The EMBER-3 trial addresses a central challenge in the management of ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: endocrine resistance, particularly after progression on aromatase inhibitors and CDK4/6 inhibitors. ESR1 mutations, which emerge under endocrine pressure, are a well-established mechanism of resistance and are associated with diminished benefit from standard endocrine therapies. There is a critical need for effective, chemotherapy-free, all-oral strategies that can overcome endocrine resistance, prolong disease control, delay chemotherapy, and maintain quality of life.
The Trial was designed to address this unmet need by evaluating imlunestrant, a next-generation, brain-penetrant oral selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), both as monotherapy and in combination with abemaciclib, across clinically relevant patient populations.
Study Design of EMBER-3 Trial
EMBER-3 is a global, randomized, phase III trial enrolling men and pre- and postmenopausal women with ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who experienced recurrence or progression on an aromatase inhibitor, with or without prior CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy.
Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to one of three arms:
- Imlunestrant 400 mg once daily
- Standard-of-care endocrine therapy (investigator’s choice of fulvestrant or exemestane)
- Imlunestrant 400 mg once daily plus abemaciclib
Randomization was stratified by prior CDK4/6 inhibitor use, presence of visceral metastases, and geographic region.
The primary endpoints were investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS):
- Imlunestrant vs standard endocrine therapy in patients with ESR1 mutations
- Imlunestrant vs standard endocrine therapy in all patients
- Imlunestrant plus abemaciclib vs imlunestrant in all patients
Key secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS), PFS by blinded independent central review, objective response rate (ORR), and safety. Exploratory endpoints included time to chemotherapy (TTC).
The current presentation reports results from a pre-specified interim OS analysis (IA2) with 14 additional months of follow-up, corresponding to approximately 255 OS events and a median follow-up of 28.5 months.
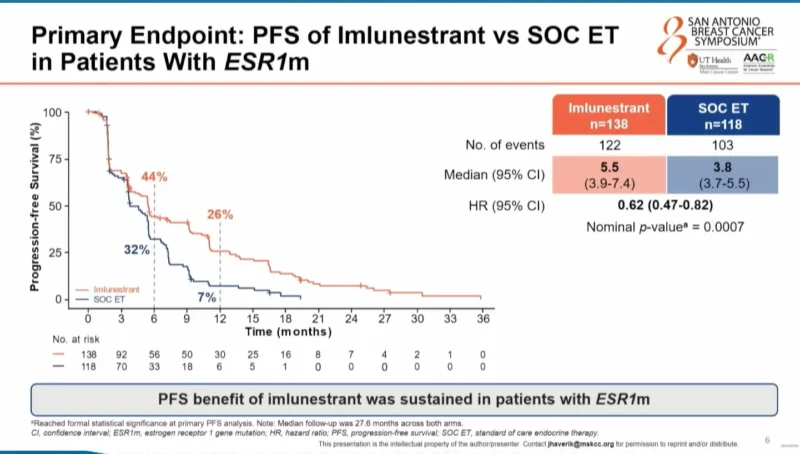
Sustained PFS Benefit With Imlunestrant in ESR1-Mutated Disease
In patients with ESR1-mutated tumors, the PFS benefit of imlunestrant over standard endocrine therapy was maintained with longer follow-up.
Median PFS was 5.5 months with imlunestrant versus 3.8 months with standard endocrine therapy, corresponding to a 38% reduction in the risk of progression or death (HR 0.62; 95% CI, 0.47–0.82; nominal p = 0.0007).
At the 12-month landmark, the clinical impact was pronounced: 26% of patients treated with imlunestrant remained progression-free compared with 7% in the standard endocrine therapy arm, representing nearly a four-fold difference.
Interim Overall Survival: Clinically Meaningful Improvement in ESR1-Mutated Patients
At 50% OS maturity, imlunestrant demonstrated a numerical and clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival in patients with ESR1 mutations.
Median OS was 34.5 months with imlunestrant versus 23.1 months with standard endocrine therapy, reflecting an 11.4-month difference (HR 0.60; 95% CI, 0.43–0.86; p = 0.0043). Although the pre-specified statistical boundary for significance was not crossed due to limited alpha allocation, the magnitude and consistency of benefit are notable.
Importantly, the OS benefit with imlunestrant was consistent across clinically relevant subgroups, including age, region, metastatic burden, visceral disease, liver metastases, bone-only disease, and prior CDK4/6 inhibitor exposure.
Delayed Need for Chemotherapy
Time to chemotherapy represents a highly meaningful endpoint for patients with hormone-driven metastatic disease. In the ESR1-mutated population, imlunestrant significantly delayed the initiation of chemotherapy.
