Repotrectinib is an advanced targeted therapy designed to treat specific cancers caused by rare genetic mutations. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which attacks many cells in the body, Repotrectinib focuses on blocking abnormal proteins that cause cancer cells to grow uncontrollably.
It has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and NTRK gene fusion-positive solid tumors. This means it’s available for patients whose cancers have these specific gene changes, offering new treatment options, especially for those who have already tried other therapies.
How Does Repotrectinib Work?
Repotrectinib, sold under the brand name Augtyro, belongs to a group of drugs called tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). These drugs work by blocking proteins made by abnormal genes, such as ROS1 and NTRK fusions. These gene fusions cause the cancer cells to send constant “grow” signals, almost like a stuck gas pedal in a car, leading to rapid tumor growth.
By targeting and blocking these signals, Repotrectinib stops cancer cells from multiplying and spreading. It was specially designed to be small and compact, allowing it to better penetrate the brain—where cancer often spreads in patients with lung cancer—and to overcome resistance that can develop with earlier treatments. This ability to reach brain tumors and treat resistant cancer cells is an important advantage of Repotrectinib.
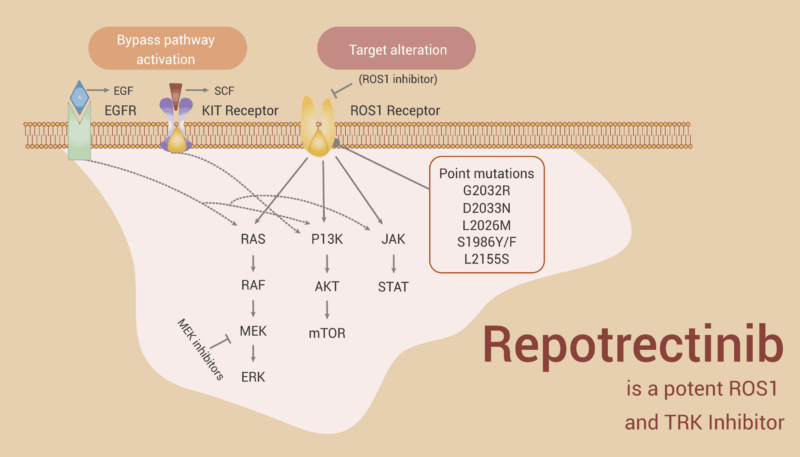
source: Network of Cancer Research
What Types of Cancer Does Repotrectinib Treat?
Currently, Repotrectinib is FDA-approved for two main cancer types:
- ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): This is a lung cancer caused by a ROS1 gene rearrangement. Repotrectinib works both in patients who are new to ROS1-targeted treatment and in those whose cancer has returned or progressed after previous ROS1 therapies. It is especially effective in patients with brain metastases, which are cancer spread to the brain.
- NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors: These are cancers from various body sites that have a rare genetic change called NTRK gene fusion. Repotrectinib was approved for patients 12 years and older with locally advanced or metastatic tumors that have either progressed after prior treatments or for which no satisfactory treatment options exist.
What Is a Clinical Trial and Why Does It Matter?
A clinical trial is a research study designed to test new drugs and treatments in patients to determine their safety and effectiveness. Before Repotrectinib was approved, it went through multiple phases of clinical trials to assess how well it worked, what side effects it caused, and whether it was better than existing treatments. Clinical trials are essential because they provide scientific evidence that a drug can help patients while ensuring it is safe for widespread use.
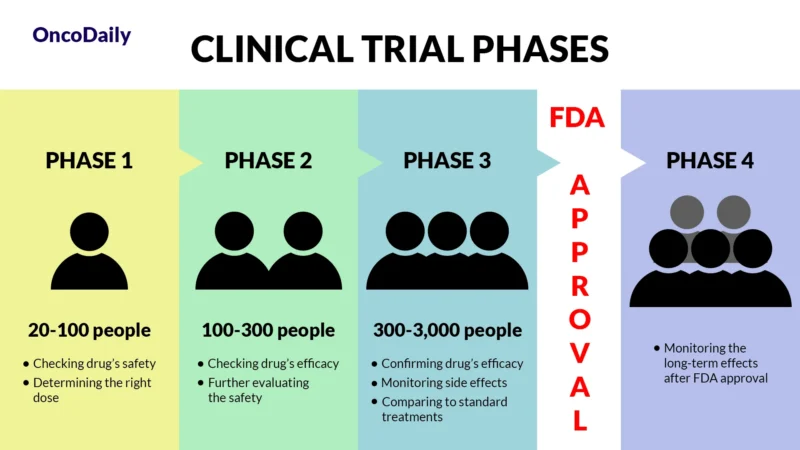
What Does FDA Approval Mean?
When a drug receives FDA approval, it means that after rigorous testing in clinical trials, it has been shown to be both safe and effective for treating a specific condition. This approval makes the drug widely available for doctors to prescribe and helps patients access new, cutting-edge treatments sooner.
What Does the Research Say? Clinical Trial Results
Repotrectinib has been carefully studied in a large international clinical trial called TRIDENT-1. This research looked at how well the drug works for people with certain types of advanced cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and solid tumors with NTRK gene fusions. Here’s what the trial found
TRIDENT-1 Trial in Lung Cancer
The FDA approved Repotrectinib for lung cancer based on results from the TRIDENT-1 trial, a large international study. For patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC who hadn’t received prior ROS1 treatment, 79% experienced tumor shrinkage, and the response lasted on average more than 34 months. For patients who had prior ROS1 therapies, 38% responded, with an average response duration of nearly 15 months.
Importantly, Repotrectinib also showed effectiveness in patients with brain metastases and those whose tumors carried resistance mutations, such as the ROS1 G2032R mutation.
Learn more about Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Latest 2025 Advances in Targeted and Immunotherapy on OncoDaily.
TRIDENT-1 Trial in NTRK Fusion Tumors
In patients with NTRK fusion-positive cancers, the TRIDENT-1 trial showed that 58% of treatment-naïve patients responded to Repotrectinib, while 50% of patients who had prior TRK inhibitor therapy responded. Many of these responses lasted several months, with some still ongoing at the time of the study report.
Updated Findings Published in 2024
The detailed results of the TRIDENT-1 trial were published in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) in 2024, confirming that Repotrectinib provides long-lasting benefit with a good safety profile. For lung cancer patients new to ROS1 treatment, progression-free survival was almost 36 months, meaning patients went that long without cancer worsening. For those previously treated, progression-free survival was about 9 months.

