The study led by Asfand Yar Cheema were presented as an abstract at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) 2024
Cardiometabolic comorbidities, such as hypertension (HTN), obesity, diabetes mellitus (DM), dyslipidemia, and chronic kidney disease (CKD), are linked to higher mortality and poorer outcomes in breast cancer patients.
This study evaluates how these conditions influence overall survival (OS) and pathologic complete response (pCR) in patients undergoing neoadjuvant pembrolizumab with chemotherapy (Keynote-522 regimen). Insights from this analysis may support personalized treatment strategies to improve clinical outcomes.
Authors: Asfand Yar Cheema, Jasmin Hundal, Olga Lytvynova, Serhan Unlu, Baidehi Maiti
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted on 107 patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant pembrolizumab and chemotherapy.
Cardiometabolic conditions—including CKD, HTN, obesity (BMI >30), DM, low HDL (<50 mg/dL), and high triglycerides (>150 mg/dL)—were assessed. Rates of pCR and OS at 1 and 2 years were calculated.
The log-rank test was used to assess differences in survival, while Fisher’s exact test and Wilcoxon rank-sum test compared characteristics between groups based on cardiometabolic status. Kaplan-Meier curves estimated OS.
Results
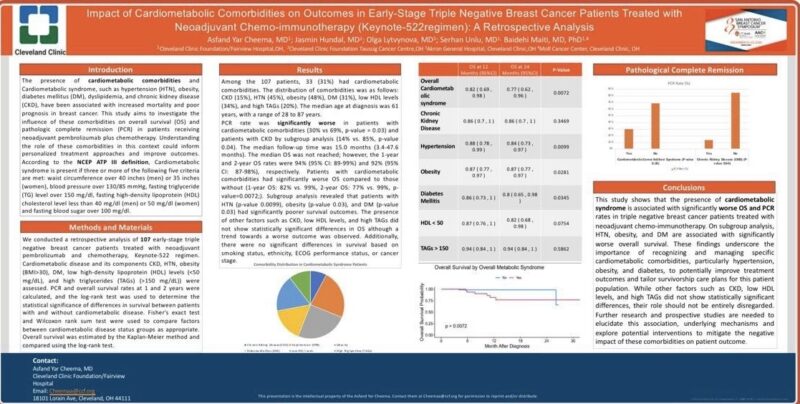
Of the 107 patients, 33 (31%) had cardiometabolic comorbidities, distributed as follows: CKD (15%), HTN (45%), obesity (48%), DM (31%), low HDL (34%), and high triglycerides (20%). Median age at diagnosis was 61 years (range: 28–87).
Patients with cardiometabolic comorbidities had lower pCR rates compared to those without (30% vs. 69%, p = 0.03), with CKD subgroup analysis showing particularly poor pCR rates (14% vs. 85%, p = 0.04).
Median follow-up was 15 months (range: 3.4–47.6 months). While the median OS was not reached, the 1-year and 2-year OS rates were 94% (95% CI: 89–99%) and 92% (95% CI: 87–98%), respectively.
Patients with cardiometabolic comorbidities had worse OS outcomes (1-year OS: 82% vs. 99%; 2-year OS: 77% vs. 99%; p = 0.0072).
Subgroup analysis identified HTN (p = 0.0099), obesity (p = 0.03), and DM (p = 0.03) as significantly associated with poorer OS. CKD, low HDL, and high triglycerides did not show statistically significant differences in OS but trended toward worse outcomes.
Survival was not significantly affected by smoking status, ethnicity, ECOG performance status, or cancer stage.
This study demonstrates that cardiometabolic syndrome is associated with significantly worse pCR and OS in triple-negative breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemo-immunotherapy.
Specifically, HTN, obesity, and DM were linked to worse survival outcomes. These findings highlight the need to identify and manage cardiometabolic comorbidities, particularly hypertension, obesity, and diabetes, to improve treatment outcomes and guide survivorship care.
While CKD, low HDL, and high triglycerides did not reach statistical significance, their potential impact warrants further investigation. Prospective studies are needed to clarify the mechanisms underlying these associations and explore interventions to mitigate the adverse effects of these comorbidities on patient outcomes.
About Asfand Yar Cheema
Asfand Yar Cheema, MD is an Internal Medicine Resident at Cleveland Clinic Foundation/Fairview Hospital, President ASCO OSIG CCF FV, Founder of Ask a Doctor, Aspiring Hematology and Oncology. Interested in Medical Education, Research and Patient Care.
About SABCS 2024

The SABCS 2024 (San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium) took place from December 10th to 13th, 2024 at the Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center in San Antonio, TX, USA.
The San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) is an annual conference focused on the latest advancements in breast cancer research, treatment, and care.
This year, more than 11,000 individuals attended either in-person or virtually, setting an all-time record for the event. They were able to experience remarkable presentations, including clinical trial studies on promising drugs that may soon be available for use in clinics.
Further Reading:
Highlights from Day 1 of SABCS 2024
Highlights from Day 2 of SABCS 2024
Highlights from Day 3 of SABCS 2024