Median TTC was 15.6 months with imlunestrant compared with 10.2 months with standard endocrine therapy (HR 0.66; 95% CI, 0.48–0.92), translating into a 5.4-month delay in chemotherapy initiation.
Imlunestrant Plus Abemaciclib: Robust PFS Benefit in All Patients
Across the overall study population, the combination of imlunestrant plus abemaciclib continued to demonstrate a robust and durable PFS advantage over imlunestrant monotherapy.
With extended follow-up, median PFS reached 10.9 months for the combination compared with 5.5 months for imlunestrant alone (HR 0.59; 95% CI, 0.47–0.74; nominal p < 0.0001).
The PFS benefit was maintained across key subgroups, including:
- Patients with and without ESR1 mutations
- Patients previously treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors (approximately 65% of the population)
- Patients with PI3K pathway alterations, including those with dual ESR1 and PI3K mutations
- In patients with both ESR1 mutations and PI3K pathway alterations, median PFS reached 12 months with the combination versus 5.5 months with imlunestrant alone (HR 0.48).
Emerging Overall Survival Signal With the Combination
At 33% OS maturity, an emerging separation of OS curves was observed for imlunestrant plus abemaciclib versus imlunestrant monotherapy, becoming apparent around the 24-month mark.
Median OS was not yet reached for the combination and was 34.4 months for imlunestrant alone (HR 0.82; 95% CI, 0.59–1.16). While not statistically significant at this interim analysis, these findings suggest a favorable OS trend with continued follow-up.
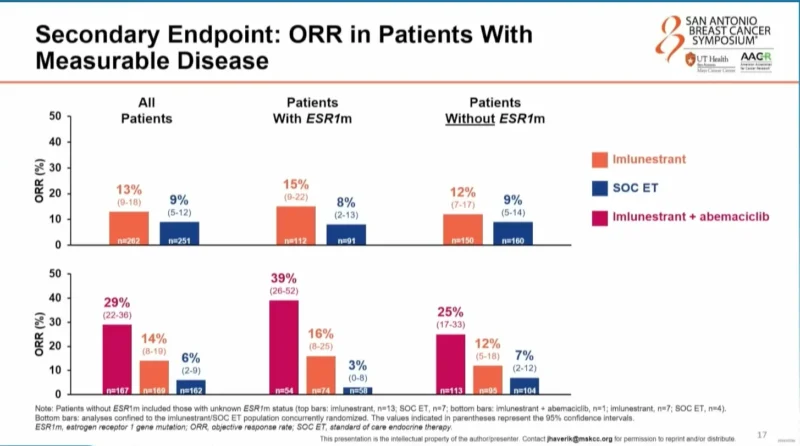
Objective Response and Subsequent Therapy
Objective response rates were numerically higher with imlunestrant compared with standard endocrine therapy and were nearly doubled with the addition of abemaciclib, regardless of ESR1 mutation status.
Patterns of first subsequent therapy after study discontinuation were similar across treatment arms. Chemotherapy was the most common subsequent treatment, followed by endocrine therapy with or without a targeted agent, indicating that post-progression treatment did not differ meaningfully between groups.
Safety and Tolerability
With longer follow-up, the safety profiles of imlunestrant monotherapy and the combination with abemaciclib remained consistent with known safety data.
Imlunestrant demonstrated a favorable safety profile, characterized primarily by low-grade gastrointestinal toxicities and no oral SERD-specific safety signals, including ocular or cardiac findings. Discontinuation rates remained low for both monotherapy and combination therapy and were lower than those observed with currently available combination regimens.
Conclusions and Clinical Implications
With extended follow-up, EMBER-3 confirms the durability and clinical relevance of imlunestrant in ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer.
In patients with ESR1-mutated disease, imlunestrant monotherapy delivers sustained PFS benefit, a clinically meaningful 11.4-month improvement in median OS, and a substantial delay in chemotherapy initiation, with a favorable safety profile.In the overall population, the combination of imlunestrant plus abemaciclib provides a robust and consistent PFS benefit, with an emerging OS signal and predictable tolerability.
Together, these data support imlunestrant, as monotherapy or in combination with abemaciclib, as an all-oral, chemotherapy-free treatment option following progression on endocrine therapy for patients with ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer.
Looking Ahead: EMBER-4
Enrollment has now been completed for EMBER-4, a global, randomized, open-label phase III trial in the adjuvant setting, enrolling approximately 8,000 patients with ER-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer at increased risk of recurrence after 2–5 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy, in the context of established CDK4/6 inhibitor use.
For more information click here.


