Dikembe Mutombo, the towering basketball legend, has passed away at the age of 58 after a courageous battle with brain cancer. Diagnosed in early 2023, Mutombo faced his illness with the same determination he displayed on the court. He underwent various treatments, including surgery and radiation, and shared updates on his condition to raise awareness about the disease.

What Were Inital Symptoms of Dikembe Mutombo’s cancer?
Dikembe Mutombo publicly shared that he experienced symptoms such as persistent headaches and vision problems prior to his diagnosis of a brain tumor. He mentioned that these symptoms prompted him to seek medical attention, ultimately leading to his diagnosis in early 2023.
What Are The Most Common Symptoms of a Brain Tumor?
Headaches are a common symptom experienced by individuals with brain tumors, with approximately 35-50% reporting this issue, according to the American Brain Tumor Association. Nausea and vomiting affect around 25-40% of patients, as noted by the National Brain Tumor Society. Seizures occur in about 20-40% of individuals with brain tumors, as reported by the Cleveland Clinic.
Cognitive changes, such as difficulties with memory or concentration, are noticed by around 30% of those affected. Vision problems, including visual disturbances, are reported by roughly 20-30% of patients. Additionally, speech difficulties impact about 15-20% of individuals, while weakness or numbness is experienced by approximately 30%. Balance issues, including coordination problems, affect about 15-25% of patients. Finally, fatigue is a significant concern, impacting 30-40% of individuals with brain tumors.
Dikembe Mutombo: Legendary Career
Dikembe Mutombo, born on June 25, 1966, in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo, had a storied NBA career that spanned 18 seasons.
Dikembe Mutombo had a distinguished NBA career, playing for several teams, including the Denver Nuggets, Atlanta Hawks, Philadelphia 76ers, New Jersey Nets, New York Knicks, and Houston Rockets. He won an NBA Championship with the Houston Rockets in 2009. Known for his defensive prowess, Mutombo was a four-time winner of the Defensive Player of the Year award, taking home the honor in 1995, 1997, 1998, and 2001. He was selected to the NBA All-Star Game eight times and was named NBA Rookie of the Year in 1992, marking a significant start to his professional career. All-NBA Team: Recognized on the All-NBA First and Second Teams multiple times.

Dikembe Mutombo: Legacy Beyond Basketball
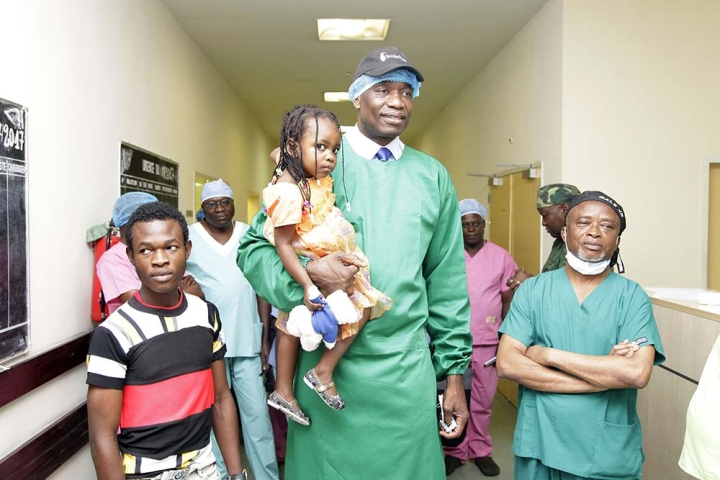
Dikembe Mutombo has made significant contributions to philanthropy through various health initiatives and educational programs. He played a crucial role in the construction of the Biamba Marie Mutombo Hospital in Kinshasa, which provides vital medical services to thousands of people. Additionally, his foundation supports scholarship programs and educational initiatives, helping young people access quality education.
Mutombo’s influence extends beyond health and education; he has served as a cultural ambassador for the Congo, promoting the country’s heritage and potential on the global stage. His humanitarian efforts have garnered numerous awards, including the NBA’s Community Assist Award, as well as recognition from various organizations for his charitable contributions.
As one of the first prominent African players in the NBA, Mutombo serves as a role model and inspiration to many young athletes. He encourages them to leverage their platforms for positive change, demonstrating the impact that sports figures can have on their communities and beyond.
Support from Family and Friends
Dikembe Mutombo’s journey with brain cancer highlighted the importance of support from family and friends in coping with illness. Dikembe Mutombo received significant emotional support from his wife, Omelie Mutombo, and their children, who provided a strong foundation as he navigated the challenges of his diagnosis and treatment. Close relatives often stood by his side, offering encouragement and comfort during difficult times.
In addition to familial support, friends and fellow athletes, including Shaquille O’Neal and Kareem Abdul-Jabbar, rallied around him to amplify his message about brain cancer awareness. Their advocacy helped bring attention to his situation and the importance of health advocacy.
