The 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting in Chicago showcased transformative developments in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), spanning imaging, neoadjuvant and adjuvant strategies, and evolving systemic treatments. Ilya Tsimafeyeu of BUCARE highlighted several landmark studies that are poised to reshape clinical practice across clear-cell and non-clear cell RCC.
Next-Generation Imaging: 68Ga-NY104 PET-CT Raises Diagnostic Standards
A Phase 2 trial by Zhu et al. introduced a novel PET-CT tracer, 68Ga-NY104, which targets CAIX—a hallmark of clear-cell RCC. The agent demonstrated exceptional diagnostic accuracy, with both sensitivity and specificity exceeding 95%, approaching 100% in some parameters. By comparison, FDG-PET-CT underperformed, with specificity below 12% and significantly lower sensitivity. These results underscore the potential of CAIX-targeted imaging in RCC and justify a forthcoming Phase 3 trial.
Neoadjuvant Therapy: Promising Activity Without Complete Pathologic Responses
The PELUR study evaluated lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in 23 patients with high-risk, resectable RCC. Tumor shrinkage was observed in all patients, with nearly half achieving partial responses. However, no complete pathological responses (pCR) were documented. Despite this, only five patients had relapsed after a median 22-month follow-up, supporting the regimen’s potential for further exploration.
The NEOAVAX trial (avelumab + axitinib) also revealed encouraging partial and major pathological responses, although MPR did not align with radiographic outcomes. Intriguingly, the presence of CD8⁺CD39⁺ T cells post-treatment correlated strongly with relapse, while memory T cells, B cells, and macrophages were associated with improved responses—highlighting the role of tumor microenvironmental profiling.
Similarly, a pooled analysis of two Phase 2 trials by Peng et al. assessed toripalimab + axitinib. Tumor thrombus length was reduced in 45% of patients, suggesting preoperative advantages.
Adjuvant Therapy: 5-Year KEYNOTE-564 Results Cement Pembrolizumab’s Role
The long-term findings of KEYNOTE-564 reinforce pembrolizumab’s benefit in resected high-risk RCC. At five years, overall survival was 87.7% vs. 82.3% for placebo (HR=0.66), while disease-free survival remained superior in the immunotherapy arm (median not reached vs. 68.3 months; HR=0.71). Notably, less than half of placebo patients received immunotherapy upon recurrence, potentially biasing OS comparisons.
Although grade 3–5 adverse events were higher with pembrolizumab (32% vs. 17.7%), the toxicity remained manageable. Biomarker analysis from IMmotion010 revealed that high KIM-1 levels and strong T-effector gene signatures may help identify future responders to anti–PD-L1 therapy, suggesting a personalized approach to adjuvant therapy.
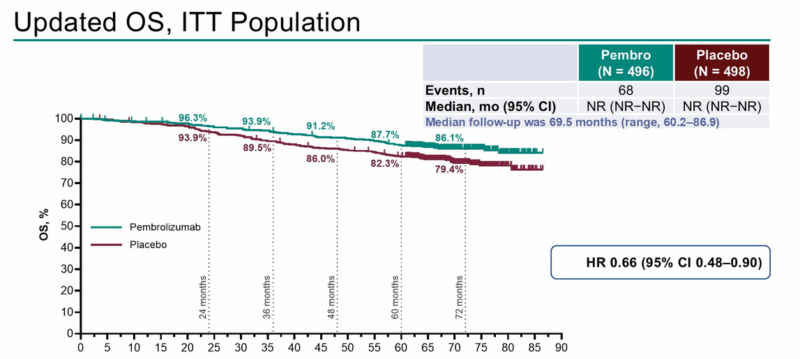
OS in the KEYNOTE-564 Study (5-Year follow-up)
Long-Term Immunotherapy: CheckMate-214 Shows 9-Year Durability
Nine years after the CheckMate-214 trial began, dual immunotherapy (nivolumab + ipilimumab) continues to show remarkable results in intermediate/poor-risk RCC. Thirty percent of patients are still alive, and 21% remain progression-free. Half of the responders have maintained responses for nine years. Importantly, only 49% of patients discontinued therapy due to progression—indicating durable disease control post-treatment.
