Ipilimumab plus nivolumab (IO/IO) is an established first-line therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC) in patients with IMDC intermediate or poor risk, based on the pivotal CheckMate 214 trial. However, clinical trial populations represent a selected subset of patients, often excluding those with comorbidities, poor performance status, organ dysfunction, or brain metastases. Real-world data are crucial to understand how IO/IO performs in routine clinical practice.
This multi-center GUARDIANS cohort evaluated real-world outcomes, toxicity, and predictors of survival in patients treated outside the controlled environment of a clinical trial.
Patient Population
A total of 356 patients initiated ipilimumab + nivolumab between 2015–2023.
Key characteristics:
- Median age: 64 years
- Male: 69%
- Clear cell histology: 74%
- IMDC intermediate risk: 62%
- IMDC poor risk: 29%
- Not eligible for CheckMate 214: 37% (poor ECOG, autoimmune disease, brain metastases, impaired renal function)
- Metastases at ≥2 sites: 76%
Approximately half of patients (55%) completed all four induction cycles.
Efficacy Outcomes
In this real-world cohort, ipilimumab plus nivolumab demonstrated meaningful clinical activity, with outcomes closely aligned to what has been seen in clinical trials, particularly among intermediate-risk and clear-cell RCC patients.
Across the full population, the objective response rate was 37.4%, including a complete response rate of 8.7% and partial responses in 28.7% of patients. Disease control was achieved in more than half of the cohort (DCR 57.3%).
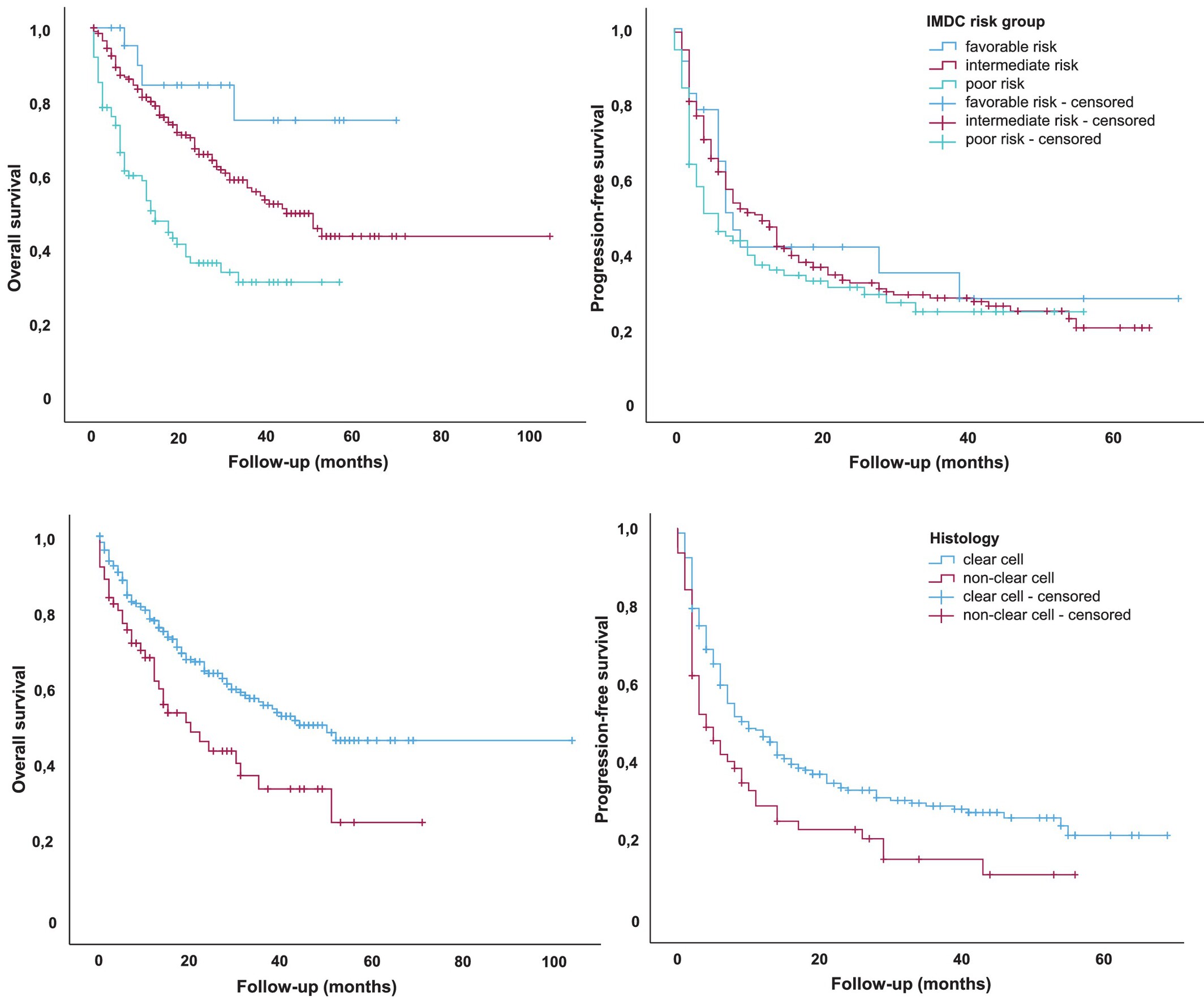
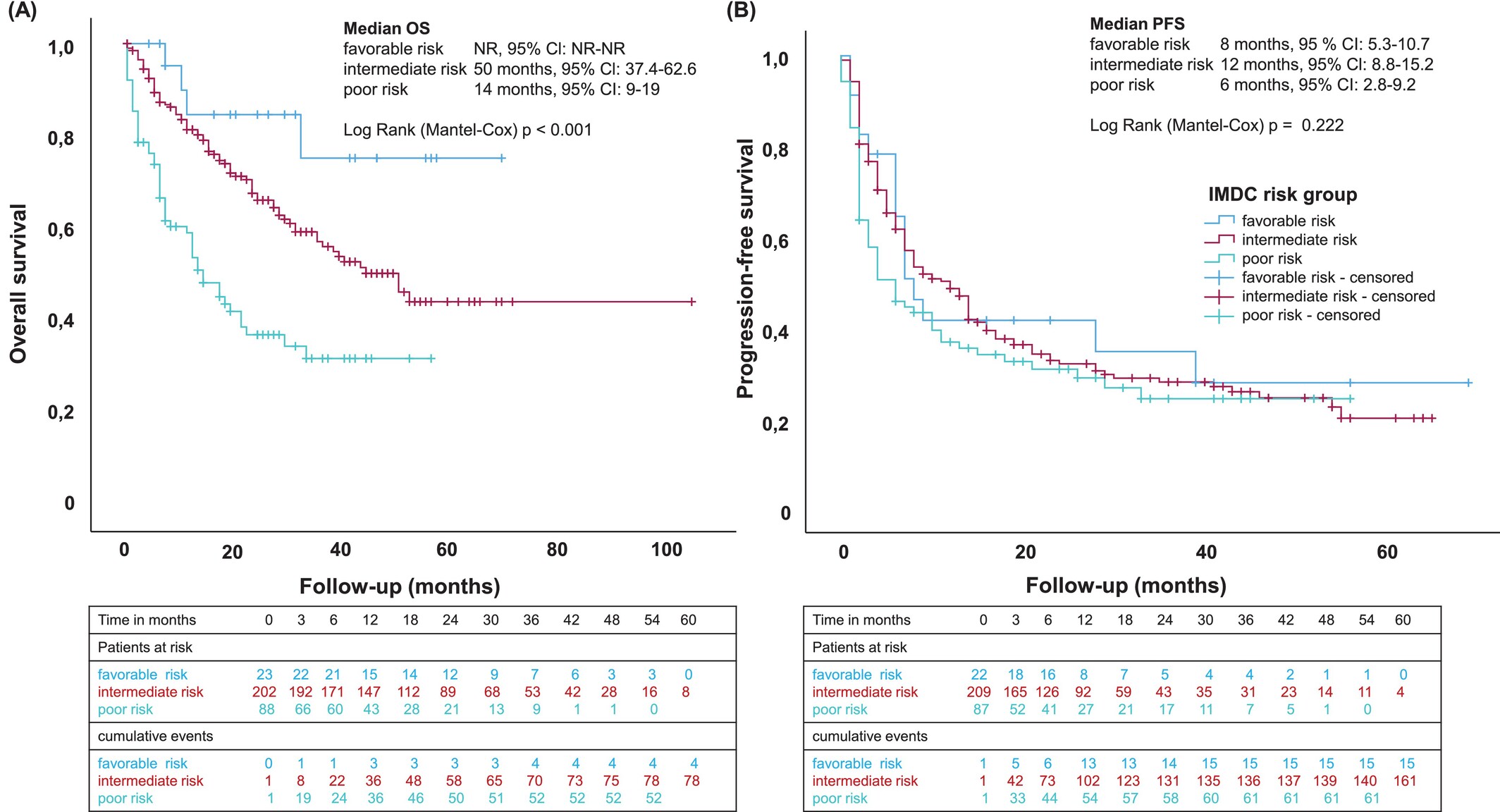
Median progression-free survival was 8 months overall, but outcomes varied by IMDC risk. Patients in the intermediate-risk category achieved a median PFS of 12 months, whereas poor-risk patients had a shorter PFS of 6 months. A similar pattern was seen in overall survival: the median OS was 39 months in the full cohort, extending to 50 months in the intermediate-risk group but dropping to 14 months among poor-risk patients.
