Francesco Maura, Assistant Professor of Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, posted on X about recent paper by him as co-author, titled “CD38 biallelic loss is a recurrent mechanism of resistance to anti-CD38 antibodies in multiple myeloma” published on bioRxiv.
Authors: Benjamin Diamond, Linda Baughn, Mansour Poorebrahim, Alexandra M. Poos, Holly Lee, Marcella Kaddoura, Erin Wiedmeier-Nutor, Michael Durante, Gregory Otteson, Dragan Jevremovic, Hongwei Tang, Stefan Frohling, Marc A. Baertsch, Marios Papadimitriou, Bachisio Ziccheddu, Tomas Jelinek, Cendrine Lemoine, Alexey Rak, Damian J. Green, Ola Landgren, Paola Neri, Leif Bergsagel, Esteban Braggio, Shaji Kumar, Marc S. Raab, Rafael Fonseca, Nizar Bahlis, Niels Weinhold, Francesco Maura

“Just before the holidays, new preprint from the lab on bioRxiv!
Super talented Ben Diamond reports CD38 loss as mechanisms of resistance to anti-CD38 MoAb in myeloma.
Large chromosome 4 deletions were enriched in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) compared to newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM), and this was observed in both dara/isa and non-dara/isa-exposed patients.
On the contrary, focal deletions, nonsynonymous mutations and biallelic events were only found in post-anti-CD38 MoAb RRMM. We report a loss of CD38 in 20% (10/50) of patients post-CD38 therapy, three of which exhibited a loss of both copies.
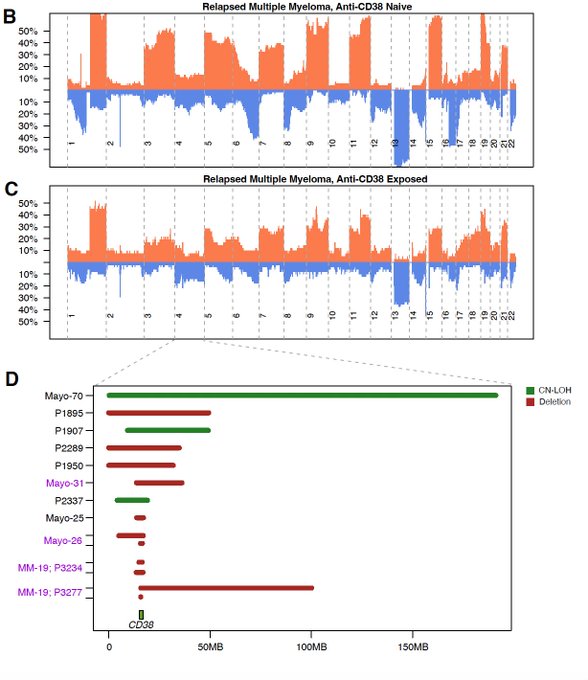
Similarly to what was reported before with Nizar Jacques Bahlis in post-anti-BCMA and -GPRC5D myelomas, we observed 3 patients with evidence of convergent evolution, where multiple CD38 neg clones were selected.
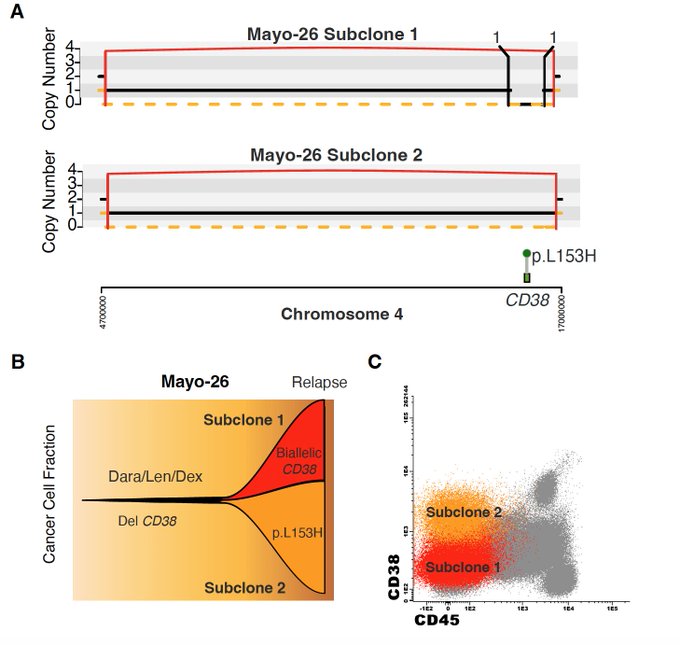
We also found 6 nonsynonymous mutations involving CD38. Some were clearly associated with CD38 downregulation, other not. Therefore we decided to dig little bit more into this.
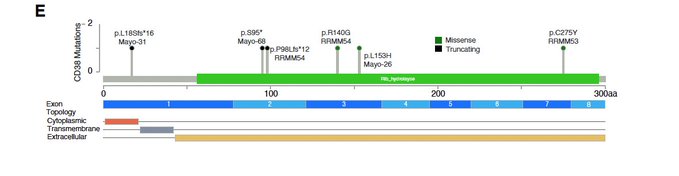
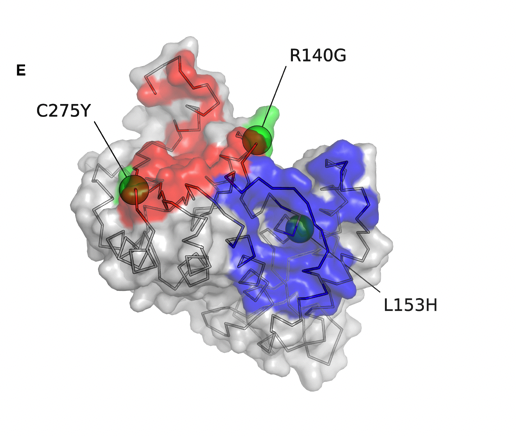
To do so, Nizar Jacques Bahlis, Holly Lee and Mansour Poorebrahim performed multiple functional validations showing how two mutations (L153H and C275Y), decreased binding affinity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of the commercial antibodies Daratumumab and Isatuximab.
In contrast, a third mutation, R140G, fund in a patient who relapsed after dara, conferred resistance to Daratumumab, but not to Isatuximab.
Next we asked help to Sanofi Myeloma to predict how these mutations affect the CD38 structure. C275Y and L153H both destabilize CD38 integrity, potentially affecting the both antibodies.
In constrast, Arginine 140 is located near the Dara binding site and mutation to a glycine increases the flexibility of the neighboring amino acid residues forming the epitope and likely affects Dara binding, but not Isa.
Overall, this data reveals that loss of CD38 can occur in 5-10% of patients. Mutations in CD38 may still result in expressed protein but selectively impair the binding and efficacy of specific anti-CD38 therapies.
Kudos to Ben Diamond for finalizing this new project, and to all our collaborators at Heidelberg Myeloma, Mayo Clinic, and University of Calgary! Over the last two years, I’ve been so lucky and blessed to work with such talented and brilliant collaborators. Looking forward to what’s next!”


