This research from the LIBRETTO-431 trial, published in JTO Clinical and Research Reports (June 2025), reports outcomes from patients in East Asia with RET fusion–positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Selpercatinib, a selective RET inhibitor, has shown strong efficacy globally. This subgroup analysis provides important regional data comparing first-line selpercatinib to pemetrexed–platinum chemotherapy ± pembrolizumab.
Title: First-line Selpercatinib or Chemotherapy and Pembrolizumab in Patients From East Asia With RET Fusion–Positive NSCLC: A LIBRETTO-431 Subgroup Analysis
Published in JTO Clinical and Research Reports
Authors: Koichi Goto, MD, PhDa kgoto@east.ncc.go.jp ∙ Herbert H. Loong, M.B.B.S.b ∙ Caicun Zhou, MD, PhDc ∙ Kazumi Nishino, MD, PhDd ∙ Dae Ho Lee, MD, PhDe ∙ Se-Hoon Lee, MDf ∙ James Chih-Hsin Yang, MD, PhDg ∙ Dan Liu, PhDh ∙ Minji Kim Uh, PhDh ∙ Hongmei Han, MS, MASh ∙ Tarun Puri, MDh ∙ Aimee Bence Lin, PhDh ∙ Ying Cheng, MDi
Introduction
RET fusion–positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represents a distinct molecular subtype that often affects younger, never-smoker, and female patients. Standard first-line treatment with platinum–pemetrexed chemotherapy ± pembrolizumab has provided only modest benefit, with median progression-free survival (PFS) around 11 months.
Selpercatinib, a highly selective RET inhibitor with central nervous system (CNS) activity, has previously demonstrated consistent efficacy in global studies such as LIBRETTO-001 and LIBRETTO-321. Early data from the global LIBRETTO-431 trial showed selpercatinib more than doubled PFS compared with chemo-immunotherapy, and importantly, delayed or prevented new brain metastases.
Because over half of LIBRETTO-431 participants were enrolled in East Asia, a detailed subgroup analysis is crucial to confirm outcomes in this population. The present study reports the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of first-line selpercatinib versus chemotherapy ± pembrolizumab in 142 East Asian patients with RET fusion–positive NSCLC, providing region-specific insights for clinical practice.
Methods
LIBRETTO-431 was a randomized, open-label, phase 3 study (NCT04194944). Patients were stratified by geography, brain metastases, and physician choice to use pembrolizumab. In East Asia, 142 patients (54% of all enrolled) participated, and 116 were included in the pembrolizumab analysis set. Most were female, younger than 65, and never-smokers. RET fusions were detected by next-generation sequencing (common partners: KIF5B 36%, CCDC6 9.5%) or PCR.
Treatment arms:
- Selpercatinib (160 mg BID) vs
- pemetrexed + platinum ± pembrolizumab, with maintenance allowed in the control arm.
Endpoints: primary was progression-free survival (PFS) by blinded central review; secondary included objective response rate (ORR), duration of response (DoR), safety, and pharmacokinetics.
Results
At a median follow-up of nearly 20 months, selpercatinib showed a clear advantage over chemotherapy ± pembrolizumab in East Asian patients. Treatment duration was longer with selpercatinib (16.6 months) compared to the control arm (9.7 months), and efficacy outcomes consistently favored the targeted therapy.