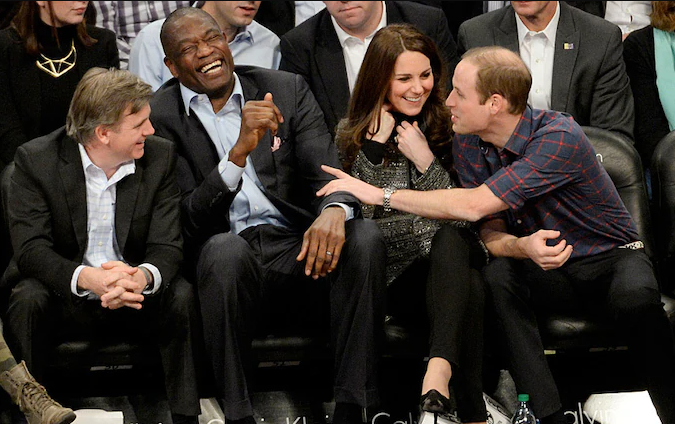

Dikembe Mutombo with Prince and Princes of Wales
Mutombo’s family and friends actively participated in efforts to raise awareness about brain cancer, engaging in events and campaigns focused on educating the public about symptoms and the need for research funding. Supporters, including former teammates and members of the basketball community, organized fundraising events in his honor, contributing to brain cancer research and furthering his philanthropic goals, particularly through the Dikembe Mutombo Foundation.
“Dikembe Mutombo was simply larger than life. On the court, he was one of the greatest shot blockers and defensive players in the history of the NBA. Off the floor, he poured his heart and soul into helping others.”
-written by NBA commissioner Adam Silver
Regular communication and visits from friends, such as Yao Ming and other NBA stars, helped him maintain a sense of normalcy and community, serving as reminders of the love and support surrounding him during his health challenges.
With his wife Omelie Mutombo after win of Laureus 2010
What Is the Prognosis for Brain Cancers?
Brain tumors can be classified into two main types: primary and metastatic. Primary brain tumors originate within the brain tissue and include various subtypes. Gliomas are a significant category, encompassing glioblastomas (GBMs), astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas, with GBM being particularly aggressive. Meningiomas are typically benign tumors that arise from the protective layers surrounding the brain. Another type, pituitary adenomas, affects the pituitary gland and can influence hormone levels, although they are often less aggressive.
Metastatic brain tumors originate from cancers in other parts of the body, such as the lung or breast, and spread to the brain. These tumors are more common than primary brain tumors.
Survival rates for brain cancer vary significantly based on tumor characteristics. For glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the median survival is approximately 15 months post-diagnosis, with a 5-year survival rate of about 5%. Despite aggressive treatment, GBM often recurs. In contrast, low-grade gliomas generally have a more favorable prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate ranging from 60% to 90%, depending on specific characteristics and treatment response. Meningiomas, being mostly benign, are often treated effectively, with 5-year survival rates exceeding 70-90%, especially for non-invasive tumors. Overall, the aggregate 5-year survival rate for all types of brain tumors is around 36%.
What Are the Risk Factors for Brain Tumors?
Genetic factors play a significant role in the risk of developing brain tumors. Individuals with a family history of brain tumors have an increased risk, as noted by the American Brain Tumor Association. Certain genetic disorders, such as neurofibromatosis, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, and tuberous sclerosis, are also associated with a heightened risk, according to the National Brain Tumor Society.
Environmental factors can contribute to brain tumor risk as well. Prior radiation exposure, particularly radiation therapy to the head, has been linked to an increased likelihood of developing brain tumors, as highlighted by the Mayo Clinic. Additionally, there are possible connections between brain tumors and exposure to chemicals like pesticides and industrial solvents, as reported by the National Brain Tumor Society.
Age and gender are important considerations, as certain types of brain tumors are more common in children or older adults, according to the American Brain Tumor Association. Gender differences also exist, with some tumors being more prevalent in men and others more common in women, as noted by the Mayo Clinic.
Other risk factors include immune system disorders, such as HIV/AIDS, which can increase the likelihood of brain tumors, according to the Mayo Clinic. Individuals with a history of brain tumors face a higher risk of developing new tumors, as mentioned by the National Brain Tumor Society.
Lifestyle factors, particularly smoking, may contribute to the risk of some brain tumors, as suggested by the American Brain Tumor Association.
