FDA approvals in the second half of 2025 continued the rapid expansion of immunotherapy across solid tumors and hematologic malignancies, with a strong emphasis on earlier disease settings, perioperative strategies, and next-generation immune platforms such as CAR T cells and bispecific antibodies.
These decisions further solidified immunotherapy as a backbone of modern oncology, extending its impact from relapsed disease into curative-intent and high-risk populations.

FDA Immunotherapy Approvals: First Half of 2025
Lisocabtagene maraleucel for relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma
FDA Approval Date: December 4, 2025
The FDA approved lisocabtagene maraleucel, a CD19-directed autologous CAR T-cell therapy, for adults with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma after at least two prior lines of systemic therapy. This approval marked a major milestone by bringing CAR T-cell therapy into indolent B-cell lymphomas.
Lisocabtagene maraleucel is manufactured from autologous T cells engineered to express a CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor. Following lymphodepleting chemotherapy with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, patients receive a single infusion of 90–110 × 10⁶ CAR-positive viable T cells, delivered as a defined 1:1 ratio of CD4 and CD8 cells.
In the TRANSCEND FL-MZL cohort, treatment produced high and durable response rates, with more than half of patients achieving complete remission and a median duration of response not reached. Toxicities were consistent with the CAR T-cell class, including cytokine release syndrome and neurologic events.
Durvalumab for perioperative treatment of resectable gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
FDA Approval Date: November 25, 2025
Durvalumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, was approved for use with FLOT chemotherapy as neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment, followed by durvalumab monotherapy, in adults with resectable gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.
Durvalumab blocks PD-L1–mediated immune suppression, enhancing antitumor T-cell activity during the perioperative window. The approved regimen includes durvalumab 1,500 mg every 4 weeks administered alongside chemotherapy before and after surgery, followed by adjuvant durvalumab alone.
The MATTERHORN trial demonstrated significant improvements in event-free survival, pathological complete response rates, and overall survival, establishing perioperative immunotherapy as a new standard in resectable upper gastrointestinal cancers.

Pembrolizumab plus enfortumab vedotin for cisplatin-ineligible muscle-invasive bladder cancer
FDA Approval Date: November 21, 2025
The FDA approved pembrolizumab in combination with enfortumab vedotin for neoadjuvant treatment followed by adjuvant therapy after cystectomy in adults with muscle-invasive bladder cancer who are ineligible for cisplatin.
Pembrolizumab restores T-cell activity through PD-1 blockade, while enfortumab vedotin targets Nectin-4–expressing tumor cells and delivers a cytotoxic payload. Pembrolizumab is administered at 200 mg every 3 weeks, combined with enfortumab vedotin 1.25 mg/kg on days 1 and 8 of each 21-day cycle.
In KEYNOTE-905/EV-303, the combination significantly improved both event-free survival and overall survival compared with surgery alone, redefining perioperative management for cisplatin-ineligible MIBC.
Tarlatamab for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer
FDA Approval Date: November 19, 2025
Tarlatamab, a DLL3 × CD3 bispecific T-cell engager, received traditional FDA approval for adults with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer progressing after platinum-based chemotherapy.
By simultaneously binding DLL3 on tumor cells and CD3 on T cells, tarlatamab redirects endogenous T-cell cytotoxicity toward SCLC cells. Treatment employs a step-up dosing schedule (starting at 1 mg, then 10 mg every two weeks) to reduce the risk of cytokine release syndrome.
In the DeLLphi-304 trial, tarlatamab significantly improved overall survival and progression-free survival compared with standard chemotherapy, representing one of the most meaningful advances in relapsed SCLC in years.
Daratumumab for high-risk smoldering multiple myeloma
FDA Approval Date: November 6, 2025
Daratumumab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, was approved as monotherapy for adults with high-risk smoldering multiple myeloma, marking a paradigm shift toward early immune intervention before symptomatic disease develops.
Administered subcutaneously at 1,800 mg, daratumumab significantly delayed progression to active multiple myeloma compared with active monitoring in the AQUILA trial, with a substantial reduction in progression risk.

