Yu-Hung Wang, PhD student at The University of Manchester, shared a post on X about a recent paper published in Leukemia Journal.
Authors: Yu-Hung Wang, Chao-Hung Wei, Chien-Chin Lin, Jean-Jacques Kiladjian, Hwei-Fang Tien et al.

“Excited to share our latest myelofibrosis research in Leukemia Journal.
Deeply grateful for the guidance and collaboration from Prof. Jean-Jacques Kiladjian, Dan Wiseman, Carmelo Gurnari, Benajiba Lina, Andrius Žučenka, Adrián Mosquera Orgueira, Kristian Gurashi, Kiran Batta, and all our friends.
Although the clinical relevance of HMR mutations and JAK2V617F VAF is established, their relationship remains unclear. Hence, we aimed to explore and validate the prognostic implications of integrating these mutations with quantified JAK2V617F VAF across independent cohorts.
We first corroborated that the presence of HMR mutation and the number of HMR mutations robustly distinguished patients’ LFS and OS.
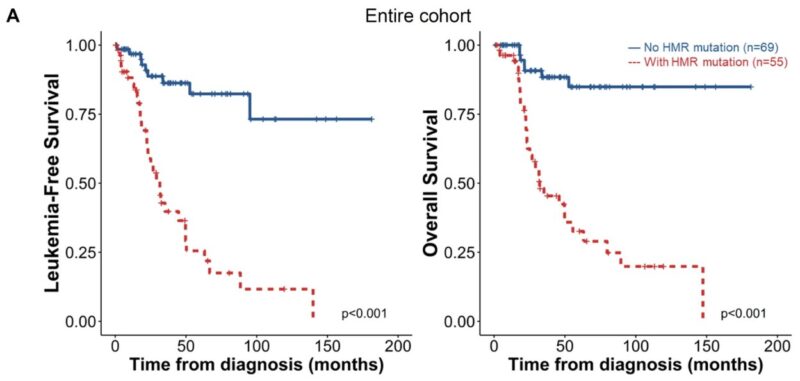
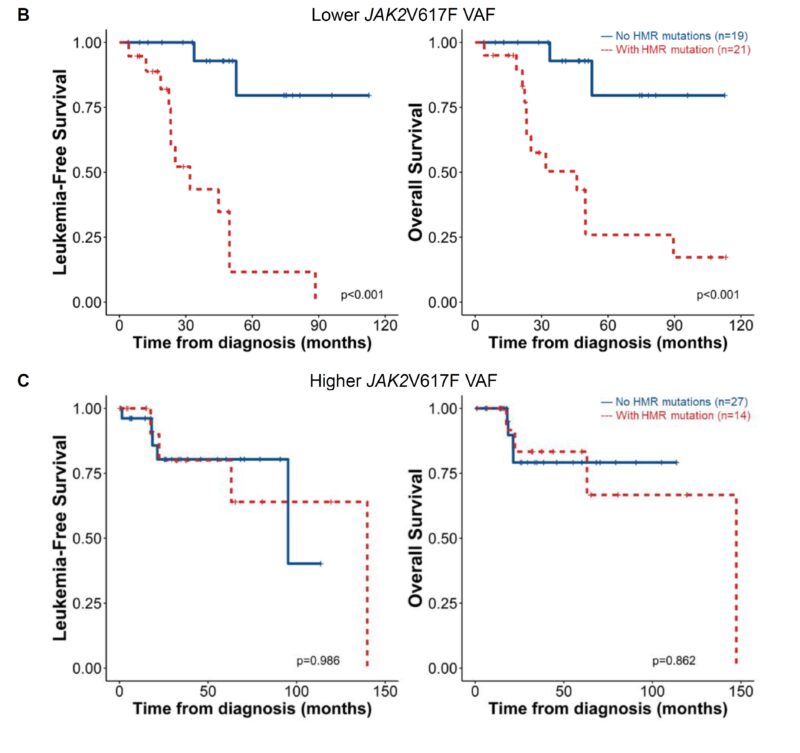
Next, we stratified patients into JAK2-Lower and JAK2-Higher groups based on the median VAF. Interestingly, our analysis revealed that HMR mutations significantly worsened prognosis in JAK2-Lower patients but not in JAK2-Higher patients.
