Nirogacestat is a targeted cancer therapy that blocks a protein complex known as gamma-secretase, which plays a key role in signaling pathways that help certain tumors grow. By disrupting these signals, Nirogacestat may help slow or stop tumor progression, especially in specific rare tumors where treatment options are limited. This article will explore how Nirogacestat is used in cancer, its dosage, and what to expect during treatment.
Which company produced Nirogacestat?
Nirogacestat, marked under the brand name Ogsiveo, is developed by SpringWorks Therapeutics, a U.S.-based biotechnology company dedicated to creating precision therapies for patients with rare diseases and cancers. Founded in 2017 as a spinout from Pfizer, SpringWorks has since built a strong pipeline of targeted treatments, with nirogacestat as one of its lead investigational drugs.
The company collaborates with major pharmaceutical companies—including GSK, Pfizer, Seagen, Regeneron, and Janssen—to evaluate nirogacestat in combination with other cancer therapies, especially in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. It also partners with leading academic institutions such as Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the Children’s Oncology Group to explore its use in additional tumor types and pediatric settings. Through these partnerships, SpringWorks aims to expand the potential impact of nirogacestat in cancer care. Since July 2025, SpringWorks has become a wholly owned subsidiary of Merck KGaA, bringing nirogacestat into their global rare‑tumor portfolio.
How does Nirogacestat work?
Ogsiveo exerts its anticancer effects by selectively inhibiting the gamma‑secretase enzyme complex, which is involved in critical cell signaling pathways. Notably, gamma‑secretase cleaves transmembrane proteins like the Notch receptor, releasing the Notch intracellular domain (NICD). Once in the nucleus, NICD activates genes involved in cell proliferation and survival. By blocking this cleavage, nirogacestat prevents NICD formation, disrupting Notch signaling and reducing tumor cell growth—an effect seen especially in desmoid tumors.
Additionally, gamma‑secretase cleaves BCMA (B cell maturation antigen) on multiple myeloma cells, releasing a soluble fragment that can hinder BCMA-targeted therapies. Nirogacestat’s inhibition of this process preserves BCMA on the cell surface, increases target density for drugs, and lowers soluble BCMA “decoys,” potentially enhancing the effectiveness of BCMA-directed treatments
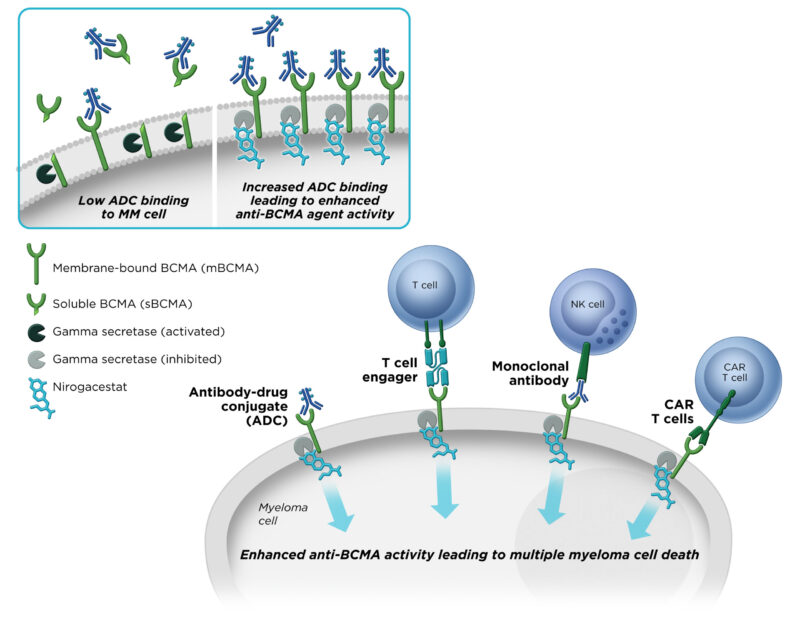
Photo from SpringWorks Therapeutics Official Website
What Cancers Is Ogsiveo Approved to Treat?
Nirogacestat is FDA‑approved for treating progressing desmoid tumors in adults who need systemic therapy. This approval, granted on November 27, 2023, represents the first targeted treatment for this rare, locally aggressive soft-tissue tumor.
What research is behind the approval?
