Catherine O’Hara’s rectal cancer was kept entirely private, with no verified public details on diagnosis timing, symptoms, or treatment beyond the death certificate naming it as the underlying cause of her fatal pulmonary embolism on January 30, 2026. Her representatives’ “brief illness” description masked its true extent, avoiding speculation on onset or care duration.
Catherine O’Hara’s rectal cancer originated in the rectum, the final portion of the large intestine, where malignant glandular cells often develop silently in the mucosal lining. Her diagnosis was handled entirely privately sometime before March 2025, reflecting her reserved nature amid emerging symptoms that remained undisclosed. Oncologist-led care commenced in March 2025, encompassing likely chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapies standard for rectal cancer staging, with consistent monitoring through her last documented visit on January 27, 2026—mere days prior to her passing on January 30.
The CAA’s public statement framed her death as resulting from a “brief illness,” a phrasing that concealed nearly 10 months of intensive cancer management, including potential side effects like profound fatigue, gastrointestinal distress, and escalating treatment complications. This extended battle highlights rectal cancer’s capacity for insidious progression, even under specialized intervention, ultimately fueling the hypercoagulable state that precipitated her fatal pulmonary embolism.
Catherine O’Hara: Cancer’s Role in Death
The immediate cause of Catherine O’Hara’s death was a pulmonary embolism (PE), characterized by a thrombus—typically originating from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the lower extremities embolizing to occlude pulmonary arteries, impairing gas exchange and right ventricular function. This acute event occurred on January 30, 2026, at age 71, with rectal cancer identified on the death certificate as the principal underlying condition, per the February 9, 2026, release from the Los Angeles County Medical Examiner.
Oncogenic Hypercoagulability Mechanism
Cancer-associated venous thromboembolism (VTE), including PE, affects up to 20% of oncology patients and carries a 4-7-fold elevated risk in colorectal malignancies like rectal adenocarcinoma, per established epidemiology (e.g., Khorana score stratification). Rectal tumors arising from epithelial glandular cells in the rectal mucosa induce a prothrombotic state through multifaceted Virchow’s triad disruptions:
- Stasis: Treatment sequelae (e.g., neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy or palliative chemotherapy such as FOLFOX/bevacizumab regimens) often enforce prolonged immobility due to cytopenias, neuropathy, or cachexia-induced deconditioning, reducing venous return and fostering DVT formation.
- Endothelial Injury: Tumor-derived microparticles and circulating extracellular vesicles express tissue factor (TF), the primary initiator of the extrinsic coagulation cascade, triggering thrombin generation and fibrin deposition.
- Hypercoagulability: Mucin-producing rectal cancers classically exemplify Trousseau’s syndrome (migratory thrombophlebitis), with tumor cells overexpressing TF pathway inhibitor antagonists, podoplanin (CLEC-2 ligand for platelet aggregation), and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8).This amplifies platelet activation, fibrinogen consumption, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) upregulation, culminating in unbalanced fibrinolysis.
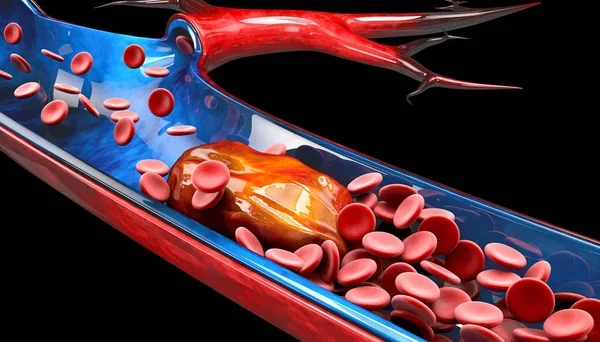
Photo: Depositphotos
In advanced disease, hepatic metastases (common in stage IV rectal cancer) further exacerbate this via portal vein compression or paraneoplastic syndromes, though her private status precludes staging confirmation.
Clinical Trajectory and Terminal Events
Her terminal PE likely presented with acute dyspnea, hypoxemia, and hemodynamic instability hallmarks prompting hospitalization—exacerbated by cancer-driven anemia and right heart strain. Prophylactic anticoagulation (e.g., low-molecular-weight heparin like enoxaparin, per ASCO guidelines) is standard in ambulatory high-risk patients but may fail in overt hypercoagulable states or contraindications (e.g., bleeding risk from tumor erosion).
Postmortem, cremation was expedited per family wishes, with ashes interred privately to husband Bo Welch (production designer, married 1992), reflecting her lifelong discretion amid a 50-year career. This case exemplifies malignancy’s vascular lethality, where PE accounts for 10-30% of cancer mortality, underscoring NCCN/ASCO imperatives for VTE risk assessment (e.g., Khorana score ≥2 mandates prophylaxis) and early colorectal screening to avert such trajectories.
You Can Also Read Shopaholic Author Sophie Kinsella Dies After Brain Cancer Fight by OncoDaily

Written by Aharon Tsaturyan, MD, Editor at OncoDaily Intelligence Unit
FAQ
How did Catherine O'Hara die?
Catherine O'Hara died on January 30, 2026, from a pulmonary embolism, a blood clot in her lungs triggered by rectal cancer.
What was Catherine O'Hara's cause of death?
The immediate cause was pulmonary embolism; rectal cancer was the underlying condition per her February 9, 2026, death certificate.
Did Catherine O'Hara have cancer?
Yes, she had rectal cancer, kept private until revealed on her death certificate as contributing to her fatal pulmonary embolism.
Catherine O'Hara rectal cancer details?
Rectal cancer originated in her rectal mucosa; it induced hypercoagulability (4-7x clot risk), leading to PE—no public diagnosis or treatment timeline exists.
Catherine O'Hara Home Alone cancer death?
Kate McCallister from Home Alone (Catherine O'Hara) succumbed to rectal cancer complications—pulmonary embolism—on January 30, 2026, at 71.
When did Catherine O'Hara get diagnosed with cancer?
No verified diagnosis date; it was private, with reps calling it a "brief illness" masking the true extent.
Kate McCallister pulmonary embolism cause?
Cancer hypercoagulability from rectal tumor inflammation and treatment stasis caused the PE that killed Catherine O'Hara (Kate McCallister).
Catherine O'Hara death certificate cancer?
The LA County certificate lists rectal cancer as underlying, pulmonary embolism as immediate cause of her January 30, 2026, death.
Catherine O'Hara brief illness explained?
CAA's "brief illness" understated nearly 10 months of hidden rectal cancer management ending in fatal PE.