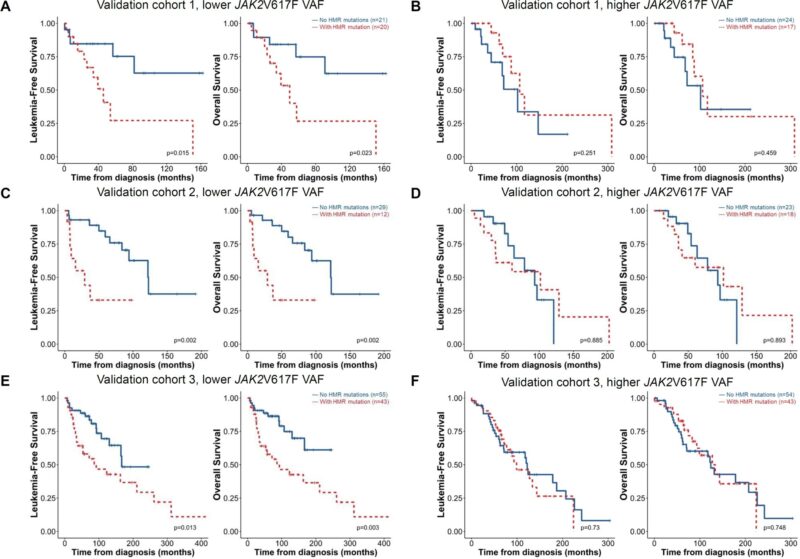
We then leveraged our validation cohorts 1-3 to further confirm the discriminating power of integrating HMR and JAK2V617F VAF status for LFS and OS, using either the median as the cutoff in each cohort or a universal cutoff of 50%.
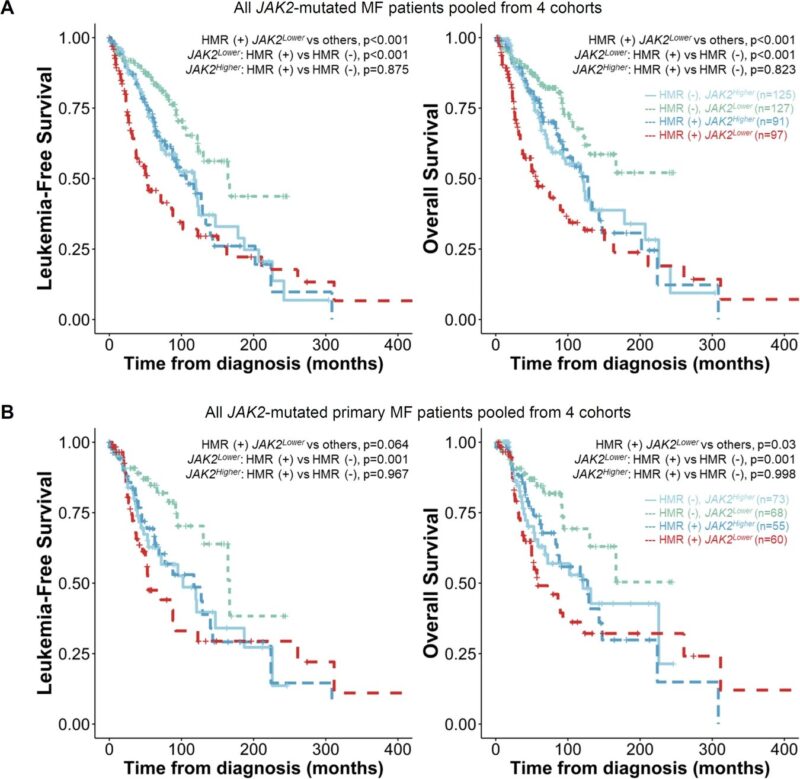
We subsequently aggregated patient data from all four cohorts. Again, while HMR mutations significantly correlated with poorer survival among JAK2-Lower patients, the presence or absence of HMR mutations did not significantly alter median LFS or OS in JAK2-Higher patients.
In multivariable Cox regression analysis, the concurrent presence of HMR mutation and a lower VAF of JAK2V617F was identified as an independent adverse prognostic factor for both LFS and OS, irrespective of age and existing risk stratification models (MIPSS70, MIPSS70+v2, GIPSS).
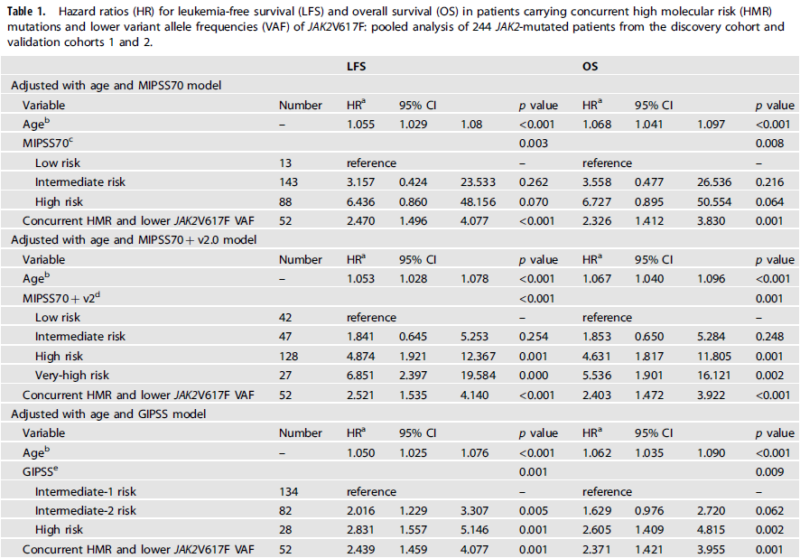
To delve deeper, we examined the interactions between JAK2 and HMR mutation VAFs. Interestingly, we found significant mutual negative effects between JAK2 VAF & HMR VAFs, including the highest HMR VAF per pt, potentially implicating the dominant or secondary dominant clone.
