Cemiplimab (Libtayo): A Patient Guide for 2025 to Treatment, Side Effects, Dosage, and Research
Cemiplimab is a newer cancer treatment that has brought hope to patients with advanced skin and lung cancers. It is part of an exciting group of drugs called immune checkpoint inhibitors, which help the body’s immune system fight cancer more effectively. Cemiplimab is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat advanced forms of skin cancers, including cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma, as well as certain types of lung cancer. This article will explain what cemiplimab is, how it works, the types of cancers it treats, clinical trial results, what to expect during treatment, potential side effects, and what the future holds for this drug.
What Is Cemiplimab and How Does It Work?
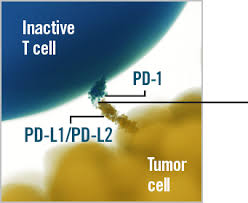
Cemiplimab, marketed under the brand name Libtayo, is a monoclonal antibody, which means it is a lab-made protein designed to recognize and bind to a specific target in the body. In this case, cemiplimab targets a receptor called PD-1 (programmed cell death-1) found on immune cells known as T cells.
Normally, PD-1 acts like a brake on the immune system to prevent it from attacking healthy cells. However, some cancer cells use this system to hide from the immune response. They produce proteins called PD-L1 or PD-L2 that latch onto PD-1, effectively switching off the immune attack against the tumor.
Cemiplimab works by blocking PD-1, preventing cancer cells from turning off the immune system. This “releases the brakes,” allowing T cells to recognize and kill cancer cells more effectively. Instead of attacking the cancer directly, cemiplimab helps your own immune system do the job. This approach has opened new doors in cancer therapy, especially for patients with cancers that have been difficult to treat with traditional methods.
Source: LIBTAYO Official Website
What Cancers Does Cemiplimab Treat?
Cemiplimab is FDA-approved to treat certain advanced skin and lung cancers where other treatments may not be suitable or have stopped working.
Skin Cancers
Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (CSCC): This is a type of skin cancer that can become advanced or spread when surgery or radiation is not possible. Cemiplimab was the first FDA-approved treatment for advanced CSCC back in 2018. It’s used for patients whose tumors cannot be removed or treated with radiation.
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): In 2021, cemiplimab gained approval for advanced BCC in patients who had already tried or could not use a class of drugs called hedgehog pathway inhibitors. This marked the first immunotherapy approved for basal cell carcinoma, especially in cases where other treatments failed.
Lung Cancer
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Cemiplimab is approved to treat advanced NSCLC in patients whose tumors have high PD-L1 expression (≥50%) and who do not have specific gene mutations (EGFR, ALK, ROS1). Initially approved as a single therapy in 2021, it was later approved in 2022 to be combined with platinum-based chemotherapy, broadening its use regardless of PD-L1 status or tumor type.
What Is a Clinical Trial and Why Does It Matter?
A clinical trial is a research study designed to test new drugs and treatments in patients to determine their safety and effectiveness. Before Libtayo was approved, it went through multiple phases of clinical trials to assess how well it worked, what side effects it caused, and whether it was better than existing treatments. Clinical trials are essential because they provide scientific evidence that a drug can help patients while ensuring it is safe for widespread use.
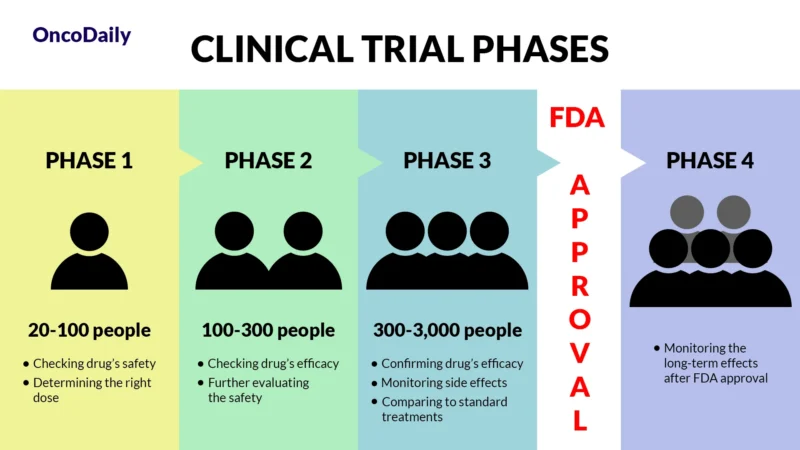
What Does FDA Approval Mean?
When a drug receives FDA approval, it means that after rigorous testing in clinical trials, it has been shown to be both safe and effective for treating a specific condition. This approval makes the drug widely available for doctors to prescribe and helps patients access new, cutting-edge treatments sooner.
How Effective Is Cemiplimab? Results from Clinical Trials
Clinical trials have played a crucial role in showing how cemiplimab benefits patients with these cancers. Here are some key findings from the major studies that led to its approval:
Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Two clinical trials involving 108 patients with advanced CSCC showed that nearly 47% of patients responded to cemiplimab treatment, with over 60% of those responses lasting six months or longer. Patients saw significant tumor shrinkage, and the drug helped both those with tumors that had spread and those with locally advanced disease.
Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma
A phase 2 study enrolled 84 patients who had already tried other treatments. After about 15 months of follow-up, 31% showed a positive response: 6% had complete tumor disappearance, while 25% had partial shrinkage. Disease control, which includes responses and stable disease, was seen in 80% of patients. Almost half maintained their response for more than a year. Side effects were manageable, with no treatment-related deaths reported.
