Futibatinib is a targeted cancer therapy that inhibits FGFR2, a protein involved in tumor growth and progression. It is approved for use in cholangiocarcinoma, a rare bile duct cancer, in patients with tumors that have specific FGFR2 alterations. This article explores its role in cancer treatment, including its uses, dosage, side effects, and what patients can expect during therapy.
Which company produced Futibatinib?
Futibatinib is produced by Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., a Japanese specialty pharmaceutical company. Taiho Pharmaceutical focuses on oncology and is a subsidiary of Otsuka Holdings Co., Ltd. The company’s U.S. subsidiary, Taiho Oncology, Inc., is responsible for the development and commercialization of futibatinib in the United States. Taiho Pharmaceutical is committed to research and development in oncology, as well as in allergy and immunology, urology, and consumer healthcare products. Their corporate philosophy emphasizes improving human health and contributing to a society enriched by smiles.
How Does Futibatinib work?
Futibatinib, marketed under the brand name Lytgobi, is a targeted cancer therapy designed to inhibit the activity of fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs), particularly FGFR2, which are involved in cell growth and survival. By blocking these receptors, futibatinib aims to slow down or stop the growth of cancer cells that rely on FGFR signaling. Futibatinib is a small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor that irreversibly binds to FGFR1–4. It forms a covalent bond with a conserved cysteine residue in the ATP-binding pocket of these receptors, leading to sustained inhibition of their kinase activity.
This action disrupts downstream signaling pathways that promote tumor cell proliferation and survival. Notably, futibatinib has demonstrated efficacy against various FGFR2 mutations, including those that confer resistance to reversible FGFR inhibitors.
In preclinical studies, futibatinib has shown potent antitumor activity in cell lines and animal models with FGFR alterations. Its ability to irreversibly inhibit FGFRs may offer advantages over reversible inhibitors, potentially leading to more durable responses in tumors driven by FGFR signaling.
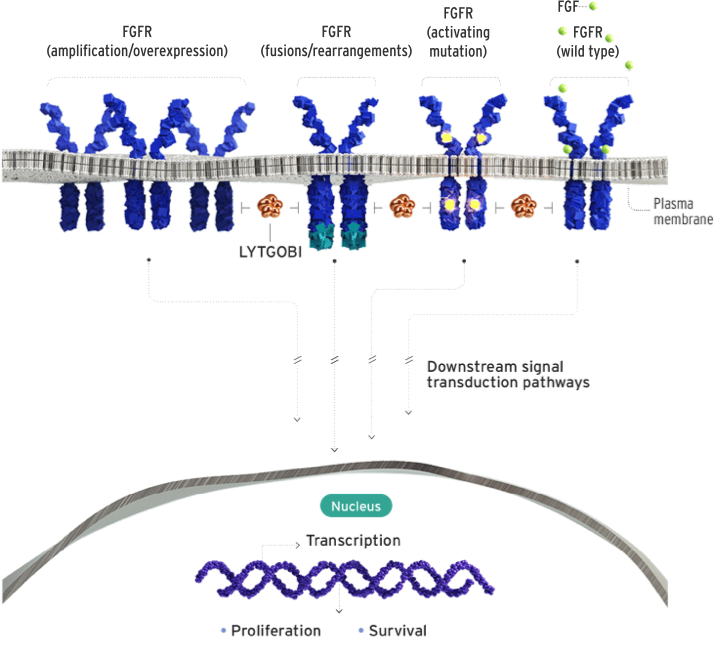
Photo from LYTGOBI official website
What Cancers Is Futibatinib Approved to Treat?
On September 30, 2022, the FDA granted accelerated approval to futibatinib (Lytgobi) by Taiho Oncology for adults with previously treated, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) that harbors FGFR2 gene fusions or rearrangements.
What research is behind the approval?
The FOENIX-CCA2 trial (TAS-120-101, NCT02052778) evaluated futibatinib in patients with previously treated, unresectable or metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) with FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements. This open-label, multinational phase 2 study enrolled 103 patients who received futibatinib 20 mg once daily. The overall response rate was 42%, with a median duration of response of 9.7 months. Median progression-free survival was 9.0 months, and median overall survival reached 21.7 months. Responses were consistent across subgroups, including older adults and patients with TP53 mutations.
Common grade 3 adverse events included hyperphosphatemia (30%), elevated AST (7%), stomatitis (6%), and fatigue (6%). Only 2% discontinued treatment due to side effects, and no treatment-related deaths occurred. Quality of life was maintained during treatment.
These results, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2023, support futibatinib as a targeted therapy option in FGFR2-altered cholangiocarcinoma.

Futibatinib Combinations and Treatment Outcomes
A phase 1b study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology in 2024 assessed futibatinib plus pembrolizumab, with or without chemotherapy, in advanced or metastatic esophageal carcinoma patients. In the first-line cohort (chemotherapy- and ICI-naïve), the overall response rate (ORR) was 68.4% with a disease control rate (DCR) of 89.5% and a median duration of response (mDOR) of 5.6 months. Notably, one patient’s tumor shrank enough to become resectable.
Among previously treated patients, the ICI-naïve group had an ORR of 42.9%, DCR of 71.4%, and mDOR of 16.0 months, while the ICI-refractory group showed an ORR of 6.1%, DCR of 51.0%, and mDOR of 4.7 months. The most common treatment-related adverse events included hyperphosphatemia (up to 91.7%), neutrophil count decrease, stomatitis, diarrhea, and nail disorders. The combination was generally well tolerated, with one dose-limiting toxicity of grade 3 stomatitis reported. These findings demonstrate encouraging antitumor activity and manageable safety for futibatinib plus pembrolizumab, with or without chemotherapy, in esophageal cancer.