It is crucial to recognize that the observed negative interaction suggests more than a direct inverse correlation—it points to complex modulation where JAK2-mutant and HMR-mutant clones may compete or compensate, with HMR mutations’ effects potentially mitigated by high JAK2 VAF.
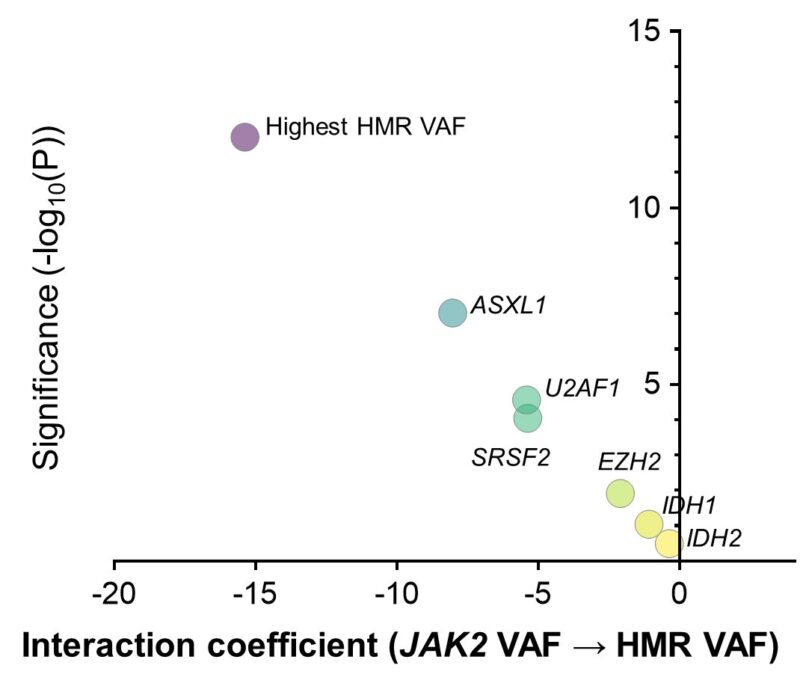
Next, we conducted mutation co-occurrence tests. No consistent co-occurrence pattern was observed across cohorts, whether based on gene function groups or individual genes, with or without secondary MF, ruling out potential confounding effects from other concurrent mutations.
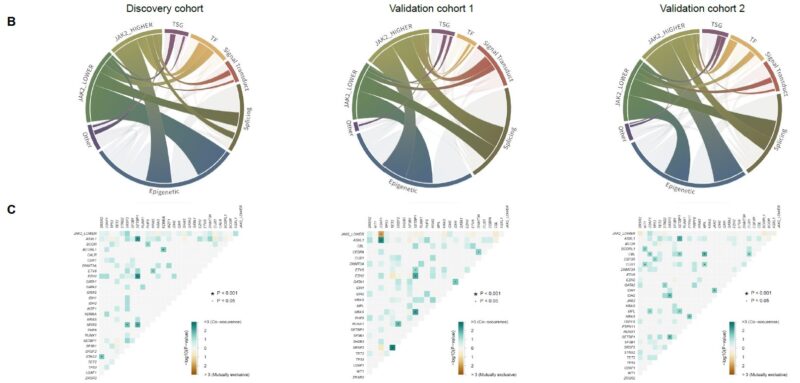
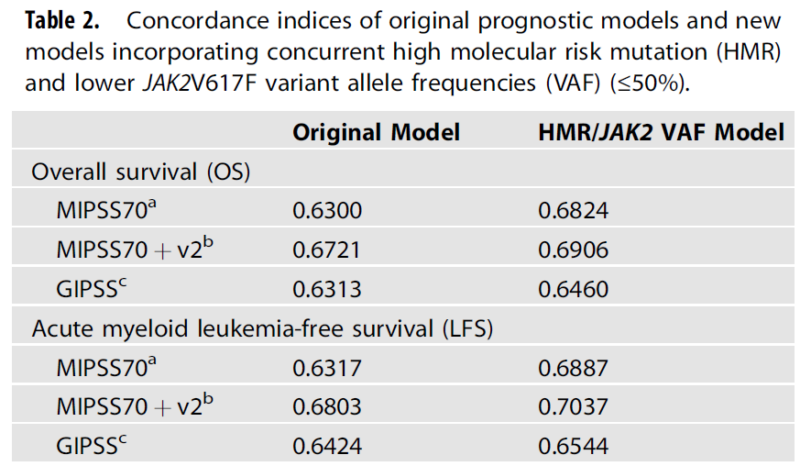
Considering the synergistic prognostic significance of the co-occurrence of HMR mutations with a lower JAK2V617F VAF, we sought to improve the existing molecular models by incorporating concurrent HMR mutations with a lower JAK2V617F VAF (≤50%) as an adverse prognosticator.
