Perioperative Modified FOLFIRINOX Improves Survival in Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: Results from a Phase 2 Trial
Authors: Michael Cecchini, MD; Ronald R. Salem, MD; Marie Robert, MD; Suzanne Czerniak, MD, PhD; Ondrej Blaha, PhD; Daniel Zelterman, PhD; Moein Rajaei, PhD; Jeffrey P. Townsend, PhD; Guoping Cai, MD, MS; Sumedha Chowdhury, BS; Deanne Yugawa, BS; Robert Tseng, BS; Carlos Mejia Arbelaez, MD; Jingjing Jiao, MD; Kenneth Shroyer, MD, PhD; Jaykumar Thumar, MBBS; Jeremy Kortmansky, MD; Wajih Zaheer, MD; Neal Fischbach, MD; Justin Persico, MD; Stacey Stein, MD; Sajid A. Khan, MD; Charles Cha, MD; Kevin G. Billingsley, MD, MBA; John W. Kunstman, MD, MHS; Kimberly L. Johung, MD, MHS; Christina Wiess, BA; Mandar D. Muzumdar, MD, PhD; Erik Spickard, PhD; Vasily N. Aushev, PhD; George Laliotis, MD, MHA, MPH, MBA; Adham Jurdi, MD; Minetta C. Liu, MD; Luisa Escobar-Hoyos, MsC, PhD; Jill Lacy, MD
Published in JAMA Oncology on June 20, 2024
Introduction:
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the deadliest cancers, with poor survival rates even for patients with resectable disease. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of perioperative modified FOLFIRINOX (mFOLFIRINOX) in patients with resectable PDAC, hypothesizing that early systemic treatment could improve outcomes compared to the standard adjuvant approach.
Design and Methods:.
This single-arm, phase 2 trial enrolled 46 patients with resectable PDAC at Yale Smilow Cancer Hospital between 2014 and 2021. Patients received 6 cycles of neoadjuvant mFOLFIRINOX, followed by surgery and 6 cycles of adjuvant mFOLFIRINOX.
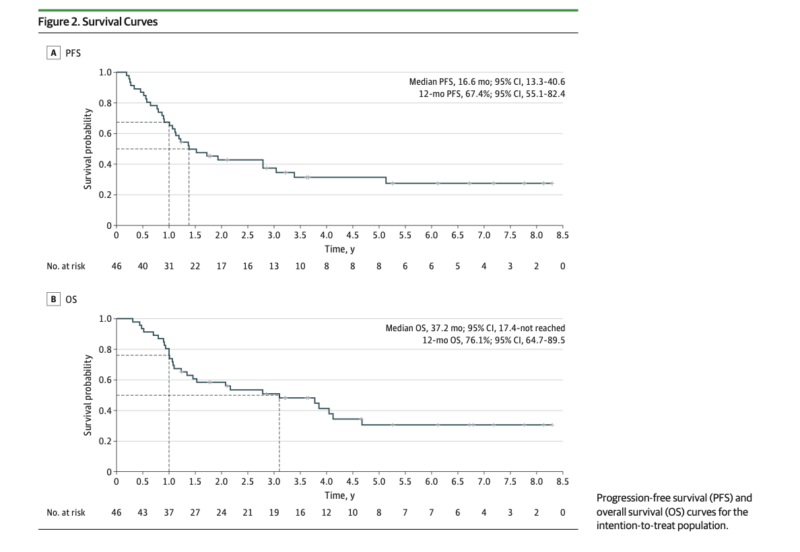
The primary endpoint was 12-month progression-free survival (PFS) rate. Secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS), median PFS, and safety. Exploratory analyses examined circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels and keratin 17 (K17) expression as potential biomarkers.
Key Results:
- The study met its primary endpoint with a 12-month PFS rate of 67% (90% CI, 56.9-100).
- Median PFS was 16.6 months (95% CI, 13.3-40.6), and median OS was 37.2 months (95% CI, 17.5-not reached).
- The 2-year OS rate was 59% (95% CI, 45.8-74.7).
- Of 37 patients who completed all 6 preoperative cycles, median OS was 46.2 months (95% CI, 24.9-not reached).
- R0 resection rate was 93% (25/27 patients).
- Postoperative ctDNA detection was associated with significantly worse PFS (HR 34.0, P=0.006) and OS (HR 11.7, P=0.02).
- High K17 expression showed a trend towards decreased survival, though not statistically significant.
What We Learned:
This study demonstrated that perioperative mFOLFIRINOX is feasible and potentially effective for patients with resectable PDAC. The observed survival outcomes were promising compared to historical controls, particularly for patients who completed the full treatment course. The high R0 resection rate suggests that neoadjuvant treatment may improve surgical outcomes.
The exploratory biomarker analyses provided valuable insights. Postoperative ctDNA detection emerged as a strong prognostic indicator, potentially identifying patients at high risk of recurrence. While not statistically significant, K17 expression showed a trend as a potential biomarker for aggressive disease and may warrant further investigation.
Key Highlights:
- Perioperative mFOLFIRINOX demonstrated feasibility and promising efficacy in resectable PDAC.
- The study met its primary endpoint with a 12-month PFS rate of 67%.
- Median OS of 37.2 months is encouraging compared to historical data.
- High R0 resection rate (93%) suggests potential benefits of neoadjuvant treatment.
- Postoperative ctDNA detection strongly correlated with worse outcomes.
- K17 expression showed potential as a prognostic biomarker, though further validation is needed.
Key Takeaway Messages:
- Perioperative mFOLFIRINOX warrants further investigation in larger, randomized trials for resectable PDAC.
- Early initiation of systemic therapy may improve outcomes in PDAC patients.
- ctDNA detection could be a valuable tool for identifying high-risk patients post-surgery.
- Molecular biomarkers like K17 may help stratify patients and guide treatment decisions in the future.
- The challenges in completing per-protocol therapy highlight the need for careful consideration of endpoints in neoadjuvant PDAC trials.
- Randomized trials are necessary to definitively compare perioperative and adjuvant approaches in resectable PDAC.
This study provides important insights into the potential benefits of perioperative mFOLFIRINOX for resectable PDAC. The promising survival outcomes and high R0 resection rates support further investigation of this approach.
Additionally, the exploratory biomarker analyses open new avenues for personalized treatment strategies in PDAC. While these results are encouraging, larger randomized trials are needed to confirm the superiority of perioperative mFOLFIRINOX over the current standard of care.
Summary by Amalya Sargsyan, MD
Perioperative Modified FOLFIRINOX for Resectable Pancreatic Cancer A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial


