Tremelimumab, also known by its brand name Imjudo, is a type of cancer immunotherapy. Instead of directly killing cancer cells like chemotherapy, it helps your own immune system recognize and attack them more effectively. Today, tremelimumab is used together with another immunotherapy called durvalumab (Imfinzi) to treat some people with advanced liver cancer and advanced lung cancer. It is also being studied in several other cancers in clinical trials.
This article explains how tremelimumab works, which cancers it is used for, what you can expect during treatment, possible side effects, and how ongoing research may expand its role in cancer care.
What is Imjudo and How Does It Work?
Tremelimumab, produced by AstraZeneca, is a monoclonal antibody, a lab-made protein that attaches to a specific target in the body. Its target is a protein on immune cells called CTLA-4.
CTLA-4 acts like a “brake” on the immune system. It helps prevent T cells (a type of white blood cell) from becoming too active. This is important in normal life, because it protects healthy tissues. But in cancer, this brake can be too strong, allowing cancer cells to hide from the immune system.
Tremelimumab blocks CTLA-4. When this brake is released, T cells become more active, recognize cancer cells more easily, and can attack them more strongly and for a longer period of time.
Tremelimumab is almost always used in combination with durvalumab (Imfinzi), which blocks a different immune “brake” called PD-L1. You can think of it this way:
- Tremelimumab gives the immune system a strong push at the beginning (a “priming” dose).
- Durvalumab helps keep that immune response going over time.
Together, this dual immunotherapy helps the immune system stay active against the cancer.
What Is a Clinical Trial and Why Does It Matter?
A clinical trial is a research study designed to test new drugs and treatments in patients to determine their safety and effectiveness. Before Imjudo was approved, it went through multiple phases of clinical trials to assess how well it worked, what side effects it caused, and whether it was better than existing treatments. Clinical trials are essential because they provide scientific evidence that a drug can help patients while ensuring it is safe for widespread use.
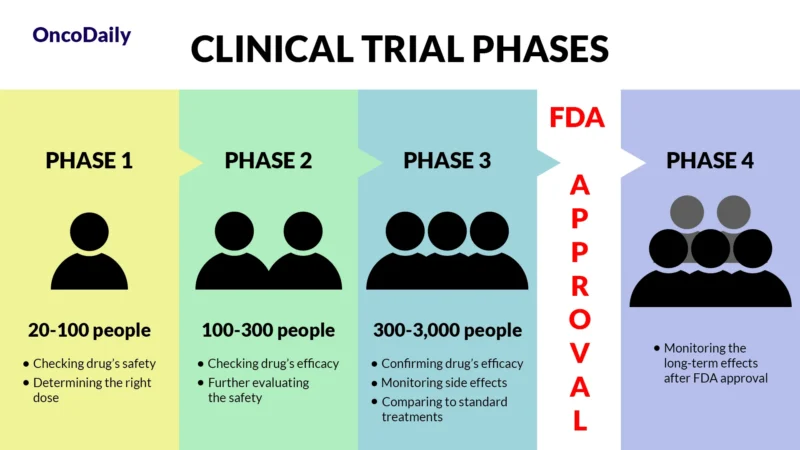
What Does FDA Approval Mean?
When a drug receives FDA approval, it means that after rigorous testing in clinical trials, it has been shown to be both safe and effective for treating a specific condition. This approval makes the drug widely available for doctors to prescribe and helps patients access new, cutting-edge treatments sooner.
What Cancers Does Tremelimumab Treat?
Imjudo is currently approved for use in combination therapy for two major cancer types.
In unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of primary liver cancer, tremelimumab is given together with durvalumab as part of the STRIDE regimen. This approval was granted by the FDA in October 2022 and marked the first time a CTLA-4–based immunotherapy combination was approved for advanced liver cancer.
In metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), tremelimumab is approved in combination with durvalumab and platinum-based chemotherapy. This approval was granted in November 2022 for patients with stage IV disease, regardless of PD-L1 expression level, as long as they do not have certain targetable mutations such as EGFR or ALK.
At this time, tremelimumab does not target a specific gene mutation. Instead, it works by enhancing the immune system, making it useful across a broad range of patients whose cancers are sensitive to immune-based treatments.

You can also read about Durvalumab (Imfinzi): What patients need to know on OncoDaily.
How Effective Is Tremelimumab? Results From Clinical Trials
The benefits of tremelimumab come from large clinical trials that tested it in combination with other treatments. In metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, the POSEIDON phase III trial studied more than 1,000 patients who received durvalumab and chemotherapy with or without tremelimumab. Patients who received tremelimumab as part of the combination had a 23% lower risk of death and a 28% lower risk of disease progression or death compared with chemotherapy alone. Two years after starting treatment, about one-third of patients in the immunotherapy group were still alive, compared with just over one-fifth in the chemotherapy group. Longer follow-up showed that the survival benefit lasted for several years.