You can also read about Colon Cancer Cure Rate: What Patients Should Know in 2025 on OncoDaily.
What Are Side Effects of Repotrectinib?
Like many cancer treatments, Repotrectinib can cause side effects. Many people take Repotrectinib without major problems, but it’s important to know what side effects may happen, how to spot them early, and what can be done to manage them so treatment can continue safely.
Common Side Effects
The most common side effects reported with Repotrectinib include dizziness, changes in taste (dysgeusia), constipation, tiredness, and shortness of breath. Some people may also notice muscle aches, nausea, or a reduced appetite. Dizziness is especially common at the start of treatment and can affect daily activities. Most of these symptoms are mild to moderate and often improve over time or with supportive care.
Less Common Side Effects
Less frequent but more serious side effects can include changes in liver function (seen in blood tests), a drop in white blood cells (which can increase the risk of infections), anemia (low red blood cells), and vision changes like blurred vision. Rarely, Repotrectinib may cause lung inflammation (pneumonitis) or affect the heart’s rhythm, leading to QT prolongation. These issues may require closer monitoring or changes to the medication, such as lowering the dose or taking a break from treatment.
Side effects Management
Managing side effects is most effective when there is open communication between patients and their healthcare team. Dizziness can often be improved by standing up slowly and avoiding sudden movements. Taste changes may be eased by adding lemon juice, herbs, or spices to food. Constipation can be relieved by staying well hydrated, eating foods rich in fiber, and using gentle laxatives or stool softeners if necessary. Fatigue can be managed by balancing light physical activity with rest, while nausea may be treated with anti-nausea medicines prescribed by the doctor.
Regular blood tests are important to check liver function and blood counts, and any changes may lead to a dose adjustment or temporary pause in treatment. Any vision changes or new breathing difficulties should be reported immediately, as they may require urgent medical attention. In most cases, side effects can be controlled or reversed, allowing treatment to continue. The healthcare team will work closely with each patient to ensure they are supported and safe throughout their therapy with Repotrectinib.

How Is Repotrectinib Taken?
Repotrectinib comes as capsules taken by mouth. Patients usually start with a dose of 160 mg once daily for 14 days. If well tolerated, the dose increases to 160 mg twice daily as the maintenance dose. You can take the capsules with or without food but must swallow them whole—do not open, crush, or chew them. If you miss a dose or vomit after taking it, simply skip that dose and continue as normal with your next scheduled dose.

Read more about Pancreatic Cancer: What patients should know on OncoDaily.
What Should You Avoid While Taking Repotrectinib?
It’s important to avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice, as they can interfere with how your body breaks down the medicine. Alcohol should also be limited to protect your liver.
Since dizziness is common, be careful when driving or operating heavy machinery. Always inform your healthcare provider about any other medications or supplements you are taking to prevent harmful interactions.
What Can You Expect During Treatment?
Your healthcare team will regularly monitor your response with scans and blood tests. Treatment continues as long as the cancer is controlled and side effects are manageable. If side effects become severe, your doctor may adjust your dose or temporarily pause treatment. Open communication with your care team is important for the best experience.
The Future of Repotrectinib
Ongoing studies are exploring Repotrectinib’s use in other cancers and in combination with other treatments. Trials like REPOSE are investigating its effect on patients with brain metastases from ROS1-positive lung cancer, hoping to provide new options for this challenging condition. With continued research and development, Repotrectinib represents a promising future for patients with rare genetic forms of cancer.
f you’re a healthcare provider, access the professional version here.