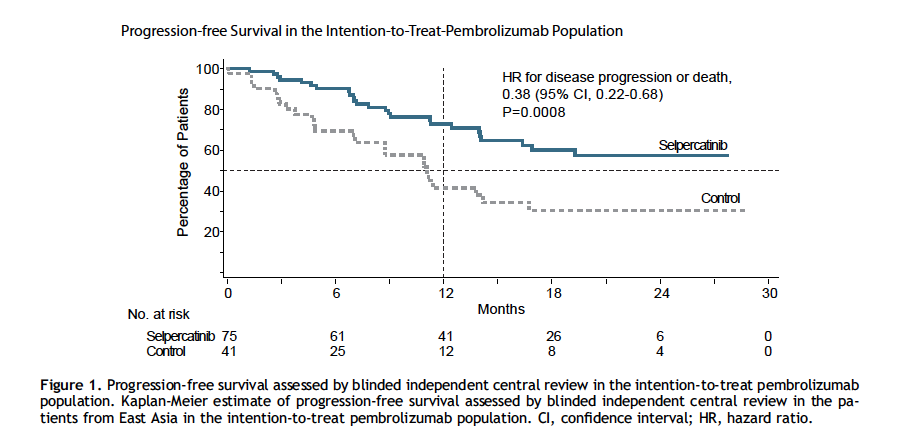
Progression-Free Survival (PFS)
- Median PFS: Not reached with selpercatinib vs 11.1 months with control
- Hazard ratio: 0.38 (95% CI 0.22–0.68; p = 0.0008)
- 12-month PFS rate: 72.8% vs 41.7%
Response Outcomes
- Objective response rate (ORR): 86.7% with selpercatinib vs 61.0% with control
- Duration of response (DoR): not reached vs 11.5 months
- 12-month DoR rate: 76.9% vs 46.9%
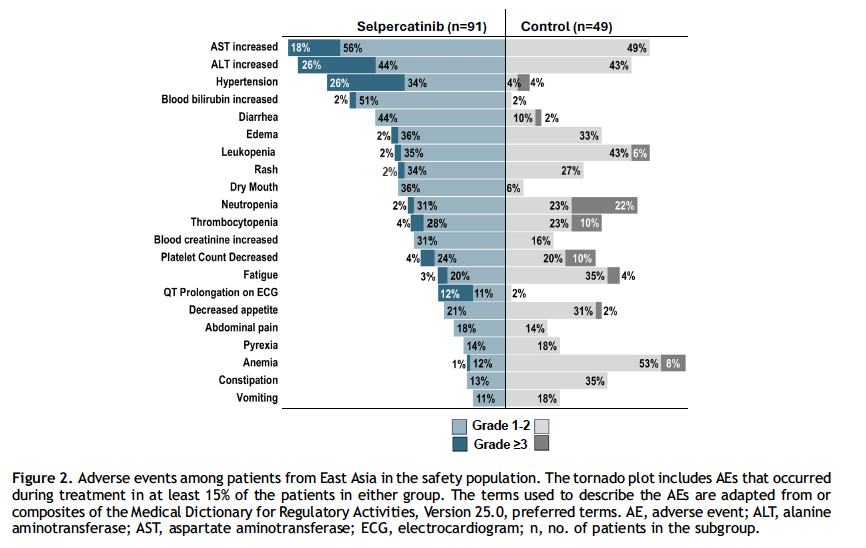
Safety profiles differed between the two treatment arms. Patients treated with selpercatinib more frequently experienced liver enzyme elevations, hypertension, and QTc prolongation, while those receiving chemotherapy plus pembrolizumab had higher rates of anemia, fatigue, and leukopenia. Overall, the incidence of grade 3 or higher adverse events was greater with selpercatinib (87%) compared with the control arm (65%). Importantly, most side effects were manageable with dose modifications, although treatment discontinuation due to adverse events occurred in 12% of patients receiving selpercatinib versus only 2% in the control group. Despite the higher rate of severe events, selpercatinib maintained a tolerable safety profile, consistent with global LIBRETTO-431 findings, and its clinical benefits outweighed the risks.
Key Takeaways
- Selpercatinib more than doubled PFS compared to chemotherapy + pembrolizumab.
- Responses were more frequent (87%) and more durable with selpercatinib.
- Safety was consistent with prior studies; side effects remained manageable.
- These results support selpercatinib as the preferred first-line option in RET fusion–positive NSCLC across East Asia.
You Can Read the Full Article here