Exploring the Potential of 18F-BMS-986229 PET for Noninvasive Assessment of PD-L1 Expression in Gastroesophageal Cancer
Authors: Samuel L. Cytryn, Neeta Pandit-Taskar, Melissa A. Lumish, Steven B. Maron, Ping Gu, Geoffrey Y. Ku, Joanne F. Chou, Marinela Capanu, Ariel Antoine, Diane Loegel, Lara Feder, Steven Philemond, Serge K. Lyashchenko, Jason S. Lewis, Viktoriya Paroder, Amitabh Srivastava, Laura H. Tang, Heiko Schoder, and Yelena Y. Janjigian
Published in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine, on April 1, 2024
Introduction:
Gastroesophageal cancer (GEC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression has been associated with better outcomes for anti-PD-1 therapies, but pathologic assessment has several limitations, including inadequate capture of disease heterogeneity and the invasive nature of repeated biopsies. This study aimed to evaluate the safety and feasibility of using 18F-BMS-986229, a PD-L1-targeting radiotracer, with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging (PD-L1 PET) for noninvasive assessment of PD-L1 expression in patients with GEC.
Design and Methods:
This prospective pilot study enrolled 10 patients with GEC between February 2020 and February 2022. Patients received an intravenous injection of 18F-BMS-986229 (370 MBq) and underwent whole-body PET/CT imaging 60 minutes later. The primary objective was to evaluate the safety and feasibility of 18F-BMS-986229 PET imaging. Secondary objectives included comparing PD-L1 PET findings with pathological PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS), 18F-FDG PET/CT, and CT.
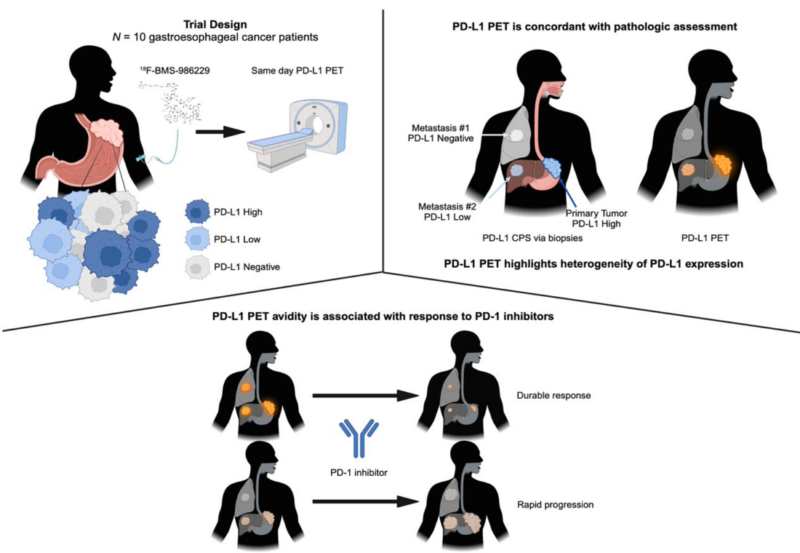
What We Learned:
- There were no adverse events associated with 18F-BMS-986229, and imaging did not result in treatment delays, meeting the primary safety and feasibility endpoint.
- Radiographic evaluation of PD-L1 expression by PD-L1 PET was concordant with pathologic assessment by PD-L1 CPS in 88% of biopsied lesions (Spearman rank correlation coefficient, rs = 0.64).
- PD-L1 PET highlighted intrapatient heterogeneity, with 71% of patients having lesions with and without tracer accumulation, suggesting spatial heterogeneity in PD-L1 expression.
- Patients treated with frontline PD-1 inhibitors who had 18F-BMS-986229 accumulation in any lesions on PD-L1 PET had longer progression-free survival (PFS) than patients without tracer accumulation (median PFS: 28.4 vs. 9.9 months).
Key Highlights:
- PD-L1 PET imaging with 18F-BMS-986229 was safe and feasible in patients with GEC.
- The radiographic assessment of PD-L1 expression by PD-L1 PET correlated well with pathologic evaluation by PD-L1 CPS.
- PD-L1 PET revealed intrapatient heterogeneity in PD-L1 expression, highlighting a potential advantage over single-site biopsies.
- Patients with tracer accumulation on PD-L1 PET had longer PFS when treated with frontline PD-1 inhibitors, suggesting the potential prognostic value of PD-L1 PET.
Key Takeaway Messages:
- PD-L1 PET imaging with 18F-BMS-986229 is a safe and feasible noninvasive tool for assessing PD-L1 expression in patients with GEC.
- This imaging modality may provide a comprehensive evaluation of PD-L1 expression, capturing spatial heterogeneity that single-site biopsies may miss.
- PD-L1 PET has the potential to improve patient selection and predict outcomes for anti-PD-1 therapy, which could ultimately lead to better treatment decisions and improved clinical outcomes for patients with GEC.
Summary by Amalya Sargsyan, MD
18F-BMS-986229 PET to Assess Programmed-Death Ligand 1 Status in Gastroesophageal Cancer
About OncoDaily
OncoDaily was founded in 2023. It is a US-based oncology media platform, which features the latest news, insights, and patient stories from the world of oncology. Within a short period of time it became one of the leading oncology media platforms globally.
OncoDaily gathers content from various sources, including social media posts from renowned oncologists from all over the world, news from oncology societies and cancer centers, patient and survivor stories, and career-related information for professionals.
The mission of OncoDaily is to empower patients, survivors, and professionals with the knowledge and inspiration they need to fight cancer. The motto of OncoDaily is “Cancer doesn’t take a day off – neither do we”.


