RC48-C016 trial (NCT—), presented by Dr. Zhou and colleagues at the ESMO Congress 2025, reported practice-changing findings for patients with HER2-expressing locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (la/mUC). The study demonstrated that disitamab vedotin (DV) plus toripalimab (T) significantly improved both progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared with standard platinum-based chemotherapy, setting a new benchmark for first-line therapy in this population.
Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) remains one of the most aggressive malignancies of the urinary tract, and outcomes for patients with metastatic disease are historically poor. While platinum-based chemotherapy remains the first-line standard, the benefit is modest, and patients with HER2-expressing tumors represent a biologically distinct subgroup that may respond better to targeted approaches.
Disitamab vedotin (DV) is a HER2-directed antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) that delivers a potent cytotoxic payload directly to HER2-expressing cancer cells, while toripalimab (T) is a PD-1 inhibitor designed to enhance immune-mediated tumor destruction. Earlier phase 1b/2 data (Zhou et al., Ann Oncol, 2024) showed strong efficacy for DV+T in HER2-unselected urothelial cancer, particularly in patients with HER2-positive tumors. Building on those results, RC48-C016 was designed to confirm the benefit of this combination in the first-line setting for HER2-expressing disease.
Methods
RC48-C016 was an open-label, randomized, multicenter phase 3 trial enrolling 484 patients with previously untreated, unresectable HER2-expressing la/mUC (centrally confirmed as IHC 1+, 2+, or 3+). Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive either:
- DV+T (disitamab vedotin plus toripalimab), or
- Chemotherapy (C) with gemcitabine + cisplatin/carboplatin.
Stratification factors included cisplatin eligibility, visceral metastases, and HER2 expression level.Tumor assessments were performed every 8 weeks per RECIST v1.1 by both investigators and a blinded independent review committee (BIRC). The dual primary endpoints were PFS and OS, with objective response rate (ORR) and safety as key secondary endpoints.
Results
At a median follow-up of 18.2 months (data cutoff: March 31, 2025), both primary endpoints were met, demonstrating clear superiority of DV+T over chemotherapy across all efficacy measures.
- Median PFS: 13.1 vs 6.5 months (HR 0.36; 95% CI 0.28–0.46; p < 0.0001)
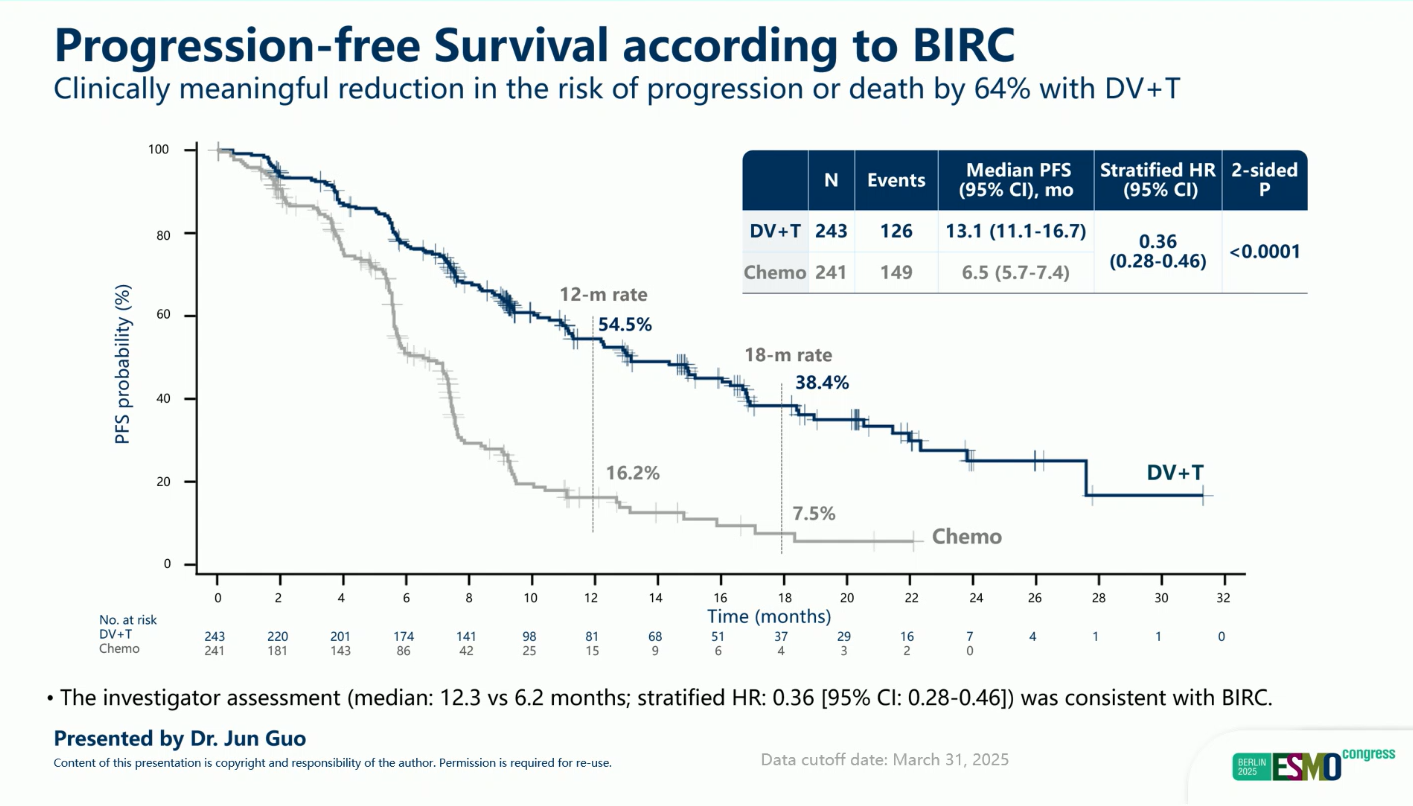
- Median OS: 31.5 vs 16.9 months (HR 0.54; 95% CI 0.41–0.73; p < 0.0001)
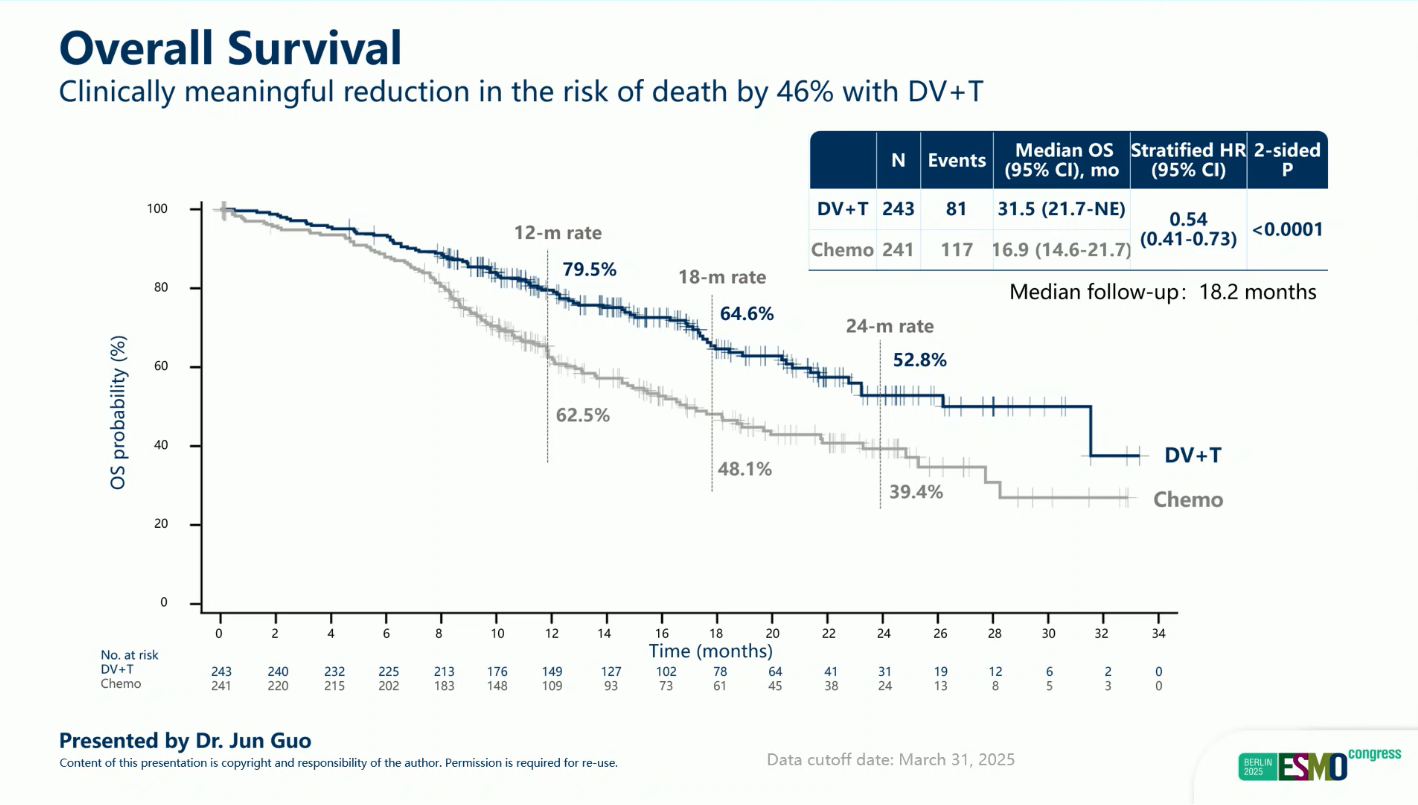
- Objective Response Rate (BIRC): 76.1% vs 50.2%
- Durability of response: Responses with DV+T were deeper and more sustained than with chemotherapy.