Following adjustments of the risk category score cutoffs to accommodate concurrent HMR mutations and lower JAK2V617F VAF, 130 (44.5%), 135 (46.2%), and 250 (85.6%) patients were restaged in the MIPSS70, MIPSS70 + v2.0, and GIPSS models, respectively.
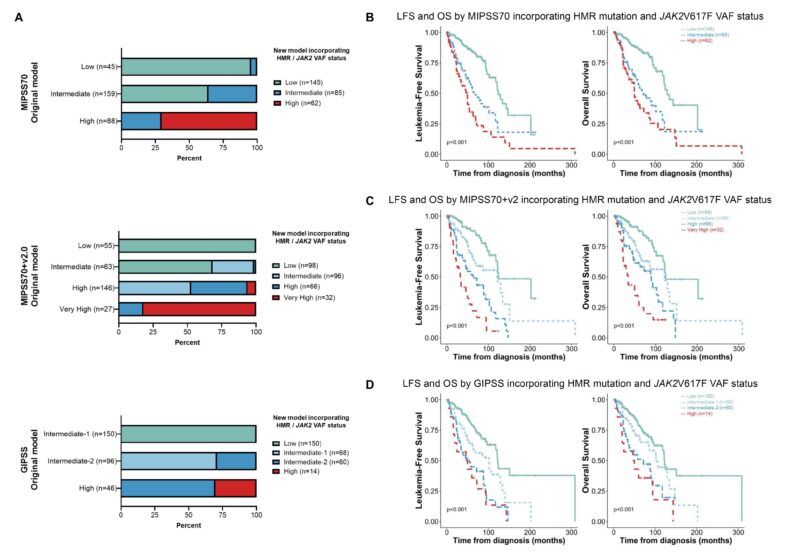
Across all three new models, the inclusion of HMR/JAK2V617 VAF status led to enhanced prognostication compared to the original models, as evidenced by higher concordance indices and improved performance than the parental models in time-dependent ROC analyses in each case.
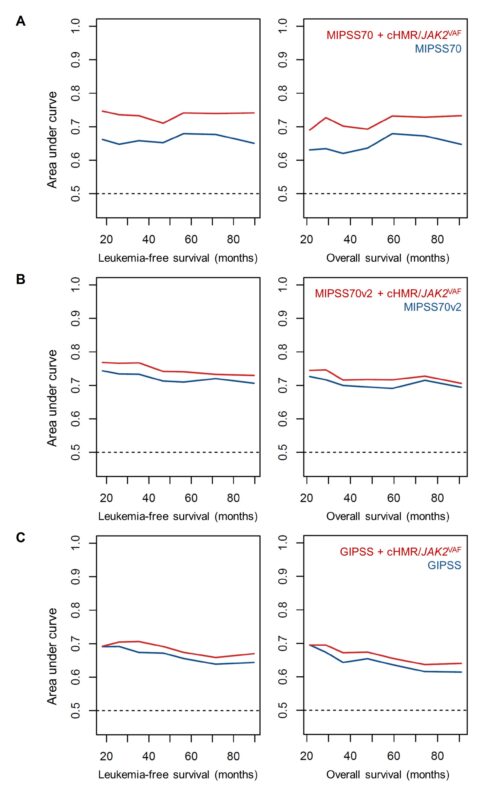
In summary, we observed that HMR mutations accompanied by a lower JAK2 VAF identified a distinct MF population with significantly reduced survival, and their independent prognostic relevance was demonstrated by multivariable analysis and externally validated in multiple cohorts.
Moreover, while the addition of HMR/ JAK2V617F VAF status to existing molecularly integrated MF risk models enhanced prognostic performance, prospective validation of the proposed refined models is warranted.
These results underscore the importance of studies with single-cell resolution and serial follow-up, which will be instrumental in deciphering the clonal architecture and evolution of MF, and how that relates to JAK2V617F VAF dynamics.”
Source: Yu-Hung Wang/X
More posts featuring Yu-Hung Wang.


