Ivosidenib is a targeted therapy designed for adults with a specific genetic mutation known as IDH1. This mutation affects the bone marrow by preventing immature blood cells from maturing into healthy adult blood cells, which can contribute to the development of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). To determine if Ivosidenib is an appropriate treatment, doctors first conduct genetic testing to confirm the presence of the IDH1 mutation.
Which company produced Tibsovo?
Agios Pharmaceuticals developed Ivosidenib (brand name Tibsovo). They were first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on July 20, 2018, for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with an IDH1 mutation. In 2022, Servier Pharmaceuticals acquired the oncology portfolio of Agios, including Ivosidenib. Since then, Servier has been responsible for its commercialization and further development. Tibsovo (Ivosidenib) is protected by multiple patents with varying expiration dates. The earliest of these patents is set to expire on January 18, 2033, covering methods of treating cancers characterized by an IDH1 mutation. Subsequent patents extend protection, with the latest expiring on June 7, 2039, which includes strategies for treating previously treated, locally advanced, or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with a specific dosing regimen.
Mechanism of action of Tibsovo
IDH1 is a mutation that is found in about 5-10% of patients who have acute myeloid leukemic. In healthy cells, IDH1 helps convert isocitrate into α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), a process essential for normal cell function. Instead of producing α-KG, the mutant enzyme generates D-2-hydroxyglutarate (D-2HG), an abnormal byproduct that interferes with normal blood cell development and contributes to cancer growth. By inhibiting the mutant IDH1 enzyme, Ivosidenib effectively reduces D-2HG levels, allowing blood cells in the bone marrow to mature properly rather than remaining stuck in an immature, cancerous state. This causes cells to grow out of control and lead to leukemia, where the accumulation of immature white blood cells, or blasts, prevents the production of healthy blood cells. By restoring normal cell differentiation, Ivosidenib helps reduce the number of leukemic cells and improve blood cell production, leading to better disease control. IDH1 mutation can be found through next-generation sequencing, which is performed on a bone marrow biopsy sample collected at diagnosis.
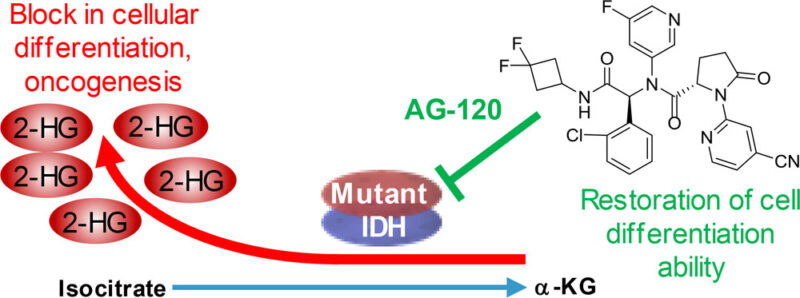
ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 4, 300-305
What Cancers is Tibsovo Approved to Treat?
Tibsovo is currently approved for two major types of cancer: acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer). For AML, Tibsovo is an option for patients with newly diagnosed disease who cannot undergo intensive chemotherapy, either due to age (75 and older) or other health conditions. It is also used in relapsed or refractory AML, where the cancer has either stopped responding to treatment or has returned after prior therapy. By blocking the mutant IDH1 enzyme, Tibsovo helps restore normal blood cell development, reducing the number of cancerous cells in the bone marrow. In cholangiocarcinoma, Tibsovo is approved for patients with locally advanced or metastatic disease whose cancer has progressed after at least one prior treatment. Targeting the IDH1 mutation helps slow tumor growth and offers a new treatment option for those with limited choices. With its precision-targeted approach, Tibsovo provides a personalized treatment option for patients whose cancers are driven by IDH1 mutations, helping improve outcomes where other treatments may not be effective.
Learn more about Leukemia, symptoms, causes, types on OncoDaily.
Tibsovo Combinations and Treatment Outcomes.
For patients with newly diagnosed AML who are unable to tolerate intensive chemotherapy, combining Tibsovo with azacitidine has shown remarkable benefits. The AGILE Phase 3 trial, which was published in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) by Montesinos P. on June 3, 2022, revealed that patients receiving this combination had a median overall survival (OS) of 24.0 months, a significant improvement compared to 7.9 months for those treated with azacitidine alone. Furthermore, progression-free survival (PFS) was also prolonged, reaching 13.9 months versus 4.7 months in the control group. This combination not only improved survival but also led to a higher complete remission rate (47% vs. 15%), making it a preferred frontline therapy for older or unfit AML patients. For patients whose AML has relapsed or become resistant to previous treatments, Tibsovo alone has been an important therapeutic option.
In clinical studies, patients treated with Tibsovo monotherapy had a median OS of 8.8 months, with 21.6% achieving complete remission. These results highlight Tibsovo’s role in extending survival and offering disease control in patients who have exhausted other treatment options. Tibsovo has also proven effective in treating IDH1-mutant cholangiocarcinoma, particularly in patients who have already undergone prior treatment.
