At ESMO 2025, Javier Martin-Broto (Madrid, Spain) presented data from Phase II of sunitinib plus nivolumab in advanced alveolar soft-part sarcoma, reporting results from the GEIS, ISG, and UCL IMMUNOSARC II cohort in this ultra-rare sarcoma.
Introduction
Alveolar soft-part sarcoma (ASPS) is an ultra-rare, indolent-but-metastatic tumor that is resistant to conventional cytotoxic chemotherapy yet shows recognized sensitivity to anti-angiogenic TKIs and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Combining sunitinib (multi-target TKI with anti-angiogenic activity) and nivolumab (PD-1 inhibitor) aims to enhance antitumor activity through vascular normalization, immune activation, and complementary mechanisms. The IMMUNOSARC II study evaluates whether this strategy delivers clinically meaningful and durable disease control in advanced ASPS.

Methods
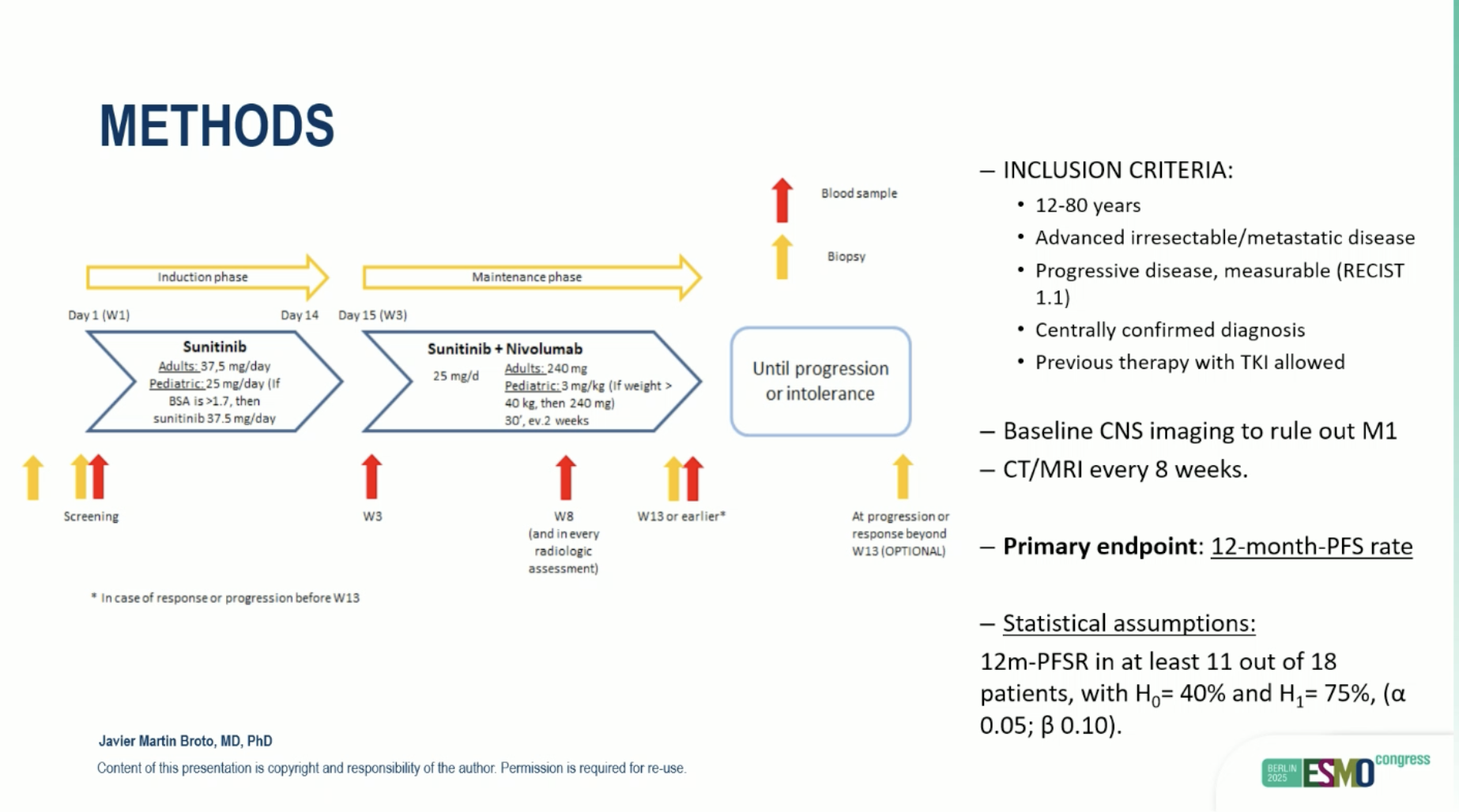
This phase II, multi-center study enrolled adults with progressing, measurable, centrally molecularly confirmed ASPS. Patients received sunitinib plus nivolumab as previously reported in IMMUNOSARC, until progression or intolerance. Imaging was performed every 8 weeks.
The primary endpoint was 12-month progression-free survival rate (12m-PFSR), with statistical design targeting ≥61% (H0=40%, H1=75%; α=0.05; β=0.10). Key secondary endpoints included median PFS (mPFS), overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR; RECIST 1.1), and safety.
From Oct 2019 to Jun 2024, 18 patients were enrolled across 9 centers (Spain, Italy, UK); median age 30 years (18–52), female 61%. All were metastatic at baseline; 67% (12/18) were treatment-naïve.
Treatment: Sunitinib + nivolumab, per IMMUNOSARC protocol, continued to progression/intolerance.
