
Pemigatinib (Pemazyre): Uses in Cancer, Side effects, Dosage, Expectation and more
Pemigatinib is a type of targeted cancer treatment that works by blocking abnormal FGFR (fibroblast growth factor receptor) signals that help cancer cells grow. It is designed specifically for patients whose tumors have certain FGFR2 gene alterations, which are common in some types of bile duct cancer. By targeting these changes, pemigatinib can help slow down or stop cancer progression.
This treatment is also being studied in other cancers with FGFR mutations. By interfering with these signals, pemigatinib may help slow or stop cancer growth in patients whose tumors depend on FGFR activity. This article explores how pemigatinib is used, its side effects, recommended dosage, and what to expect during treatment.
Which company produced Pemigatinib?
Pemigatinib, marketed as Pemazyre®, is produced by Incyte Corporation, a U.S.-based biopharmaceutical company known for developing targeted cancer therapies. To expand global access to pemigatinib, Incyte has partnered with several international companies. Knight Therapeutics handles distribution in Latin America, while GENESIS Pharma manages commercialization across Southeast Europe.
In Australia, New Zealand, and Singapore, Specialised Therapeutics Asia distributes the drug. Innovent Biologics holds exclusive rights for development and marketing in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. These partnerships help make pemigatinib available to more patients worldwide who may benefit from this targeted treatment.
How Does Pemigatinib work?
Pemigatinib is a targeted cancer therapy known as a fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor. It works by blocking abnormal FGFR proteins, especially FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3, that are involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. In certain cancers, such as cholangiocarcinoma and myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms, these FGFRs may be altered (through fusions, mutations, or rearrangements), causing uncontrolled cell growth. Pemigatinib binds to these receptors and blocks their activity, helping slow down or stop tumor growth.
By targeting these specific genetic alterations, Pemazyre offers a more personalized treatment option, especially for patients whose tumors test positive for FGFR alterations.
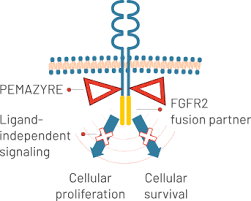
Photo form the official PEMAZYRE® website
What Cancers Is Pemigatinib Approved to Treat?
Pemigatinib has shown promising results in treating certain cancers driven by FGFR gene alterations. In April 2020, the U.S. FDA granted accelerated approval for Pemazyre to treat adults with previously treated, unresectable locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma that harbors FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements.
In August 2022, the FDA also approved pemigatinib for adults with relapsed or refractory myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms (MLNs) with FGFR1 rearrangement—an aggressive and rare form of blood cancer. These approvals position Pemazyre as a valuable targeted therapy for select patients with FGFR-driven cholangiocarcinoma and blood cancers, offering new hope where limited treatments exist.
What research is behind the approval?
The approval of Pemazyre for previously treated, unresectable locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements was based on the FIGHT-202 trial, whose results were published in The Lancet Oncology in 2020. This multicenter, open-label phase 2 study enrolled 146 patients, including 107 with FGFR2 gene alterations. Patients received 13.5 mg of pemigatinib orally once daily for 14 days followed by 7 days off in 21-day cycles.
In the FGFR2 fusion or rearrangement group, the objective response rate was 36%, with three complete responses. The median duration of response was 9.1 months, and most responders maintained their benefit for six months or longer. No responses were seen in patients without FGFR2 alterations.
Common adverse effects included hyperphosphatemia, alopecia, diarrhea, nail and eye toxicities, fatigue, and dry skin, with serious events reported in 45% of patients. Ocular toxicity and hyperphosphatemia were notable risks. Nearly half of the patients died during the study, mainly due to disease progression, with no treatment-related deaths reported.
Pemigatinib received accelerated approval with orphan drug, priority review, and breakthrough therapy designations, with continued approval dependent on confirmatory trials showing clinical benefit.
30109-1/asset/e26011c7-60e1-4227-8076-aef6152d6553/main.assets/gr4.jpg)
PEMAZYRE® was studied in the FIGHT-203 trial, a multicenter, open-label study including 28 patients with relapsed or refractory myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms (MLNs) featuring FGFR1 rearrangement. These patients had either relapsed after allogeneic stem cell transplant or disease-modifying therapy, or were not eligible for these treatments. Pemigatinib was given daily until disease progression, unacceptable side effects, or until patients could receive a transplant.