The ClarIDHy trial demonstrated that patients receiving Tibsovo had a median OS of 10.3 months, compared to 7.5 months in the placebo group. Additionally, progression-free survival (PFS) was extended to 2.7 months, whereas patients on placebo had a PFS of just 1.4 months. These findings established Tibsovo as an important second-line treatment option for advanced cholangiocarcinoma, helping to slow disease progression and improve overall survival.
The Side Effects of Tibsovo and its Management
Tibsovo (Ivosidenib) is an effective treatment for AML and cholangiocarcinoma, but like all cancer therapies, it comes with potential side effects. Proper management of these side effects is essential to ensure patient safety and maintain quality of life during treatment. Here are most common and serious complications of Tibsovo.

- Differentiation syndrome (DS) – Rapid maturation of leukemia cells causing inflammation & organ dysfunction. Symptoms include fever, low blood pressure, rapid weight gain, fluid buildup in lungs, and breathing difficulties. Management involves immediate corticosteroids (dexamethasone) at first signs, temporary discontinuation of Tibsovo in severe cases, and close monitoring to prevent complications.
- QT Prolongation: Tibsovo may affect heart rhythm, causing dizziness, fainting, and irregular heartbeat, increasing the risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. Management includes ECG monitoring before and during treatment, maintaining balanced electrolytes (K, Ca, Mg), and adjusting or discontinuing the dose if severe.
- Fatigue: A common side effect of Tibsovo that can interfere with daily activities and well-being. Management includes light exercise to boost energy, adequate hydration, proper nutrition, and treatment schedule adjustments if fatigue becomes severe.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Tibsovo may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and appetite loss, affecting nutrition and overall health. Management includes antiemetics (ondansetron) for nausea, proper hydration, bland/easily digestible foods for diarrhea, and small, frequent meals to maintain nutrition.
- Liver Toxicity: Tibsovo may cause elevated liver enzymes (AST/ALT), indicating possible liver irritation or damage. Management includes regular liver function tests (LFTs) for early detection, dose modifications or temporary discontinuation if levels are too high, and continuous monitoring to ensure treatment safety.
Less common side effects
While common side effects of Tibsovo are well-documented, it is equally important to recognize less common but potentially serious side effects that some patients may experience. Conditions like leukocytosis and an increased risk of infections require careful monitoring and timely intervention. Management includes hydroxyurea and dose adjustments for leukocytosis, infection monitoring (fever, symptoms), early antibiotic treatment, good hygiene, and avoiding sick contacts.
Pregnancy and Ivosidenib
The safety of Ivosidenib during pregnancy is not established, and its use is not recommended. Based on animal studies, the drug may cause fetal harm, including lower fetal weights and skeletal abnormalities. No human data are available to confirm these risks. Before starting treatment, pregnancy status should be verified, and patients should be informed of potential risks. Effective contraception is advised during treatment and for one month after the last dose. Since Ivosidenib may reduce hormonal contraceptive effectiveness, an additional barrier method is recommended. In animal studies, Ivosidenib exposure led to fetal harm, including spontaneous abortions and developmental abnormalities in rats and rabbits at doses higher than those used in humans. Due to these risks, healthcare providers should carefully evaluate its use in pregnant patients.
What is the Recommended Dosage of Tibsovo?
For patients with IDH1-mutant AML or cholangiocarcinoma, the standard Tibsovo dosage is 500 mg once daily, taken orally with or without food. Treatment continues until disease progression or intolerable side effects. If severe side effects occur, dose adjustments or temporary discontinuation may be required. Patients should take Tibsovo at the same time each day and swallow the tablet whole. If a dose is missed within 12 hours, it should be taken as soon as possible; otherwise, it should be skipped. In case of vomiting, the next scheduled dose should be taken without an extra dose. Regular monitoring, including ECG, liver tests, and blood counts, helps manage potential side effects and ensures safe treatment continuation.
Tibsovo’s Effectiveness Over Time
A study in JAMA, released during ASCO 2024, found that Ivonescimab plus chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In a phase 3 trial of 322 patients, those receiving Ivonescimab had a median PFS of 7.1 months versus 4.8 months with chemotherapy alone (HR 0.46). The benefit was consistent across subgroups, including those previously treated with EGFR-TKIs and patients with brain metastases. Objective response rates were also higher (50.6% vs. 35.4%). The study, funded by Akeso Biopharma, concluded that Ivonescimab offers a significant survival advantage with a manageable safety profile.
Written by Mariam Khachatryan, MD
FAQ
What is Tibsovo?
Tibsovo (Ivosidenib) is a targeted therapy that inhibits mutant IDH1 enzymes in cancer cells.
In which types of cancer is it used as a treatment?
It is used for IDH1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer).
Which kind of food should not be combined with Tibsovo?
Grapefruit and Seville oranges should be avoided as they can interfere with drug metabolism.
What is the daily dose for Tibsovo?
500 mg once daily (two 250 mg tablets), with or without food.
Is Tibsovo safe for long-term use?
Long-term safety depends on individual response and side effects; regular monitoring is required.
Can I take Tibsovo during pregnancy?
No, Tibsovo may harm the fetus; effective contraception is recommended during treatment.


