In April, the global oncology community comes together to raise awareness about Esophageal Cancer. OncoDaily joins this important initiative to promote understanding and support for those affected by this disease.
What is Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a malignant condition arising from the lining of the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. This cancer is particularly aggressive, often diagnosed in advanced stages due to the subtlety of early symptoms. Its global significance stems from its high mortality rate and its ranking among the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
The Two Most Common Forms of Esophageal Cancer:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This cancer forms in the thin, flat cells lining the esophagus and is typically found in the upper and middle parts of the esophagus, though it can occur anywhere along the tube
- Adenocarcinoma: This type begins in the glandular cells of the esophagus, which produce mucus and other fluids. Adenocarcinomas usually form in the lower part of the esophagus, near the stomach.
Despite its relatively low incidence compared to other cancers, it remains a major health concern due to its typically late diagnosis and aggressive progression. According to the American Cancer Society, in 2024, approximately 22,370 new cases of esophageal cancer were diagnosed in the United States, with about 16,130 deaths resulting from the disease.
How You Can Support Esophageal Cancer Awareness Month
Join the Movement! Whether it’s by wearing light purple/periwinkle, sharing information on social media, or encouraging loved ones to get screened, every action counts in the fight against esophageal cancer.
Why purple/periwinkle? Purple represents the courage and strength of those battling the disease. These colors were chosen to raise awareness and show support for those affected by this serious form of cancer.
Prevention is key in combating esophageal cancer. Regular medical check-ups and screenings are crucial for early detection, especially for individuals at higher risk. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use, can also help reduce the risk.
Read about Robert Kardashian’s fight against esophageal cancer.

Risk factors of Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer arises from a mix of medical conditions, lifestyle choices, genetic factors, and other elements. Understanding these risk factors is key for prevention and early detection.
Medical Conditions:
- GERD: Chronic acid reflux can damage the esophageal lining, increasing the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
- Barrett’s Esophagus: The replacement of normal esophageal lining with tissue similar to the intestines, often from prolonged GERD, raises the risk of adenocarcinoma.
Risk Factors:
- Smoking: Tobacco use damages the esophagus, raising the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Alcohol Consumption: Chronic alcohol intake, especially with smoking, increases cancer risk.
- Genetic Predispositions: A study found that 9% of those with Barrett’s esophagus who progressed to adenocarcinoma had cancer-predisposing gene mutations.
- Obesity: Visceral obesity is linked to a higher risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
- Diet: A diet low in fruits and vegetables may elevate risk, while certain dietary patterns offer protection.

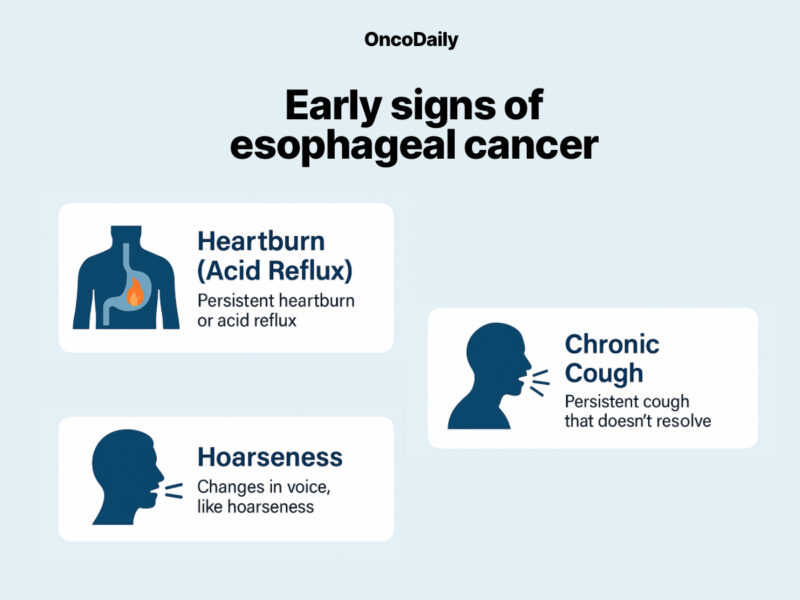
Early signs of Esophageal Cancer
Heartburn (Acid Reflux): Persistent heartburn or acid reflux can be an early sign, often mistaken for GERD, delaying diagnosis (Cancer Research UK).
Chronic Cough: A persistent cough that doesn’t resolve over time may indicate esophageal cancer, but is often misdiagnosed as a respiratory issue (National Cancer Institute).
Hoarseness: Changes in voice, like hoarseness, can occur if a tumor affects the recurrent laryngeal nerve, often overlooked as a benign cause (Moffitt Cancer Center).