Epcoritamab for follicular lymphoma
FDA Approval Date: November 18, 2025
Epcoritamab, a CD20 × CD3 bispecific antibody, received FDA approval both in combination with lenalidomide and rituximab and as monotherapy for relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.
Delivered subcutaneously using a step-up dosing schedule, epcoritamab induces T-cell–mediated killing of CD20-positive B cells. In EPCORE FL-1, the combination significantly improved progression-free survival and response rates over standard therapy, expanding bispecific antibodies into indolent lymphoma management.
Cemiplimab for adjuvant treatment of high-risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
FDA Approval Date: October 8, 2025
Cemiplimab, a PD-1 inhibitor, was approved for adjuvant treatment of adults with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at high risk of recurrence following surgery and radiation.
In the C-POST trial, cemiplimab significantly improved disease-free survival compared with placebo. Cemiplimab is administered intravenously at 350 mg every three weeks, with extended-interval dosing options available.
Lurbinectedin plus atezolizumab for maintenance therapy in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer
FDA Approval Date: October 2, 2025
The FDA approved lurbinectedin in combination with atezolizumab as maintenance therapy for adults with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer whose disease had not progressed after first-line chemo-immunotherapy.
Atezolizumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, is administered intravenously or subcutaneously, while lurbinectedin is given at 3.2 mg/m² every 21 days. In the IMforte trial, the combination significantly improved both overall survival and progression-free survival compared with atezolizumab alone.
Pembrolizumab subcutaneous formulation (Keytruda Qlex)
FDA Approval Date: September 19, 2025
The FDA approved subcutaneous pembrolizumab (pembrolizumab + berahyaluronidase) for all solid tumor indications already approved for intravenous pembrolizumab.
Pharmacokinetic and efficacy equivalence were demonstrated, with dosing options of 395 mg every 3 weeks or 790 mg every 6 weeks, offering greater convenience without compromising antitumor activity.
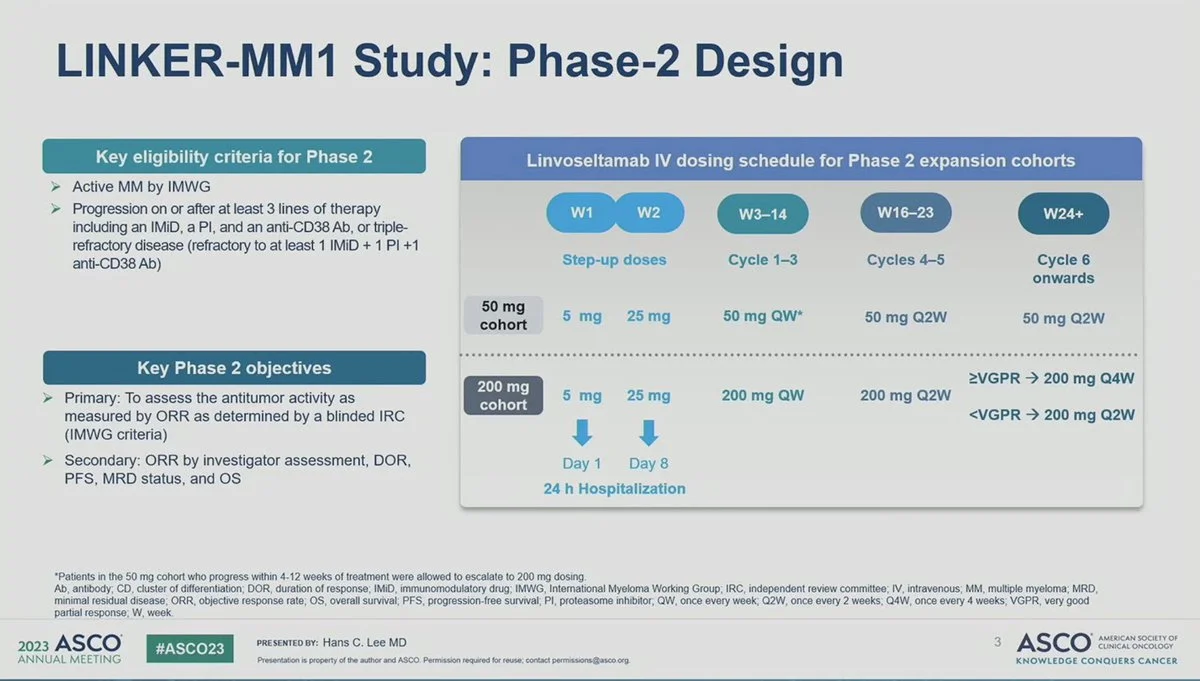
Linvoseltamab for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma
FDA Approval Date: July 2, 2025
Linvoseltamab, a BCMA × CD3 bispecific T-cell engager, received accelerated approval for adults with heavily pretreated multiple myeloma after at least four prior lines of therapy.
Administered intravenously with step-up dosing, linvoseltamab produced high response rates and durable disease control in the LINKER-MM1 study. Due to risks of cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity, treatment is available under a REMS program.
Pembrolizumab for perioperative treatment of resectable locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
FDA Approval Date: June 12, 2025
Pembrolizumab was approved as neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for adults with resectable, locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with PD-L1 CPS ≥1.
In KEYNOTE-689, perioperative pembrolizumab significantly improved event-free survival, marking the first perioperative immunotherapy approval in HNSCC in over six years.