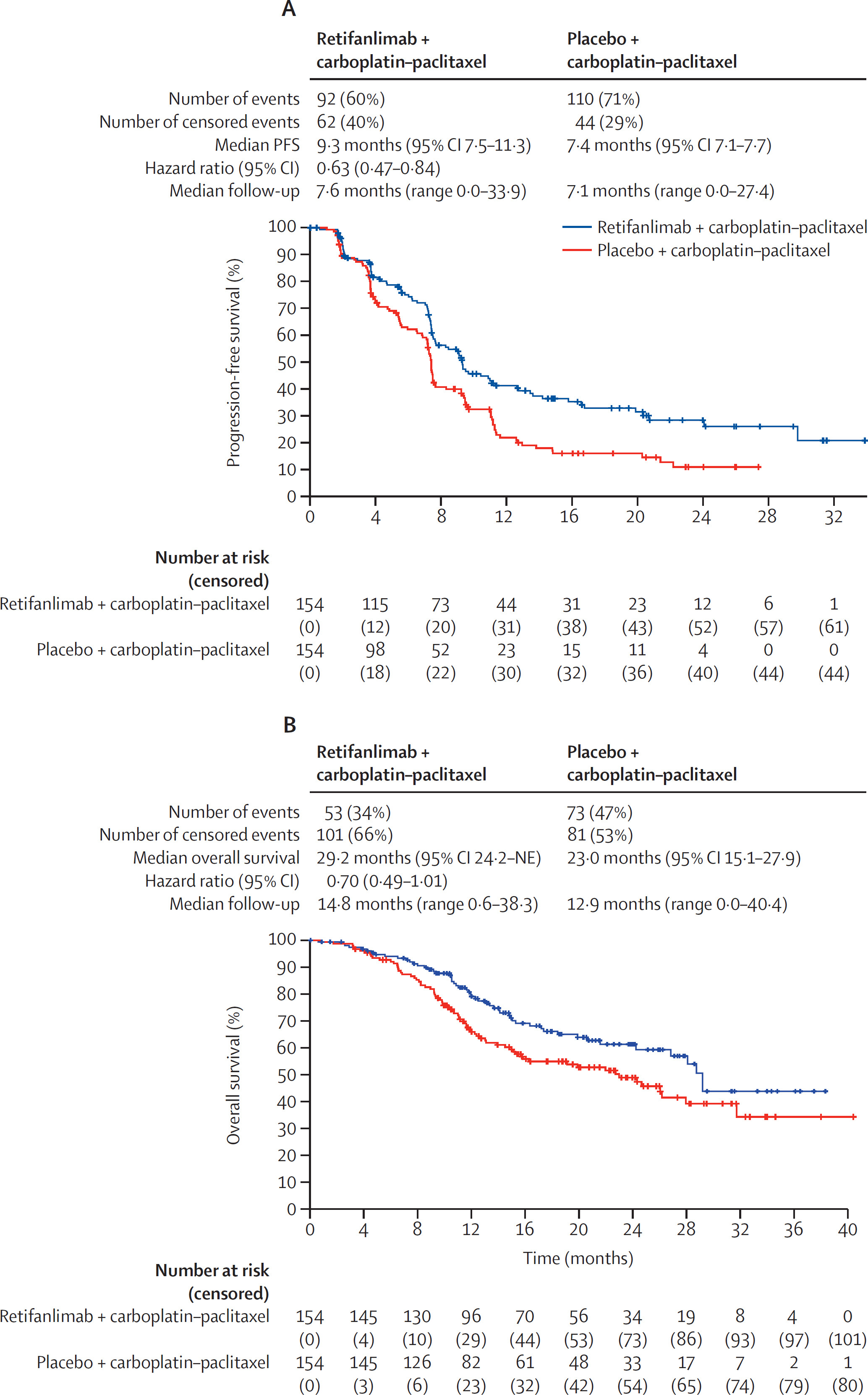
Retifanlimab for Locally Recurrent or Metastatic Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
FDA Approval Date: May 15, 2025
Retifanlimab was approved in combination with carboplatin/paclitaxel for first-line treatment of inoperable locally recurrent or metastatic anal squamous cell carcinoma, with additional approval as monotherapy for patients progressing after platinum-based therapy. In the POD1UM-303 trial, adding retifanlimab to chemotherapy significantly improved PFS (9.3 vs 7.4 months; HR 0.63) and demonstrated a favorable trend in overall survival. Single-agent retifanlimab showed durable activity in previously treated disease (ORR 14%; median DOR 9.5 months). This represents the first new systemic immunotherapy option in frontline metastatic SCAC.