In advanced liver cancer, the HIMALAYA phase III trial compared the STRIDE regimen with sorafenib, a long-standing standard treatment. Patients who received tremelimumab plus durvalumab had a 22% reduction in the risk of death. Three years after starting treatment, 31% of patients in the immunotherapy group were still alive, compared with 20% of those who received sorafenib. Importantly, this survival benefit was achieved without an increase in serious liver-related side effects, which is especially important for patients with underlying liver disease.
These results show that tremelimumab can help patients live longer when used as part of combination immunotherapy.
What Can You Expect During Treatment With Tremelimumab?
Imjudo is given through an intravenous (IV) infusion, meaning it is delivered directly into a vein. The infusion itself usually takes about one hour. When tremelimumab is used, it is given first, followed by durvalumab, and then chemotherapy if chemotherapy is part of the regimen.
In liver cancer, tremelimumab is typically given only once at the start of treatment. After that, patients continue receiving durvalumab every four weeks. In lung cancer, tremelimumab is given during the early treatment phase together with durvalumab and chemotherapy, usually over several cycles, and then stopped while durvalumab continues as maintenance therapy.
During each visit, the healthcare team monitors patients closely, checking blood tests and watching for side effects. Many patients are able to go home the same day after treatment.
Side Effects of Tremelimumab
Imjudo is a type of immunotherapy that works by activating your immune system to fight cancer. Because the immune system becomes more active, it can sometimes cause inflammation in healthy parts of the body. As a result, side effects can occur. Most are mild to moderate and can be managed, especially when they are recognized early.
Common Side Effects
The most common side effects of tremelimumab include feeling tired, diarrhea, nausea, reduced appetite, skin rash or itching, fever, and muscle or joint pain. Some changes may be seen on blood tests before symptoms appear, such as changes in liver tests, kidney function, blood sugar, or blood cell counts.
In people treated for liver cancer, changes in liver blood tests are more common, partly due to underlying liver disease. In lung cancer, especially when chemotherapy is used together with immunotherapy, low blood counts or kidney-related changes may occur more often.
Less Common but More Serious Side Effects
Less commonly, tremelimumab can cause stronger immune reactions that affect organs such as the lungs, intestines, liver, kidneys, heart, nervous system, or hormone-producing glands like the thyroid or adrenal glands. These reactions may cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, severe diarrhea, yellowing of the skin or eyes, dizziness, headaches, or significant fatigue.
Rare but serious side effects, including heart or brain inflammation, severe skin reactions, or eye inflammation, have been reported. Some immune-related side effects can appear weeks or even months after treatment has ended, which is why continued follow-up is important.
How Are Side Effects Managed?
Side effects are usually manageable when detected early. Your healthcare team will monitor you closely with regular blood tests and ask about new symptoms during treatment.
Mild symptoms are often treated with supportive medications, while more serious immune-related reactions may require pausing treatment and using medications such as corticosteroids to calm the immune system. If hormone glands are affected, hormone replacement therapy may be needed.
With prompt care and monitoring, most side effects can be controlled, and many patients are able to continue treatment safely. If you notice any new or worsening symptoms, contact your healthcare team as soon as possible.
What Is the Recommended Dosage of Tremelimumab?
Tremelimumab (Imjudo) is given by IV infusion and is always used together with other cancer treatments, most often durvalumab (Imfinzi). For advanced liver cancer, tremelimumab is usually given only once at the start of treatment (300 mg for most adults), after which treatment continues with durvalumab alone.
For advanced lung cancer, tremelimumab is given at a lower dose (75 mg for most adults) during the first few treatment cycles together with durvalumab and chemotherapy, and is then stopped while durvalumab continues.
How Is Tremelimumab Given?
Imjudo is given as a slow IV infusion, which usually takes about one hour. When used with other treatments, tremelimumab is given first, followed by durvalumab and then chemotherapy if chemotherapy is part of the plan.
Patients are monitored closely during and after the infusion to watch for side effects. Most people are able to go home the same day after treatment.
What to Expect Long-Term?
The goal of treatment is often to slow or stop cancer growth, improve survival, and maintain quality of life. Some patients experience long-lasting benefit even after tremelimumab has been stopped, because the immune system may remain active against the cancer. If the cancer eventually progresses, doctors will discuss other treatment options based on the patient’s condition and prior therapies.
What Should You Avoid During Treatment?
Patients receiving Imjudo are usually advised to avoid live vaccines, as these may not be safe while the immune system is being modified. Certain medications that suppress the immune system should also be avoided unless prescribed by the oncology team. Alcohol intake is often limited, especially for patients with liver cancer, to reduce stress on the liver.
Patients should always inform their healthcare team before taking new medications, supplements, or herbal products, and should report any new symptoms as soon as they appear.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Tremelimumab
Research on tremelimumab is ongoing. Clinical trials are exploring its use in earlier-stage liver cancer, other gastrointestinal cancers, urothelial cancer, and mesothelioma, often in combination with other immunotherapies, targeted drugs, or liver-directed treatments. These studies aim to determine whether tremelimumab can help more patients or work even better when used in new ways.
Treatment decisions are individualized, and patients should discuss whether tremelimumab is appropriate for their specific situation with their oncology team.
If you’re a healthcare provider, access the professional version here.