Diagnoses and Treatment of Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is diagnosed through a combination of techniques, including endoscopy, biopsies, and imaging like CT and MRI scans. Early detection, especially in high-risk individuals, is vital for improving survival, as symptoms often appear at advanced stages.
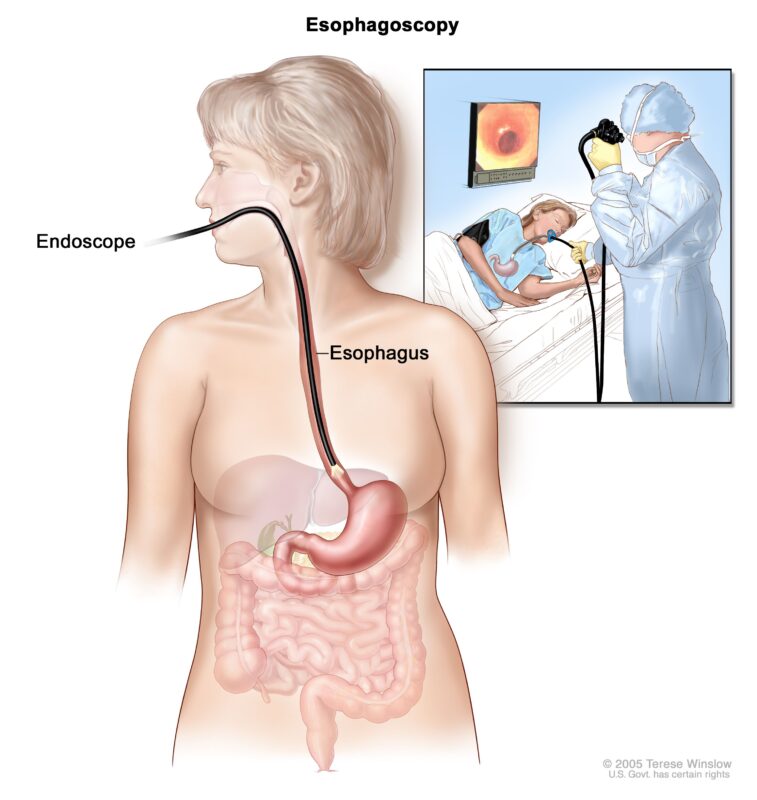
Endoscopy is the primary method, involving a flexible tube with a camera to visualize the esophagus and identify suspicious areas. During the procedure, biopsies are taken for histological analysis to confirm the cancer and determine its type (adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma).
Imaging studies, such as CT and MRI scans, help assess the extent of the cancer, lymph node involvement, and potential metastasis. CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional images, while MRI is effective for evaluating soft tissue.
For high-risk individuals, such as those with Barrett’s esophagus or a family history of esophageal cancer, genetic testing, and early screening are increasingly used to detect mutations and guide surveillance.
Non-invasive methods like the Cytosponge, a sponge-on-a-string test, offer an alternative for early detection by collecting cells from the esophagus for analysis.
Esophagoscopy/www.cancer.gov
Esophageal cancer treatment combines surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and emerging therapies like targeted treatments and immunotherapy. Early-stage cancer is treated with esophagectomy and chemotherapy, while advanced cases require chemotherapy and radiation.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIE) has favorable survival outcomes, though recovery is challenging with risks like pneumonia and digestive issues. Chemoradiotherapy improves survival in locally advanced cancer, and for unresectable ESCC, it provides tumor control with 12-18 months of survival.
Immunotherapy, such as PD-1 inhibitors, enhances outcomes when added to chemoradiotherapy, especially for patients with residual disease.
Claudin18.2 (CLDN18.2) is a promising target in gastric, GEJ, and esophageal cancers. Zolbetuximab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CLDN18.2, has improved survival in CLDN18.2-positive gastric and GEJ cancers. Ongoing studies are exploring therapies like antibody-drug conjugates and CAR-T for esophageal cancers.
For HER2-positive esophageal adenocarcinoma, trastuzumab plus chemotherapy improves survival, with strategies combining HER2-targeted therapies and checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab under investigation.
Raising awareness
It’s essential to highlight the importance of early detection, continued research, and innovative treatment options. Advances in surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy offer new hope for patients battling this aggressive cancer. Raising awareness, supporting research, and encouraging regular screenings can make a significant difference in improving outcomes and saving lives. Let’s continue to support those affected by esophageal cancer and work toward a future with better prevention, treatment, and care.
For more read OncoDaily’s special article titled “Esophageal Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, Stages, Diagnosis, and Treatment.”