Futibatinib side effects and its management
Futibatinib, like many targeted cancer therapies, can cause side effects that vary in severity. Patients should be aware of common and less common reactions to monitor their health and report any symptoms promptly to their healthcare provider. Managing side effects effectively helps maintain treatment and improves quality of life.
Common Side Effects
The most frequent side effects of futibatinib include hyperphosphatemia (high phosphate levels in the blood), which can cause muscle cramps and joint pain. Other common effects are fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, stomatitis (mouth sores), and elevated liver enzymes. Patients may also experience rash and decreased appetite.
Less Common Side Effects
Less common but important side effects include eye problems such as dry eyes or blurred vision, elevated blood sugar levels, electrolyte imbalances other than phosphate, and infections. Some patients may experience skin changes or inflammation.
Management of Side Effects
Hyperphosphatemia is managed through diet modifications, phosphate binders, and regular blood monitoring. Supportive care such as anti-nausea medications, hydration, and pain management can help with gastrointestinal symptoms and fatigue. Oral care and topical treatments may reduce stomatitis severity. Regular eye exams are recommended to monitor for vision changes. Any severe or persistent symptoms should be discussed promptly with the oncology team to adjust treatment or provide additional supportive care.
What is the Recommended Dosage of Futibatinib
Futibatinib is available as 4 mg tablets and is taken orally at 20 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Dose reductions are made if side effects occur: first to 16 mg daily, then to 12 mg. If 12 mg isn’t tolerated, treatment is stopped.
Hyperphosphatemia is managed with diet, phosphate binders, and dose reductions based on severity. If phosphate levels exceed 10 mg/dL or fail to normalize after two adjustments, treatment should be withheld or discontinued. Retinal issues like retinal pigment epithelial detachment are monitored with eye exams; dose may be continued or adjusted based on resolution. In cases of Grade 3 or 4 toxicity, the drug may be paused, reduced, or permanently discontinued depending on recovery.
No dose changes are needed in mild to moderate renal or hepatic impairment, but safety is unknown in severe cases. Treatment should only be initiated in patients with confirmed FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements.
How is Futibatinib administered?
Futibatinib should be taken by mouth once daily, with or without food, at the same time each day. Tablets must be swallowed whole—do not crush, chew, split, or dissolve them. If a dose is missed by more than 12 hours or vomited, skip it and take the next dose as scheduled. Store the tablets at room temperature, ideally between 20°C and 25°C.
What to Avoid During Futibatinib Treatment?
During futibatinib treatment, patients should avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice, as they can raise drug levels and increase side effects. Medications that strongly affect liver enzymes (especially CYP3A) or P-glycoprotein should not be used without medical advice, as they may alter the drug’s effectiveness or safety.
To manage phosphate levels, patients may need to limit phosphate-rich foods like dairy products and sodas. Pregnancy should be strictly avoided during treatment and for some time afterward, and breastfeeding is not advised. Tablets must be swallowed whole—do not crush, chew, or split them. If a dose is missed by more than 12 hours or vomited, skip it and take the next dose as scheduled.
Futibatinib Effectiveness Over Time
A phase 2 trial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology in 2025 studied neoadjuvant futibatinib combined with durvalumab in cisplatin-ineligible patients with FGFR-overexpressing muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Twenty-four patients received futibatinib 20 mg daily plus durvalumab every 28 days for three cycles before cystectomy. The primary goal was to improve pathological complete response (pCR) from 21% to 41%. The study includes safety lead-in and interim analyses to monitor dose-limiting toxicities and treatment efficacy. Secondary outcomes cover safety, pathologic downstaging, progression-free survival, and overall survival. Correlative studies will investigate immune and molecular markers predicting treatment response and resistance.
Learn more about Bladder Cancer: Symptoms ,Causes, Stages, Diagnosis and Treatment on OncoDaily.
Ongoing trials with Futibatinib
The FUTURE trial (NCT06722183) is a phase II study evaluating futibatinib combined with chemotherapy (mFOLFOX) and immunotherapy (tislelizumab) in patients with colorectal cancer. Patients receive treatment for up to 12 months or until progression or unacceptable side effects. The trial aims to assess response rate, survival outcomes, safety, and potential predictive biomarkers in a total of 33 participants.
Written by Mariam Khachatryan, MD
FAQ
What is FGFR2 in cancer?
FGFR2 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 2) is a protein involved in cell growth and division. In some cancers, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, abnormal changes (fusions or rearrangements) in the FGFR2 gene can drive tumor growth. Targeting FGFR2 with drugs like futibatinib helps slow or stop the progression of these cancers.
Is Lytgobi the same as chemotherapy?
No, futibatinib isn’t chemotherapy. It’s a targeted therapy that blocks specific cancer-causing proteins like FGFR2. Unlike chemotherapy, which affects all fast-growing cells, targeted therapies are designed to interfere with cancer growth more precisely.
How long can patients stay on Futibatinib treatment?
Patients typically take futibatinib daily until the cancer progresses or side effects become too severe. In clinical trials, some patients remained on treatment for months to over a year, depending on their individual response and tolerability.
Is Futibatinib safe during pregnancy?
No. Futibatinib can harm a developing fetus and should not be used during pregnancy. Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during treatment and for some time afterward.
What are common side effects of Futibatinib?
Common side effects include high phosphate levels, fatigue, mouth sores, nausea, and diarrhea. Most are manageable with supportive care.
How is Futibatinib taken?
One tablet (20 mg) is taken by mouth daily, with or without food, at the same time each day.