Read more about Immunotherapy for Skin Cancer: Types, Success Rate, Side Effects on OncoDaily.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The EMPOWER-Lung 1 trial included 712 patients with advanced NSCLC. It found that patients treated with cemiplimab lived significantly longer, with a median overall survival of 26.1 months, compared to 13.3 months in those treated with chemotherapy. Progression-free survival, meaning the length of time before the cancer worsened, was also better with cemiplimab (8.1 vs. 5.3 months).
Further studies combined cemiplimab with chemotherapy in 466 patients and showed an improvement in overall survival to 21.9 months compared to 13 months with chemotherapy alone. This combination also increased the time without cancer progression and the number of patients whose tumors shrank.
These results highlight cemiplimab’s effectiveness in improving survival and controlling tumor growth for patients with advanced skin and lung cancers.
You can also read about Immunotherapy for Cancer: An Overview on OncoDaily.
What Can You Expect During Treatment?
Cemiplimab is given as an intravenous (IV) infusion, which means the medicine is slowly delivered into a vein through a needle or catheter. Each infusion usually takes about 30 minutes. It is typically administered every three weeks.
Before treatment, the medication is carefully prepared and checked to ensure it is clear and safe to use. If not used immediately, it can be stored refrigerated for up to 24 hours or at room temperature for up to 8 hours before infusion.
During treatment, healthcare providers will monitor you closely for any reactions or side effects. You may receive premedications or supportive care to help reduce the chance of side effects. Treatment usually continues until the cancer progresses or side effects become too severe.
Side Effects and How They Are Managed?
Like all medicines, cemiplimab can cause side effects. Because it works by activating the immune system, it can sometimes cause the immune system to attack healthy organs and tissues. Understanding side effects and how they are managed can help patients feel prepared and confident during treatment.
Common Side Effects
Many patients experience side effects such as fatigue, rash, diarrhea, nausea, muscle or joint pain, and itchiness. These are usually mild to moderate and can often be managed with supportive care like rest, creams for rash, or medications for diarrhea.
Less Common but Important Side Effects
More serious side effects are less common but need prompt medical attention. These can include inflammation of the lungs (pneumonitis), liver (hepatitis), intestines (colitis), or hormone glands (endocrinopathies like thyroid or adrenal problems). Symptoms might include cough, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing skin), or unexplained tiredness. Some side effects may be permanent and require long-term treatment, such as hormone replacement.
Rarely, severe allergic reactions or skin problems may occur, which require immediate treatment and stopping cemiplimab.
Managing Side Effects
Doctors monitor patients closely for side effects and often use steroids or other immunosuppressive medicines to calm the immune system if needed. Mild side effects may not require stopping treatment, but more severe ones usually mean pausing or discontinuing cemiplimab. Communicating any new symptoms early to your healthcare team is essential for safe treatment.
What to Expect Long-Term with Cemiplimab?
Cemiplimab is not a guaranteed cure but is designed to help control cancer by enabling your immune system to fight it more effectively over time. Some patients experience long-lasting responses, with tumor shrinkage maintained for months or years.
If the cancer progresses during treatment, your doctor may discuss combining cemiplimab with chemotherapy or other therapies to extend control. Long-term safety data shows that cemiplimab’s side effects are manageable with proper care and that many patients continue treatment successfully.
Important Precautions During Treatment
During cemiplimab treatment, patients should avoid:
- Live vaccines, as the immune system is being activated and live vaccines could cause infections.
- Certain medications that might interfere with the immune system or increase side effects.
- Alcohol, which can worsen liver side effects.
Patients will be monitored for infusion reactions during and after the IV infusion. Any symptoms like fever, chills, rash, or breathing difficulties should be reported immediately.
Looking Ahead – The Future of Cemiplimab Treatment
Research continues to expand cemiplimab’s role in cancer care. Studies are exploring its use in earlier stages of disease, in other cancer types like cervical and colon cancer, and in combination with vaccines and novel immunotherapies. These advances may increase the number of patients who benefit and improve long-term outcomes.
With ongoing collaborations and clinical trials, cemiplimab is positioned to be a key part of future cancer treatment strategies, offering hope for patients facing difficult diagnoses.
What Other Clinical Trials Are Ongoing?
Research continues to explore cemiplimab’s potential for more cancers and in combination with other treatments. Two important ongoing trials include:
- The ARCH trial: This phase III study is testing cemiplimab as an additional therapy after surgery in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer to see if it can prevent recurrence.
- The Phoenix trial: A phase II study investigating whether cemiplimab alone can treat certain types of colon cancer without the need for surgery, aiming to preserve the organ and improve patient outcomes.
Additionally, partnerships with other companies are studying cemiplimab in combination with cancer vaccines and oncolytic viruses to enhance its effectiveness further.
If you are a health care provider, here is the professional version.
-
Challenging the Status Quo in Colorectal Cancer 2024
December 6-8, 2024
-
ESMO 2024 Congress
September 13-17, 2024
-
ASCO Annual Meeting
May 30 - June 4, 2024
-
Yvonne Award 2024
May 31, 2024
-
OncoThon 2024, Online
Feb. 15, 2024
-
Global Summit on War & Cancer 2023, Online
Dec. 14-16, 2023