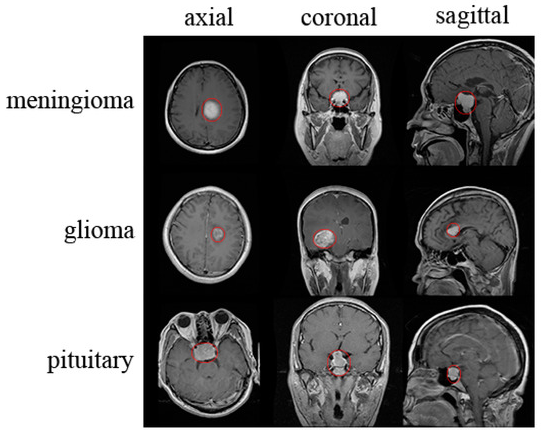
How is a Brain Tumor Diagnosed?
- Medical History and Physical Examination: The doctor will review symptoms and medical history, performing a neurological exam to check for signs of brain dysfunction, such as changes in vision, coordination, or reflexes.
- Imaging Tests: MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): The most common imaging test used to identify brain tumors. It provides detailed images of the brain and can show the size and location of the tumor. CT Scan (Computed Tomography): This can also be used to detect tumors and assess any swelling or bleeding in the brain.
- Biopsy: If a tumor is detected, a biopsy may be performed to determine whether it is benign or malignant. This can involve removing a small sample of tissue through surgery or using a needle guided by imaging.
- Neurological Tests: Additional tests may include assessments of cognitive function, vision, hearing, and coordination to evaluate how the tumor is affecting brain function.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): In some cases, a lumbar puncture may be done to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to check for tumor cells or other abnormalities.
What Are the Treatment Options for Brain Tumors?
Surgery remains mainstay of the treatment of brain tumor, with complete resection being one of the most important prediciting factors of survival.
- Tumor Removal: The primary approach often involves surgically removing as much of the tumor as possible. This can be done through:
- Open Surgery: Involves a larger incision to access the brain.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Such as endoscopic procedures, depending on the tumor’s location.
Radiation Therapy can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy, or in adjuvant setting after surgery.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Directs high-energy rays to the tumor, often used after surgery to eliminate remaining cells.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A non-invasive procedure that delivers a precise, high dose of radiation to the tumor with minimal impact on surrounding tissues.
Chemotherapy
Medications such as temozolomide are commonly used, especially for aggressive tumors like glioblastomas. Chemotherapy can help shrink tumors and slow their growth, often used in combination with surgery and radiation. However, the response rates remains very limited.
Targeted Therapy
Focuses on specific characteristics of the tumor. For example, bevacizumab targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to reduce blood supply to the tumor.
Aims to enhance the body’s immune response against the tumor. Treatments like checkpoint inhibitors are being studied for their effectiveness in treating brain tumors. They are usually used in combination of systemic agents or radiation therapy which helps to reduce Blood Brain Barrier, to let immunotherapy work more effectively.
What supportive care options are available?
This includes symptom management and supportive therapies such as:
- Physical Therapy: To help with mobility and strength.
- Occupational Therapy: To assist with daily activities.
- Palliative Care: Focused on improving quality of life, addressing pain, and providing psychological support.
Brain cancer treatment has evolved significantly in recent years, offering patients a range of options to combat this challenging disease. Here’s an overview of the most effective treatments available:
Surgical Interventions: The Cornerstone of Brain Tumor Management
Surgery remains the primary treatment for many brain tumors, with complete resection being a critical factor in patient survival. Studies show that gross total resection can increase 5-year survival rates by up to 30% compared to partial resection. Advanced surgical techniques have improved resection rates, with some centers achieving complete resection in over 90% of cases for certain tumor types.
Surgical options include
- Open Surgery: Traditional approach for larger or complex tumors
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Including endoscopic and laser-assisted procedures
Radiation Therapy: Precision Targeting of Tumor Cells
Radiation therapy plays a crucial role in brain cancer treatment, often used in combination with surgery or chemotherapy. Studies show that adding radiation therapy to surgery can increase 2-year survival rates by 10-15% for high-grade gliomas
Main radiation approaches:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Standard treatment delivering targeted radiation to the tumor site
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: Highly focused radiation beams for precise tumor targeting
Is There a Role for Chemotherapy in Brain Tumors?
Chemotherapy remains a key component in treating aggressive brain cancers, particularly glioblastomas. The addition of temozolomide to radiation therapy has been shown to increase median survival from 12.1 months to 14.6 months in glioblastoma patients
Common chemotherapy agents
- Temozolomide: Standard first-line treatment for glioblastoma
- Carmustine: Often used in wafer form for local drug delivery
Targeted Therapies: Precision Medicine for Brain Cancer
Targeted therapies focus on specific molecular characteristics of brain tumors, offering potentially more effective and less toxic treatment options. Bevacizumab has shown to improve progression-free survival by 3-4 months in recurrent glioblastoma patients
Examples of targeted therapies
- Bevacizumab: Targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
- IDH inhibitors: For tumors with IDH mutations
Is there a role for Immunotherapy in Brain Tumors?