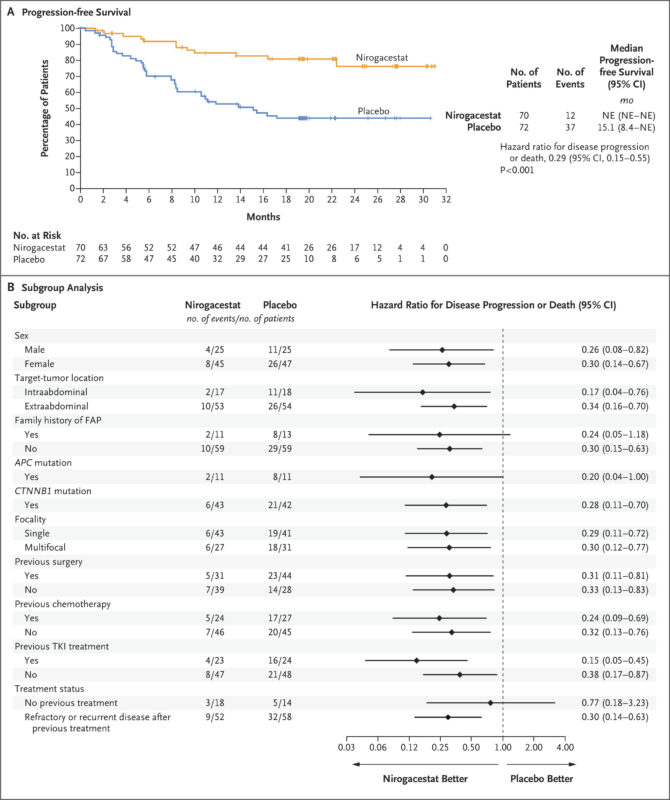
The FDA approval of Ogsiveo was based on the results of the Phase 3 DeFi trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating its safety and effectiveness in adults with progressing desmoid tumors. The full results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in March 2023.
In this international trial, 142 patients were randomly assigned to receive either nirogacestat or placebo twice daily. The primary goal was to assess progression-free survival. Nirogacestat significantly reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 71% compared to placebo (hazard ratio, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.15–0.55; p<0.001). After two years, 76% of patients treated with nirogacestat remained progression-free, compared to 44% in the placebo group.
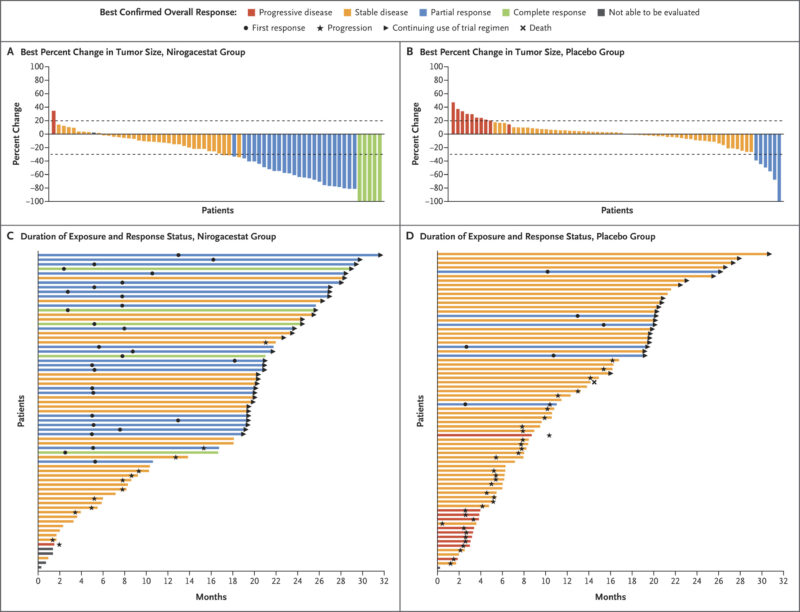
The study also reported a 41% objective response rate with nirogacestat, meaning nearly half of patients experienced tumor shrinkage, versus only 8% in the placebo group. Notably, 7% of patients receiving nirogacestat achieved a complete response, while none in the placebo group did. The median time to first response was 5.6 months with nirogacestat and 11.1 months with placebo.
Patient-reported outcomes also favored nirogacestat, with significant improvements in pain, symptom severity, physical functioning, and overall quality of life. These benefits were observed early in treatment and remained consistent over time.