Most patients were around 65 years old, with good performance status and a diverse racial background. The trial showed promising results: among 18 patients with chronic-phase disease, 78% achieved complete response (CR), with a median time to response of about 3.5 months. Responses were also seen in patients with blast phase and extramedullary disease. Overall, the complete cytogenetic response rate was 79%.
Common side effects included elevated phosphate levels, nail changes, hair loss, mouth sores, diarrhea, dry eyes, fatigue, rash, abdominal pain, anemia, and vision disturbances. The recommended dose is 13.5 mg orally once daily continuously.
More detailed information and full trial results can be found on the official PEMAZYRE® website.

Learn more about Cholangiocarcinoma: Latest Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and 2025 Advanced Treatment Options for Bile Duct Cancer on OncoDaily.
Pemigatinib side effects and its management
Pemazyre is a targeted cancer therapy approved for treating certain cancers with FGFR gene alterations. Like many cancer treatments, pemigatinib can cause side effects that vary in severity and require proper management to ensure the best possible outcome for patients. Understanding these side effects and how to manage them is essential for patients and healthcare providers.
Most Common Side Effects
The most frequently reported side effects in patients taking pemigatinib include hyperphosphatemia (elevated phosphate levels in the blood), nail toxicity such as brittle or discolored nails, alopecia (hair loss), stomatitis (inflammation and soreness of the mouth), diarrhea, dry eyes, fatigue, and skin rash. Patients may also experience abdominal pain, anemia, constipation, dry mouth, and epistaxis (nosebleeds). Vision-related symptoms such as serous retinal detachment, blurred vision, and dizziness have also been reported. These side effects are typically manageable but should be monitored closely as they can impact quality of life and treatment adherence.
Less Common Side Effects
Less common but clinically significant side effects include Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities such as decreased phosphate levels, lymphocytes, leukocytes, platelets, and neutrophils, as well as increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), which may indicate liver irritation. Peripheral edema, extremity pain, decreased appetite, dry skin, dyspepsia, back pain, and nausea are additional side effects that occur less frequently but still warrant attention. These adverse effects may require dose adjustments or temporary treatment interruptions to ensure patient safety.
Management Side Effects
Effective management of pemigatinib side effects involves close monitoring and supportive care tailored to each symptom. Hyperphosphatemia, the most common side effect, can be managed by dietary phosphate restriction and the use of phosphate binders when necessary. Regular eye exams are important to detect retinal changes early; patients experiencing vision changes should report them immediately to their healthcare provider to prevent serious complications.
Mild to moderate symptoms like fatigue, diarrhea, and stomatitis can often be treated with symptomatic therapies such as hydration, topical oral rinses, and nutritional support. Nail toxicity and alopecia, though distressing, are generally reversible after treatment ends. For more severe hematologic abnormalities, blood counts should be monitored regularly, and dose modifications or treatment pauses may be required based on severity.
Overall, timely recognition and intervention are crucial to maintaining treatment effectiveness while minimizing discomfort and risk. Patients should communicate any new or worsening symptoms promptly to their oncology team.
What is the Recommended Dosage of Pemigatinib?
Pemigatinib (PEMAZYRE®) is an oral targeted therapy available in 4.5 mg, 9 mg, and 13.5 mg tablets. It is approved for patients with unresectable or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma harboring FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements after prior treatment, and for relapsed or refractory myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms (MLNs) with FGFR1 rearrangement.
For cholangiocarcinoma, pemigatinib is taken as 13.5 mg daily for 14 days followed by 7 days off, in 21-day cycles, continuing until disease progression or unacceptable side effects. For MLNs, the dose is 13.5 mg daily continuously.
Dose reductions are recommended to manage side effects. In cholangiocarcinoma, doses may be lowered to 9 mg and then 4.5 mg daily (for 14 days each cycle). For MLNs, similar dose reductions apply, with discontinuation if the lowest dose isn’t tolerated. Side effects like retinal issues or high phosphate levels may require pausing treatment and adjusting the dose based on severity.
How is Pemigatinib administered?