Even in favorable-risk patients, the hazard ratio for OS improved to 0.8. The treatment’s safety profile remained stable over time, with no increase in immune-related adverse events.
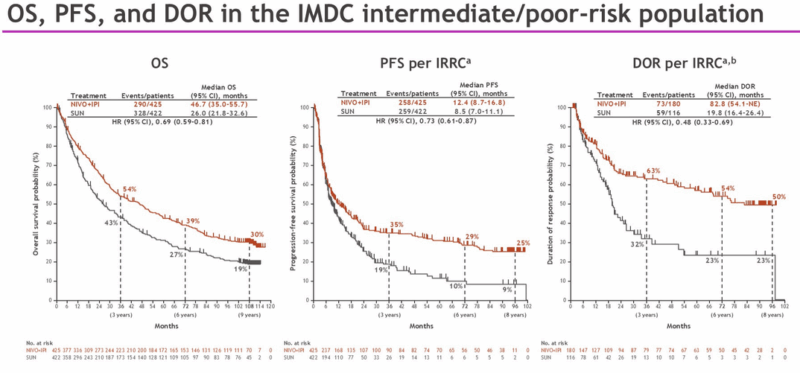
9-year efficacy in the intermediate/poor-risk group
New Therapeutics Target Tumor Microenvironment and Beyond
Several innovative approaches are targeting the tumor microenvironment and overcoming resistance mechanisms in RCC:
- Zanzalintinib, a TAM inhibitor, demonstrated a 63% response rate and 18.5-month median PFS in the STELLAR-002 trial when combined with nivolumab.
- Casdatifan + cabozantinib showed a 46% ORR in the ARC-20 study; further evaluation is ongoing in PEAK-1.
- Belzutifan, in VHL disease-associated RCC, showed a 70% ORR with 11% CR and high durability across tumor types.
- AlloCAR-T targeting CD70 demonstrated early efficacy (ORR 31% in CD70-high tumors) and remains under evaluation in TRAVERSE.
- Atezolizumab + cabozantinib, however, did not outperform cabozantinib monotherapy in the CONTACT-03 study.
Expanding Evidence in Non–Clear Cell RCC: Tailoring Treatment for Rare Subtypes
New trials are shaping treatment landscapes for historically understudied RCC subtypes:
- The AREN1721 trial found that axitinib + nivolumab achieved a 33% response rate in patients with TFE translocations, compared to 0% with monotherapy.
- In the SUNNIEFORECAST trial, nivolumab + ipilimumab outperformed physician’s choice in 12-month OS (78.3% vs. 68.3%). PD-L1 expression and absence of nephrectomy appeared to influence response, although subgroup conclusions require cautious interpretation.
- The Chinese UC-001 trial (anlotinib + everolimus) in metastatic non-clear cell RCC showed a 54.5% ORR and 20.8-month median PFS.
- A separate trial combining anlotinib + sintilimab reported a 56.8% ORR, supporting ongoing confirmatory studies.
Conclusion: A New Era for RCC Diagnostics and Treatment
ASCO 2025 underscored that renal cell carcinoma is no longer a monolithic entity. Advances in molecular imaging, tumor microenvironment modulation, and neoadjuvant/adjuvant strategies are reshaping the RCC treatment landscape. Long-term immunotherapy efficacy remains robust, while novel agents and rare subtype-specific trials offer hope for broader personalization. As summarized by Ilya Tsimafeyeu and colleagues at BUCARE, the RCC playbook is indeed being rewritten and the future of RCC care looks more precise, durable, and data-driven than ever before.
For more insights from the ASCO 2025 Annual Meeting, visit: OncoDaily – ASCO Highlights
Insights by Ilya Tsimafeyeu, Bureau for Cancer Research (BUCARE)
Written by Nare Hovhannisyan, MD



