Omar Alhalabi, Genitourinary Medical Oncologist at MD Anderson Cancer Center, posted on Twitter.
“Have you treated bladder cancer with a component of “neuroendocrine” or “small cell” carcinoma? This Tweetorial (maybe called “x”orials now) might be relevant to you! Here, I will cover our most recently published paper in European Urology Oncology Journal.

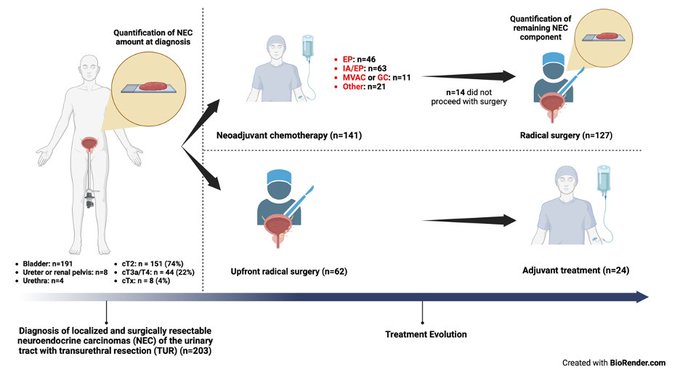
We wanted to investigate the outcomes of patients with localized bladder cancer (cT2-4aN0) + small cell or poorly diff neuroendocrine carcinoma component in the TUR sample. 20yr+ MD Anderson, 203 patients.
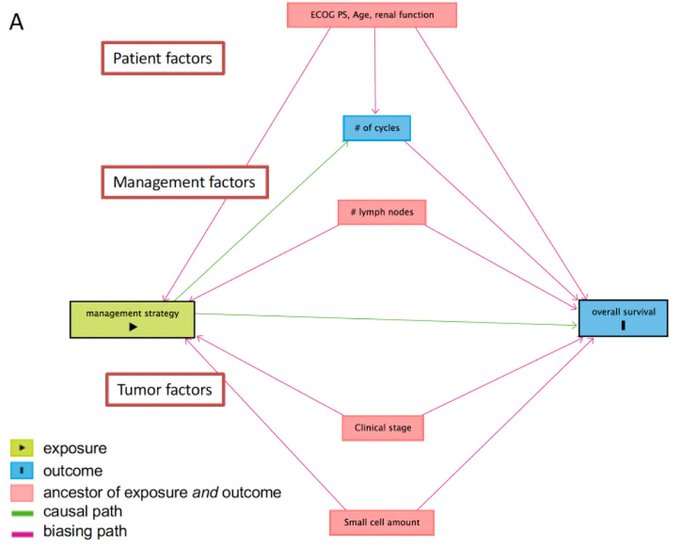
BUT FIRST, as with any retrospective study, there is always bias. We tried to control for it by putting our “assumptions” on paper and making a graph (Daggity and Pavlos Msaouel helped!). Factors that influence treatment decision and outcomes were included as confounders in our multivariable model (your usual suspects ECOG, age, renal function, stage, etc.). Mediators (e.g. number of cycles) didn’t get “adjust for” given that we already adjusted for the confounders behind them. See here.
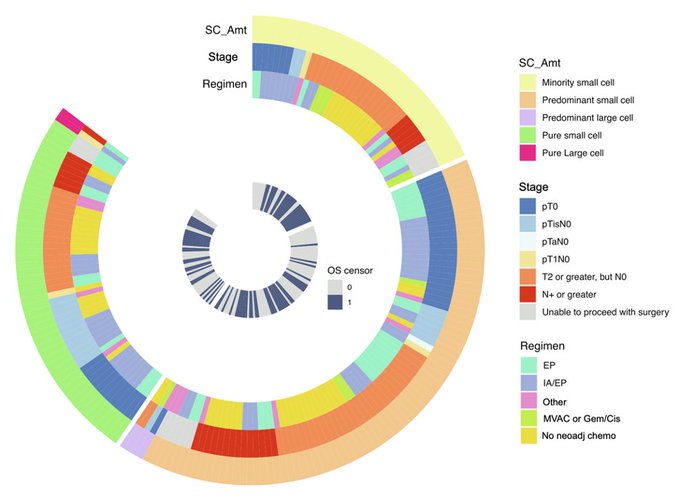
The “amount” of neuroendocrine carcinoma on TUR tissue varied from a “minority histology i.e. <50% of tumor” all the way to being the only histology seen “pure”. Here’s a donut plot summarizing all 203 patients with their surgical path, neoadjuvant regimen, survival.