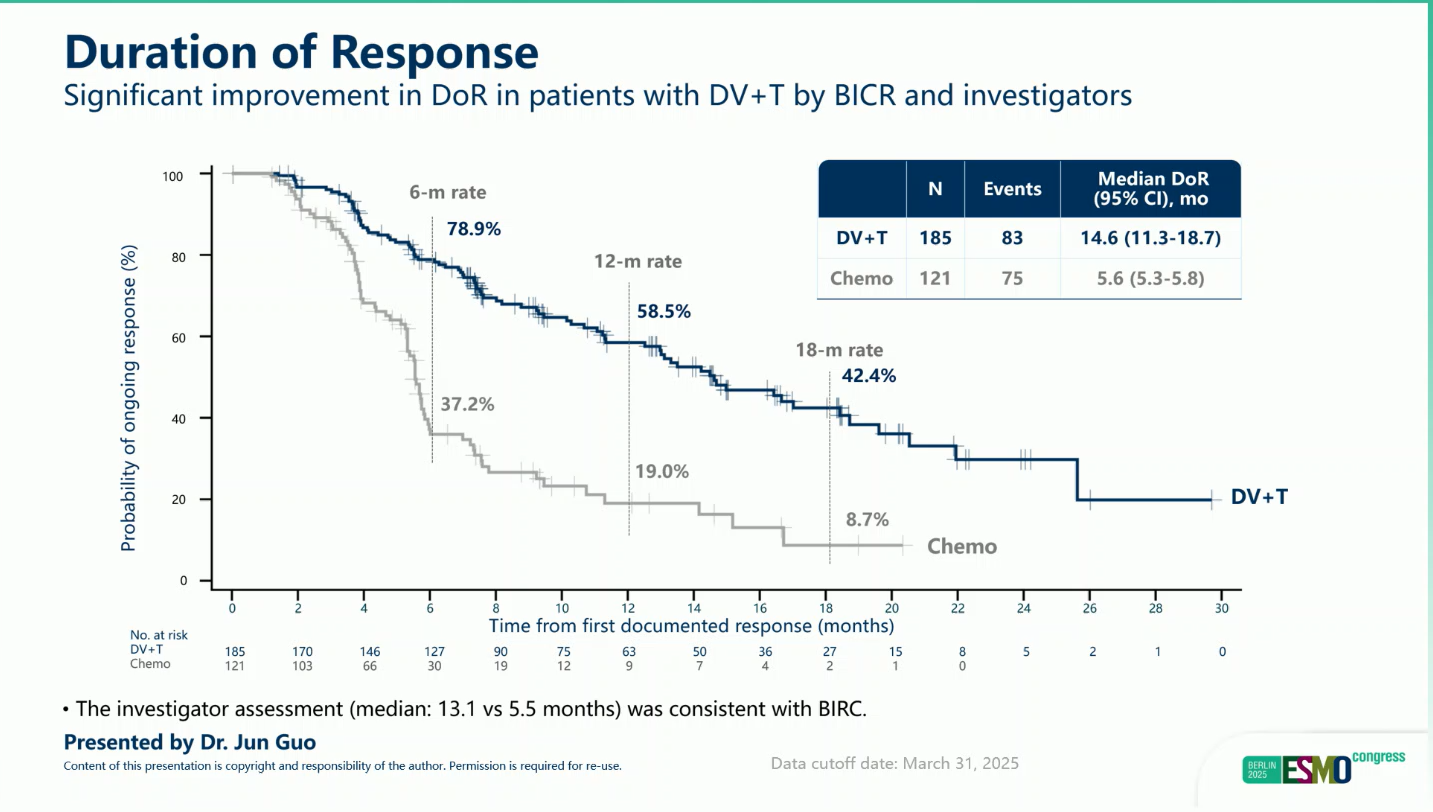
The survival advantage was consistent across all prespecified subgroups, including:
- Cisplatin-eligible and ineligible patients
- Presence or absence of visceral metastases
- HER2 expression levels (IHC 1+, 2+, or 3+)
These data underscore the broad applicability of DV+T in the HER2-expressing UC population, regardless of baseline clinical characteristics.
Safety
DV+T demonstrated a more favorable safety profile than chemotherapy.
- Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs): 55.1% with DV+T vs 86.9% with chemotherapy.
- Common AEs: Fatigue, nausea, rash, and hematologic toxicities, most of which were manageable and reversible.
- No unexpected safety signals emerged, and discontinuation rates due to toxicity were lower in the DV+T arm.
Conclusions
The RC48-C016 phase III trial, presented by Dr. Jun Guo at ESMO 2025, confirmed the superiority of disitamab vedotin plus toripalimab (DV+T) over chemotherapy in patients with HER2-expressing locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
DV+T demonstrated durable survival improvement and consistent benefit across HER2 expression levels and clinical subgroups. The regimen showed a favorable safety profile and represents a promising new first-line standard of care for this biomarker-selected population.
You can read the full abstract here.