While most side effects were mild to moderate (grade 1 or 2), they were common. The most frequently reported adverse events with nirogacestat included diarrhea (84%), nausea (54%), fatigue (51%), hypophosphatemia (42%), and skin rash (32%). One notable side effect was ovarian dysfunction, occurring in 75% of women of childbearing age receiving nirogacestat. Among them, 74% experienced recovery of ovarian function during or after treatment.
Nirogacestat side effects and its management
Ogsiveo, like many targeted cancer therapies, is associated with a range of side effects that can vary in frequency and severity. While most are manageable, understanding how to recognize and treat them is important for maintaining patient comfort and treatment continuity.
Common Side Effects
The most frequently reported side effects of Ogsiveo include diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, and skin-related issues such as rash or stomatitis. Many patients also experience laboratory abnormalities like low phosphate (hypophosphatemia), low potassium (hypokalemia), and elevated liver enzymes. Ovarian dysfunction is another notable side effect in women of childbearing age, often leading to missed periods or signs of early menopause.
Less Common Side Effects
Some patients may experience more serious or less frequent side effects. These include elevations in liver enzymes beyond five times the upper normal limit, non-melanoma skin cancers (such as basal or squamous cell carcinoma), and in rare cases, hypersensitivity reactions like swelling or rash. Infections or fevers may also occur, though less commonly, and are likely linked to the immune-related impacts of treatment. While male reproductive function has not shown notable changes, ovarian dysfunction remains a specific concern in women receiving this drug.
Side Effect Management
Managing nirogacestat-related side effects typically begins with monitoring and supportive care. Diarrhea and nausea are treated with hydration, diet changes, and medications such as loperamide or antiemetics. Fatigue is usually addressed by managing contributing factors like sleep disruption or nutritional deficiencies. Blood tests are routinely performed to monitor electrolytes and liver function; abnormalities are corrected with supplements or temporary dose interruptions.
For women experiencing ovarian dysfunction, discussions about fertility preservation are recommended before starting therapy, and most cases improve after treatment ends. Skin rashes and stomatitis are usually managed with topical treatments or oral rinses, and persistent symptoms may require dose adjustments. Due to the potential risk of developing skin cancers, patients should undergo routine dermatologic checks during long-term treatment.

What is the Recommended Dosage of Nirogacestat?
Ogsiveo is available as a 50 mg tablet and is prescribed for adults with progressing desmoid tumors who require systemic therapy. The recommended dose is 150 mg taken twice a day by mouth and is continued until the disease progresses or the patient experiences unacceptable side effects.
In some cases, certain side effects—such as severe diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes, or significant drops in phosphate or potassium levels—may require the treatment to be paused. Once the symptoms improve, treatment may be restarted at a lower dose. For patients with mild to moderate kidney problems, no dose adjustment is needed. However, data on use in people with severe liver impairment are limited.
How is Nirogacestat Administered?
Ogsiveo is taken by mouth and can be taken with or without food. Each tablet should be swallowed whole—do not break, crush, or chew it. If a dose is missed or vomited, simply take the next dose at the regular scheduled time.
During treatment, it’s important to avoid grapefruit, Seville oranges, and starfruit, as they can interfere with how the medication works. Patients should also avoid taking it with proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers, as these can reduce the drug’s effectiveness. If needed, antacids can be used, but should be taken either two hours before or two hours after the dose.
The tablets should be stored at room temperature, ideally 20°C to 25°C, though short-term exposure 15°C to 30°C is acceptable.

Learn more about Radiotherapy For Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Types, Success Rate, Side Effects on OncoDaily.
What to Avoid During Nirogacestat Treatment?
While taking Ogsiveo, certain foods and medications should be avoided to ensure the drug works properly and to minimize side effects. Patients should not consume grapefruit, Seville oranges, or starfruit, as these can interfere with how the body processes the medication. It’s also important to avoid proton pump inhibitors and H2 blockers, which can reduce the drug’s absorption.
If antacids are needed, they should be taken at least two hours before or after your Nirogacestat dose. Always let your healthcare provider know about all medications and supplements you’re taking to avoid possible interactions.
How Long Does the Drug Stay in the Body?