We asked:
– Was neoadjuvant vs adjuvant chemo associated with better survival?
– Differences at baseline?
– Which chemo regimens had the highest path response rates and survival (after adjusting for confounders)?
– Any genomic correlation with achieving a response?
Side note, chemo regimens included cisplatin/etoposide, ddMVAC, gem/cis among others. But, also the alternating IA/EP doublet regimen, which reported from MD Anderson News by my colleague Dr. Siefker-Radtke in 2008, Journal of Clinical Oncology.
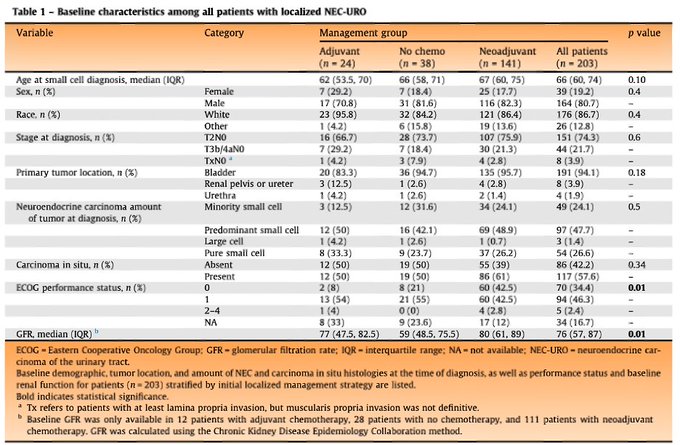
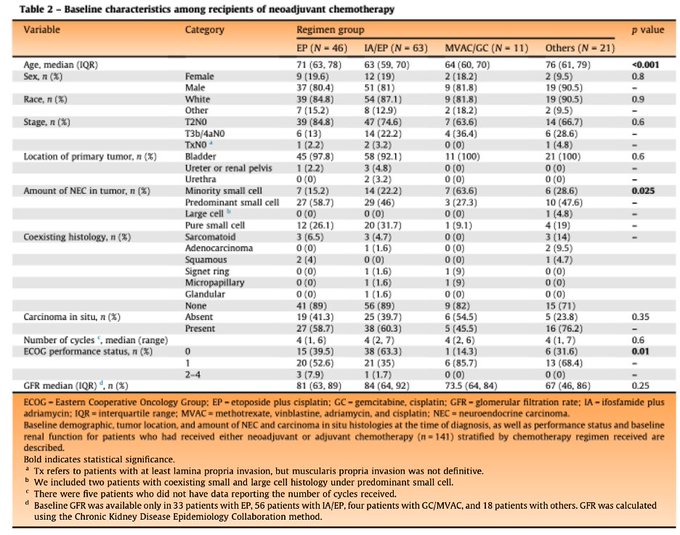
At baseline (table 1), ECOG 0-1 was equal between neoadjuvant, adjuvant or no chemo groups. Median GFR was in 70-80s in neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemo groups. When we zoomed in on the 141 pts (table 2) who received neoadjuvant regimens, EP recipients were older.
Results:
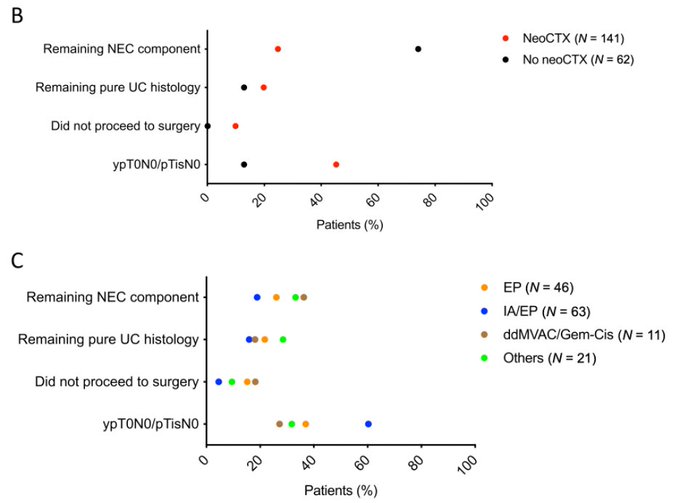
– pCR was higher with neoadjuvant chemo (~50% vs ~15%)
– pCR was higher with neoadjuvant chemo (~50% vs ~15%)
– approximately 10% of neoadjuvant recipients didn’t proceed with surgery (declining PS or progression dx)
– Remaining neuroendocrine ca component was high (~80%) if neoadjuvant chemo was not used
– Remaining neuroendocrine ca component was high (~80%) if neoadjuvant chemo was not used
