Samuel Hume, Scientist at University of Oxford, shared a post on X:
“Biggest medical discoveries of the week.
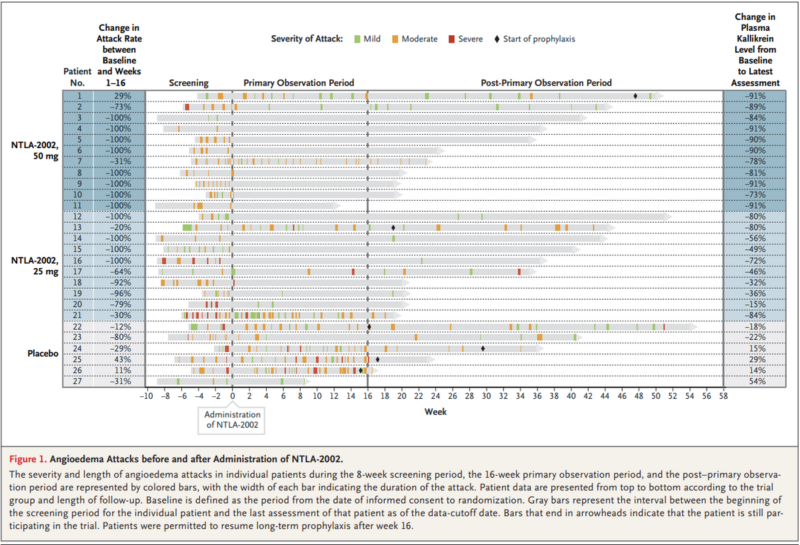
- Single dose CRISPR for hereditary angioedema, a genetic condition that causes unpredictable swelling attacks.
This phase 2, placebo-controlled randomised trial found that CRISPR editing of kallikrein (KLKB1) reduced angioedema attacks without causing serious adverse events.
Not only is this exciting for hereditary angioedema, but also for genetic conditions more widely.
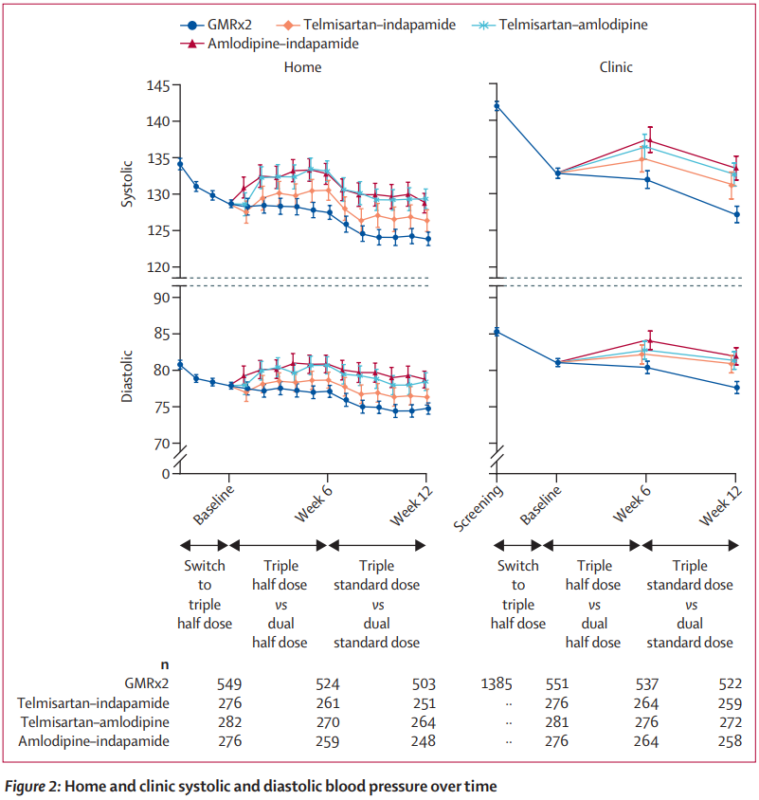
- Three blood pressure meds in one pill.
The latest guidance suggests most people with hypertension should be started on two anti-hypertensive pills, and many will move to three – which can get complex and limit adherence.
This is a randomised trial of a single-pill triple anti-hypertensive (telmisartan, amlodipine and indapamide) called GMRx2.
The triple pill was well tolerated, effective to reduce blood pressure, with >95% adherence.