Ogsiveo is metabolized primarily by the liver enzyme CYP3A4, with additional metabolism involving CYP2C19, CYP2C9, and CYP2D6. It has a half-life of about 23 hours, meaning it remains in the body for nearly a full day after each dose. The drug is eliminated through feces, urine, and exhaled air—most of it is excreted in stool, while smaller amounts are cleared through urine and breath.
Nirogacestat effectiveness over time
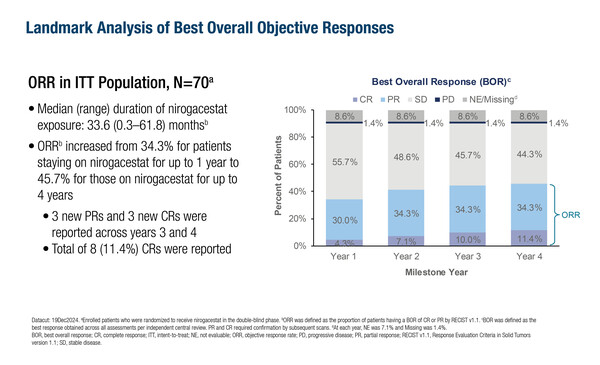
At the ESMO Sarcoma and Rare Cancers 2025 Congress, updated long-term results from the Phase III DeFi trial were shared, highlighting the continued effectiveness and safety of nirogacestat in adults with desmoid tumors. This latest analysis included patients treated continuously for up to four years, providing valuable insights into the durability of responses and ongoing patient benefits.
As of December 19, 2024, the median treatment duration was 33.6 months. Of the 70 patients initially assigned to nirogacestat, 66% remained on treatment for at least one year, 57% for two years, 47% for three years, and 21% for four years. The objective response rate improved over time, increasing from 34.3% at one year to 45.7% after four years. Additional responses observed in years three and four brought the total to 24 partial and eight complete responses.
Patients reported early and sustained improvements in pain, symptom burden, physical functioning, and overall quality of life throughout the treatment period. The safety profile was consistent with previous data, with side effects generally manageable and less frequent after the first year. Only a few dose reductions and treatment discontinuations due to adverse events occurred beyond the second year.
These findings reinforce that long-term Ogsiveo therapy provides lasting tumor control and quality-of-life improvements with a manageable safety profile in patients with progressing desmoid tumors.
Ongoing trials with Nirogacestat
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center is conducting a clinical trial (NCT05879146) to better understand why some patients with desmoid tumors respond to nirogacestat while others do not. The study is evaluating biomarkers, tumor changes on MRI, and the impact of treatment on progression-free survival and ovarian function. Results may help personalize treatment and improve outcomes.
FAQ
What type of cancer is Nirogacestat approved to treat?
rogacestat is FDA-approved for adults with progressing desmoid tumors who require systemic therapy. Desmoid tumors are rare, non-metastatic soft-tissue tumors that can be locally aggressive and painful.
How does Ogsiveo enhance BCMA-targeted therapies?
Nirogacestat blocks gamma-secretase, which prevents the cleavage and shedding of BCMA from the surface of multiple myeloma cells. By keeping BCMA available on the cell surface and reducing soluble BCMA, it enhances the effectiveness of BCMA-targeted therapies such as teclistamab, elranatamab, or ide-cel.
What is the mechanism of action of Ogsiveo?
Nirogacestat is a gamma-secretase inhibitor that interferes with Notch signaling—a pathway involved in cell survival and proliferation. By inhibiting gamma-secretase, it blocks Notch receptor cleavage, preventing tumor growth and cell survival in cancers such as desmoid tumors and potentially other solid tumors.
How long does Nirogacestat stay in the body?
Nirogacestat has a half-life of approximately 23 hours, which means it stays in the body for nearly a full day after dosing. Most of the drug is excreted in feces, with smaller amounts cleared via urine and exhaled air.
What are the most common side effects of Ogsiveo?
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, hypophosphatemia, and skin rash.
Are there any food or drug interactions with Ogsiveo?
Yes. Patients should avoid grapefruit, Seville oranges, and starfruit, as these can interfere with liver enzymes that metabolize the drug. Additionally, proton pump inhibitors and H2 blockers may reduce absorption. If needed, antacids should be spaced by at least two hours from the dose.
How is Ogsiveo administered?
Nirogacestat is taken orally, as a 150 mg dose twice daily, with or without food. Tablets must be swallowed whole—do not break, chew, or crush.