Results
The combination demonstrated meaningful activity with durable disease control, particularly in treatment-naïve patients, alongside manageable immune-related toxicities.
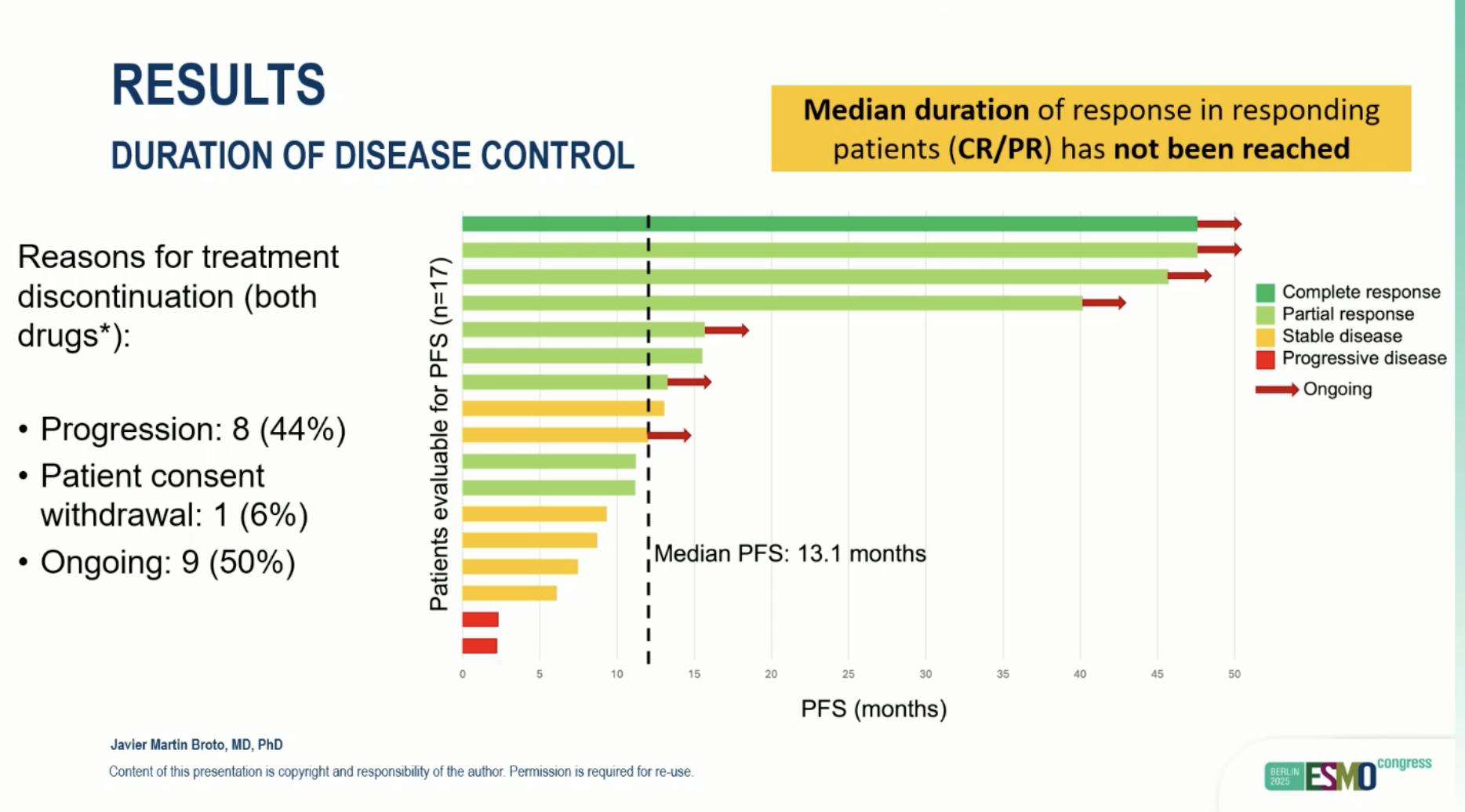
- 12-month PFS rate: 53% (95% CI 19–77).
- Median PFS: 13.1 months (95% CI 7.9–18.2).
- Median OS: 57.9 months (95% CI 0–100).
- ORR: 53% — CR 6%, PR 47%, SD 35%, PD 12%.
- Achieving CR/PR was associated with longer PFS (NR vs 7.5 months, p < 0.001).
- Treatment-naïve patients appeared to benefit more than pretreated (mPFS 15.5 months[95% CI NR] vs 8.7 months [95% CI 4.8–12.6], p = 0.058).
- Grade 3–4 toxicities were consistent with prior experience; immune-related events included G3 pneumonitis, G2 pancreatitis, G3 hepatitis. Translational analyses are ongoing.
Key takeaways
- Sunitinib + nivolumab achieved 53% ORR and 13.1-month mPFS with a 12-month PFS rate of 53% in an ultra-rare, chemo-resistant sarcoma.
- Objective responses (CR/PR) correlated with significantly longer PFS.
- Greater benefit in treatment-naïve patients suggests earlier-line positioning may maximize outcomes.
- Immune-related AEs were manageable with standard protocols; vigilance for pneumonitis, hepatitis, pancreatitis is warranted.
- Confirmation in larger, multicenter cohorts, maturation of OS data, and biomarker-driventranslational readouts to refine patient selection.
Follow ESMO 2025 live by checking the official program, abstracts, and announcements on the ESMO website, and get rolling highlights, summaries, expert takes, and Special Live Coverage on OncoDaily.