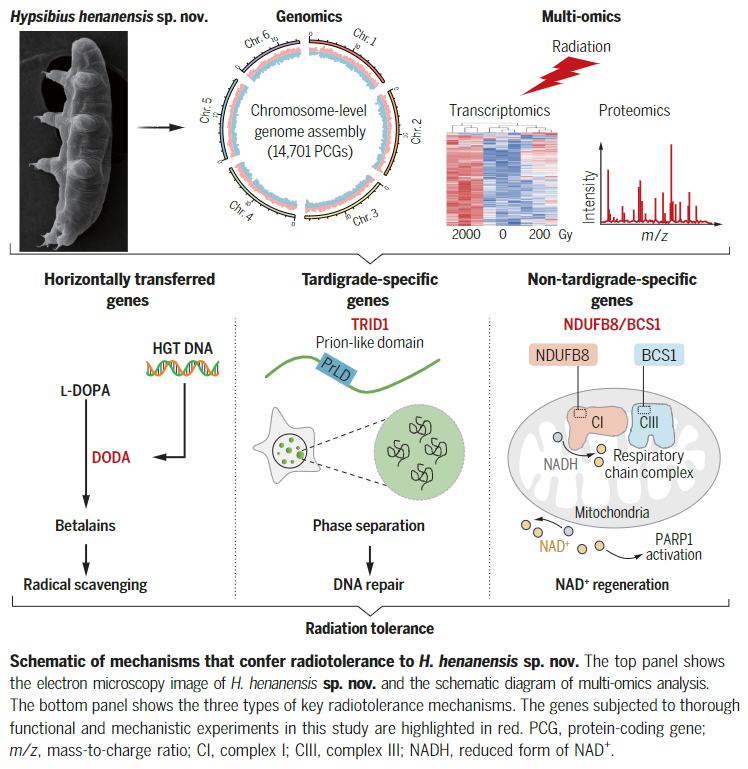
- Tardigrades can tolerate extraordinary doses of radiation ∼1000-times the lethal human dose – how?
In three ways:
1. Scavenging reactive oxygen species
2. Hyperactivating double-strand DNA break repair through a novel gene, TRID1
3. Boosting PARP1-mediated DNA repair by regenerating NAD+
- An IgG-cleaving enzyme
Discovered in Corynebacterium, the enzyme, CU43, treated IgG-mediated conditions (in mice!): autoimmune haemolytic anaemia and severe dengue
Its activity was >4000-fold higher than another IgG degrader, Efgartigimod.
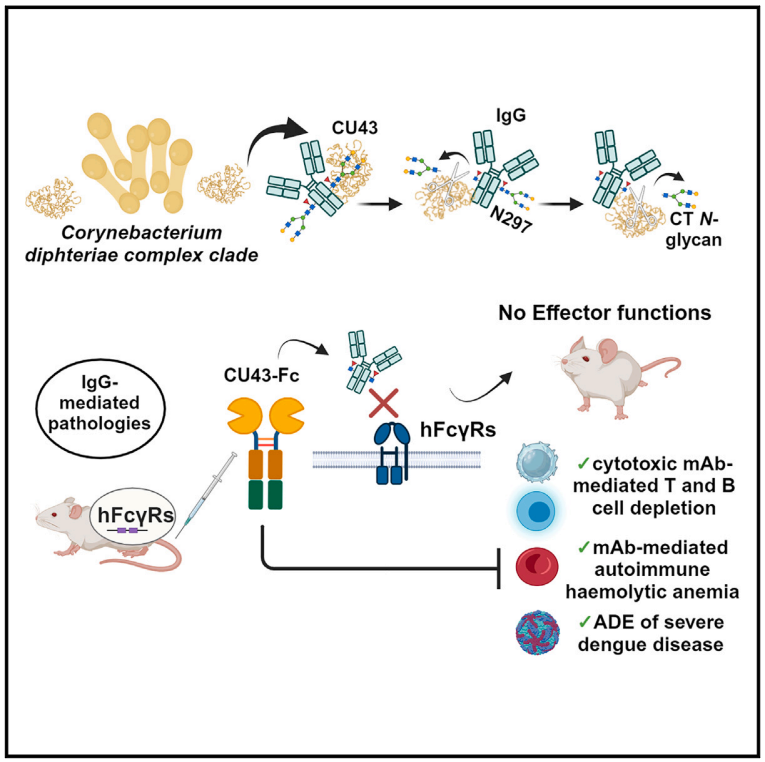
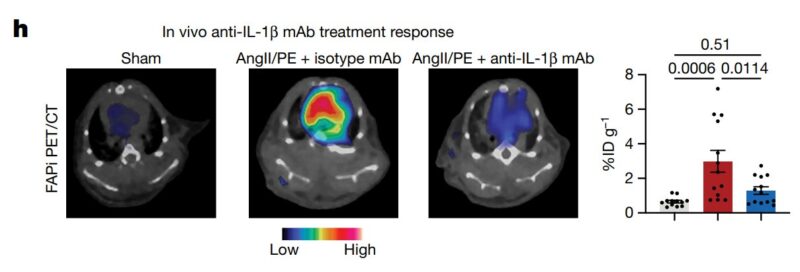
- A mAb for cardiac fibrosis
Cardiac fibrosis, which happens in heart disease, causes significant morbidity – but there are no approved treatments
This study reports that the anti-inflammatory monoclonal antibody, IL-1β, reduced cardiac fibrosis and boosted cardiac function in a mouse model.