Tumor histology had a notable impact on outcomes. Clear-cell RCC performed best, with a median OS of 50 months and a median PFS of 10 months. By contrast, non–clear cell subtypes experienced significantly poorer results, with a median OS of 20 months, median PFS of 4 months, and an ORR of roughly 32%.
Completion of all four induction cycles emerged as an important predictor of benefit. Patients who received the full induction regimen had substantially improved outcomes, with a median OS of 52 months and a median PFS of 14 months—far exceeding the outcomes of those who discontinued early.
Overall, these real-world findings reinforce the strong clinical activity of ipilimumab plus nivolumab while also highlighting the influence of risk category, histology, and treatment completeness on long-term outcomes.
Predictors of Poor Outcomes
The multivariate analysis revealed several factors that consistently predicted worse survival with ipilimumab plus nivolumab. Patients with poor ECOG performance status, liver metastases, or non–clear cell histology experienced markedly reduced overall survival and faster disease progression. High-grade (≥G3) immune-related toxicities were also associated with poorer outcomes, reflecting both treatment intolerance and more aggressive disease biology.
A substantial proportion of the cohort—about 37%—would not have qualified for the original CheckMate 214 trial due to comorbidities, impaired performance status, or challenging disease features such as brain metastases. As expected, these real-world ineligible patients had inferior results, with a median overall survival of 23 months and an objective response rate of 29%, underscoring the greater vulnerability of this population.
Overall, the findings highlight how patient fitness, disease burden, histology, and toxicity profiles shape real-world outcomes with dual checkpoint blockade.
Safety Profile
The safety profile of ipilimumab plus nivolumab in this real-world cohort closely mirrored expectations for dual checkpoint blockade, with adverse events occurring in 76.4% of patients. High-grade toxicities (≥G3) were documented in 35.4% of cases. The most frequent immune-related events included fatigue, immune-mediated hepatitis, cutaneous toxicities such as rash and pruritus, thyroiditis, and diarrhea—patterns consistent with CTLA-4/PD-1 combination therapy.
Toxicity led to treatment interruption in a notable proportion of patients: ipilimumab was discontinued in 24.7% and nivolumab in 16%. Corticosteroids were required in 37% of patients, with 27% receiving high-dose regimens of ≥40 mg prednisone for toxicity management.
Reassuringly, steroid administration did not adversely affect progression-free or overall survival, echoing observations from melanoma and RCC literature that timely immunosuppression does not compromise long-term treatment efficacy.
Safety Profile
The safety profile of ipilimumab plus nivolumab in this real-world cohort closely mirrored expectations for dual checkpoint blockade, with adverse events occurring in 76.4% of patients. High-grade toxicities (≥G3) were documented in 35.4% of cases. The most frequent immune-related events included fatigue, immune-mediated hepatitis, cutaneous toxicities such as rash and pruritus, thyroiditis, and diarrhea—patterns consistent with CTLA-4/PD-1 combination therapy.
Toxicity led to treatment interruption in a notable proportion of patients: ipilimumab was discontinued in 24.7% and nivolumab in 16%. Corticosteroids were required in 37% of patients, with 27% receiving high-dose regimens of ≥40 mg prednisone for toxicity management.
Reassuringly, steroid administration did not adversely affect progression-free or overall survival, echoing observations from melanoma and RCC literature that timely immunosuppression does not compromise long-term treatment efficacy.
Interpretation
This is the largest European real-world analysis of first-line ipilimumab + nivolumab for advanced RCC. The findings confirm that:
- IO/IO delivers meaningful and durable clinical benefit, consistent with CheckMate 214.
- Real-world patients—older, frailer, and with more comorbidities—still achieve substantial responses.
- Outcomes were modestly inferior to the pivotal trial, primarily due to poorer baseline characteristics and inclusion of non-clear cell subtypes.
- Safety remained manageable and did not exceed expectations from clinical trials.
You Can Read All Article Here.