IA/EP a/w highest pCR rate (60%)
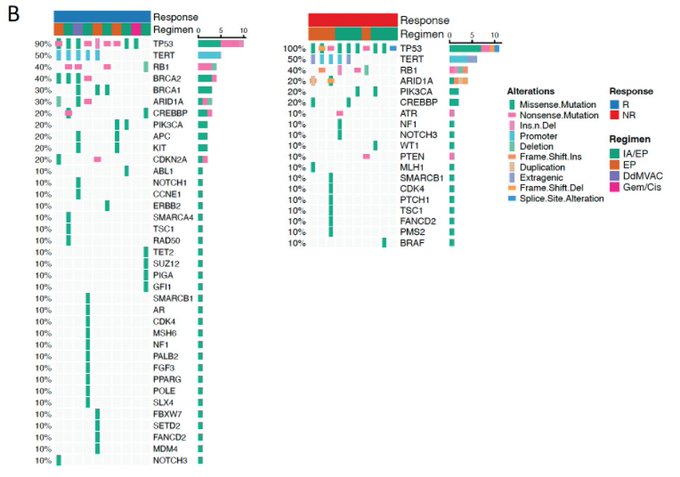
In exploratory analysis, pCR enriched for BRCA1/2 mutations. See paper for details.
Survival, we found the neoadjuvant chemo was associated with better survival as compared to adjuvant. This was still true in multivariable analysis. We also found that EP or IA/EP (small cell regimens) were associated with better survival as compared to ddMVAC/GC or others.
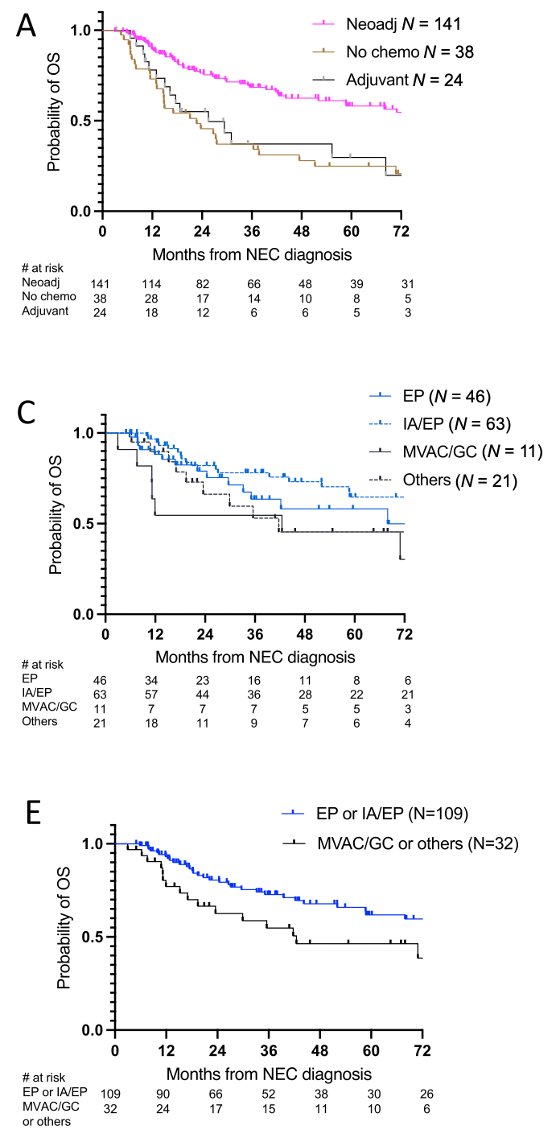
Conclusion: in this variant histology of bladder cancer, increased survival with neoadjuvant chemo rather upfront surgery. There may be a preferential path response to the small cell regimens EP or alternating IA/EP doublet. A trial would be the way to verify these findings.
Plug for ongoing trials allowing inclusion of small cell variant in early stage bladder cancer : NCT04383743 led by Petros Grivas
and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center and NCT05312671 led by Jean Hoffman-Censits and Johns Hopkins Greenberg Bladder Cancer Institute.
Many to thank. Especially. My equal first author Nate Wilson. Special thanks to the European Urology Oncology education board, and Andrew Vickers stat editor! Check out these guides.”
Source: Omar Alhalabi/Twitter