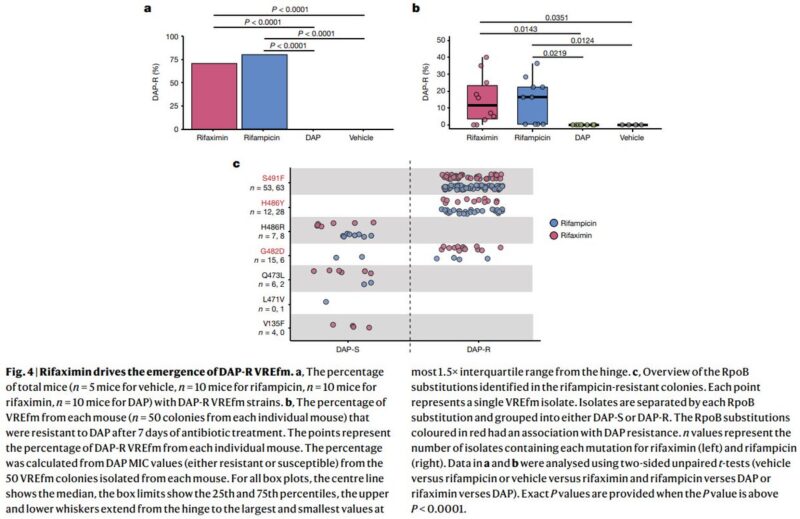
- An unexpected mechanism of antibiotic resistance.
Rifaximin, which was considered low risk for antibiotic resistance, inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase – it’s used in liver cirrhosis.
The same bacterial RNA polymerase mutants that prevent Rifaximin binding also alter transcription – expressing a new operon.
This leads to remodelling of the bacterial membrane and provides resistance to the unrelated antibiotic, daptomycin – a WHO ‘last-resort’ antibiotic.
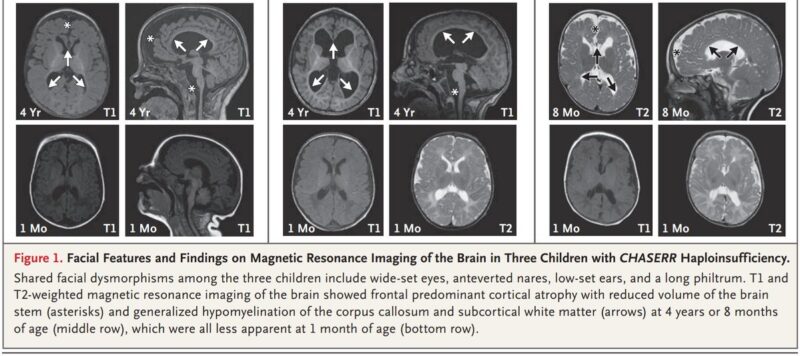
- A neurodevelopmental disorder caused by loss of a long non-coding RNA.
Three patients with developmental delay had de novo deletions of the CHASERR locus.
More focus should be placed on lncRNAs in uncharacterised neurodevelopmental disorders.
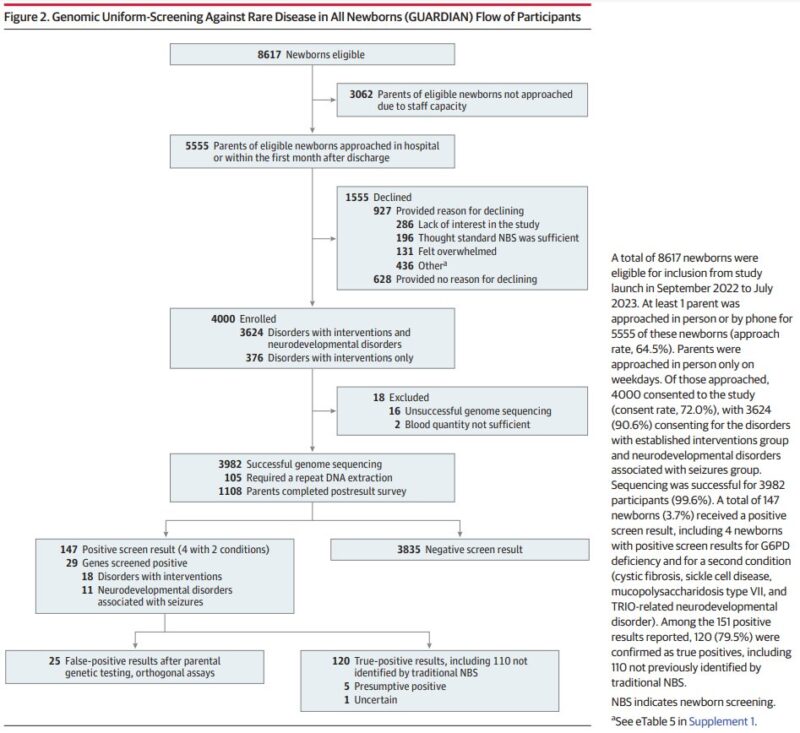
- Genome sequencing for early actionable conditions in newborns.
4000 newborns were screened for mutations in 237 genes, that cause treatable conditions.
3.7% tested positive for at least one mutation (or 0.6%, excluding G5PD deficiency).
One condition in the expanded panel, for example, is severe combined immunodeficiency – which requires a stem cell transplant, but which is not included in current screening.”