Immunotherapy represents a promising frontier in brain cancer treatment, aiming to enhance the body’s natural defenses against tumor cells. Early-phase trials of checkpoint inhibitors in combination with radiation have shown response rates of up to 30% in recurrent glioblastoma
Emerging immunotherapy approaches
- Checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., pembrolizumab, nivolumab)
- CAR T-cell therapy
Preventive Measures for Brain Tumors
- Regular Check-ups: Early detection can lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment. Regular neurological evaluations are beneficial, especially for those with a family history of brain tumors (American Brain Tumor Association).
- Genetic Counseling: Individuals with a family history of genetic disorders associated with brain tumors (like neurofibromatosis) may benefit from genetic counseling and screening (National Brain Tumor Society).
- Limiting Radiation Exposure: Minimizing unnecessary exposure to radiation, particularly in children, is recommended. Discussing alternative imaging options with healthcare providers is important (Mayo Clinic).
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: While the direct link between lifestyle factors and brain tumor prevention is unclear, maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking may contribute to overall health (World Health Organization).
- Environmental Awareness: Reducing exposure to potentially harmful chemicals in the workplace and home (like pesticides and industrial solvents) may be a proactive measure (National Institutes of Health).
Research Advancements in Brain Tumors
- Molecular Profiling: Identifies specific genetic mutations in brain tumors, enabling personalized treatment approaches (American Cancer Society).
- Targeted Therapies: Focuses on drugs that target specific molecular features of tumors, improving efficacy and reducing side effects (National Cancer Institute).
- Immunotherapy: Explores vaccines and immune checkpoint inhibitors to boost the body’s immune response against brain tumors (American Society of Clinical Oncology).
- Clinical Trials: Ongoing trials test new drugs and innovative treatments, offering access to cutting-edge therapies (ClinicalTrials.gov).
- Neuroimaging Techniques: Advanced imaging technologies enhance early detection and monitoring of treatment responses (Radiological Society of North America).
- Nanotechnology: Research into targeted drug delivery systems aims to increase treatment effectiveness while minimizing side effects (Nature Reviews).
- Tumor Microenvironment: Studies focus on how surrounding tissues influence tumor behavior and treatment responses, paving the way for new strategies (Nature).
FAQs
Did Dikembe Mutombo Have Cancer? What Type Was It?
Yes, Dikembe Mutombo was diagnosed with a brain tumor, specifically a form of brain cancer. While the exact type of tumor has not been publicly confirmed, he underwent treatments such as surgery and radiation therapy, which are common approaches for malignant brain tumors like glioblastoma or other aggressive types.
What Was Dikembe Mutombo’s Brain Cancer Diagnosis?
Dikembe Mutombo was diagnosed with a brain tumor in early 2023. He underwent surgery and radiation therapy as part of his treatment. His public journey highlighted the importance of awareness about brain cancer.
What Symptoms Did Dikembe Mutombo Experience?
Mutombo shared that he experienced persistent headaches and vision problems, which prompted him to seek medical attention. These symptoms are common indicators of brain tumors.
What Are Common Symptoms of Brain Tumors?
Brain tumor symptoms often include headaches, nausea, vomiting, seizures, cognitive changes, vision issues, and speech difficulties. These symptoms vary based on the tumor’s location and size.
What Causes Brain Cancer?
The causes of brain cancer are not fully understood, but risk factors include genetic predisposition, radiation exposure, and certain genetic disorders like neurofibromatosis and Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
How Is Brain Cancer Diagnosed?
Brain cancer diagnosis usually involves a combination of neurological exams, imaging tests (like MRI or CT scans), and biopsies to confirm the tumor type and grade.
What Treatment Options Are Available for Brain Tumors?
Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and emerging immunotherapies. The approach depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor.
What Is the Prognosis for Brain Cancer?
Prognosis varies widely depending on the tumor type. Glioblastoma, for example, has a poor prognosis with a 5-year survival rate of about 5%, while benign tumors like meningiomas have much higher survival rates.
Are There Preventive Measures for Brain Tumors?
Preventive measures include limiting radiation exposure, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and undergoing regular check-ups, particularly for those with genetic risk factors.
What Role Did Dikembe Mutombo Play in Raising Awareness for Brain Cancer?
Mutombo used his platform to raise awareness about brain cancer, sharing his personal battle and encouraging research and advocacy efforts. His foundation continues to support medical and educational initiatives.
How Did Dikembe Mutombo’s Legacy Extend Beyond Basketball?
Beyond his successful NBA career, Mutombo made significant contributions through his philanthropic work, including building hospitals and supporting health initiatives in his native Congo.
Written By Aharon Tsaturyan, MD