Pemigatinib is taken orally once daily, with or without food, ideally at the same time each day. Tablets should be swallowed whole and must not be crushed, chewed, split, or dissolved. If a dose is missed by four hours or more, or if vomiting occurs after taking the medication, patients should wait and take the next dose at the scheduled time. Store pemigatinib tablets at room temperature between 20-25ºC, with allowable variations from 15-30ºC.
What to Avoid During Pemigatinib Treatment?
During pemigatinib treatment, it’s important to follow certain precautions to ensure safety and effectiveness. According to Medscape, patients should avoid taking medications or supplements that can interact with pemigatinib, especially strong CYP3A inhibitors or inducers, as these can affect how the drug is processed in the body. Grapefruit and grapefruit juice should also be avoided since they may increase pemigatinib levels and risk of side effects. Additionally, patients should steer clear of activities requiring sharp focus or alertness if they experience side effects like dizziness or blurred vision. Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is essential to manage any potential complications during therapy.
Pemigatinib’s effectiveness over time
Pemigatinib has shown promising effectiveness over time, particularly in patients with cancers driven by FGFR alterations. Clinical trials have demonstrated durable responses, with many patients experiencing long-lasting disease control. For example, in cholangiocarcinoma with FGFR2 fusions, pemigatinib has led to sustained tumor shrinkage and prolonged progression-free survival in a significant portion of treated patients.
The durability of response varies by individual, but some patients maintain benefits for months or even years while on therapy. Continued treatment is generally recommended until disease progression or unacceptable side effects occur.
Ongoing trials with Pemigatinib
Several ongoing Phase II clinical trials are investigating pemigatinib, an FGFR inhibitor, for treating advanced cancers with FGFR genetic alterations. One trial (NCT06906562) is evaluating pemigatinib alone in adults with advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer that has FGFR alterations. The study aims to assess how effectively pemigatinib slows tumor growth and its safety profile. Patients take the drug orally for 14 days within a 21-day treatment cycle, while regular scans and blood tests monitor their response.
Another Phase II trial (NCT06728410) is exploring the combination of pemigatinib with durvalumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, in patients who have previously been treated for FGFR2 fusion–positive intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. In this study, pemigatinib is administered orally for two weeks followed by one week off, while durvalumab is given intravenously every three weeks. Treatment continues for up to 24 months or until the disease progresses.
Additionally, the PERELI trial (NCT06389799) is testing pemigatinib combined with retifanlimab, a PD-1 immunotherapy, in patients with advanced dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDLPS) who have progressed after first-line therapy. This study aims to determine whether this drug combination can slow tumor growth more effectively than either treatment alone.
Written by Mariam Khachatryan, MD
FAQ
What is Pemigatinib used to treat?
Pemigatinib is primarily approved for treating certain types of advanced bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) that have specific FGFR genetic alterations.
How does Pemazyre work against cancer?
Pemigatinib blocks abnormal FGFR proteins that promote cancer cell growth and tumor blood vessel formation, helping to slow or stop tumor progression.
Which cancers are commonly treated with Pemigatinib?
Pemazyre is FDA-approved for FGFR2 fusion-positive cholangiocarcinoma and is being researched in cancers such as pancreatic cancer, liposarcoma, and other tumors with FGFR gene alterations.
What are the most common side effects of Pemazyre?
Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, dry mouth, and changes in phosphate levels. Eye-related side effects may also occur and require monitoring.
How is Pemazyre administered?
Pemigatinib is taken orally as a tablet, usually in cycles of 14 days on treatment followed by 7 days off, repeated every 21 days.
Can Pemigatinib be combined with other cancer treatments?
Yes, ongoing clinical trials are evaluating pemigatinib in combination with immunotherapy drugs like durvalumab and retifanlimab for enhanced effects.
What should patients expect during Pemigatinib therapy?
Patients can expect routine monitoring of blood tests and imaging, possible side effects that can often be managed, and ongoing evaluation to adjust treatment as needed.
-
Challenging the Status Quo in Colorectal Cancer 2024
December 6-8, 2024
-
ESMO 2024 Congress
September 13-17, 2024
-
ASCO Annual Meeting
May 30 - June 4, 2024
-
Yvonne Award 2024
May 31, 2024
-
OncoThon 2024, Online
Feb. 15, 2024
-
Global Summit on War & Cancer 2023, Online
Dec. 14-16, 2023
