FDA Grants Accelerated Approval for Telisotuzumab Vedotin (EMRELIS™) in c-MET–Overexpressing Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
On May 14, 2025, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval for Telisotuzumab Vedotin, a c-Met-directed antibody-drug conjugate, for the treatment of c-Met overexpressing, EGFR wild-type (EGFR WT), advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in patients who have failed prior treatments. This approval was based on the positive results of the LUMINOSITY trial, a phase 2 study aimed at evaluating the efficacy of Teliso-V in patients with c-Met overexpression in advanced, non-squamous NSCLC.
Study Design of the LUMINOSITY Trial for Telisotuzumab Vedotin
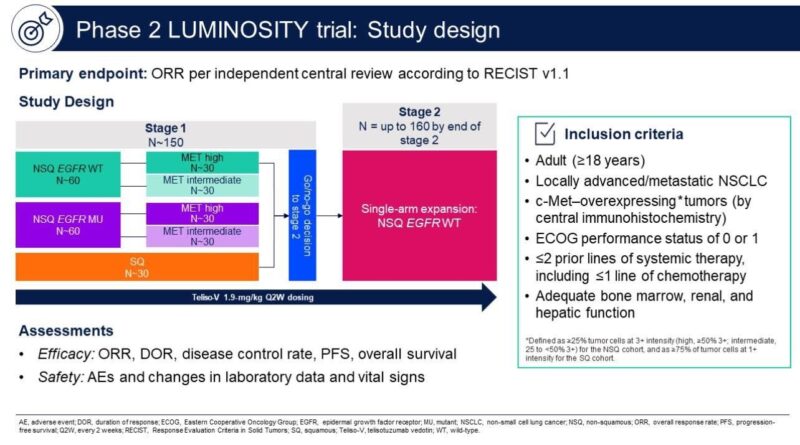
The LUMINOSITY trial (NCT03539536) was a multicenter, non-randomized phase 2 study designed to assess the efficacy of Telisotuzumab Vedotin in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC, who were EGFR wild-type and had c-Met overexpression. The trial enrolled patients who had received up to two prior lines of therapy, including chemotherapy (CTx) and immunotherapy (IO). A total of 172 patients were treated, and 161 patients were included in the efficacy analysis.
Primary Endpoint and Dosage of Telisotuzumab Vedotin
The primary endpoint of the study was the overall response rate (ORR), which was determined by independent central review using RECIST v1.1 criteria. Telisotuzumab Vedotin was administered intravenously at a dose of 1.9 mg/kg every two weeks. Patients were categorized based on c-Met overexpression using the Ventana MET (SP44) assay, which classified tumors as high (≥50%) or intermediate (25% to <49%) based on the level of 3+ staining.
Efficacy Results from the LUMINOSITY Trial for Telisotuzumab Vedotin
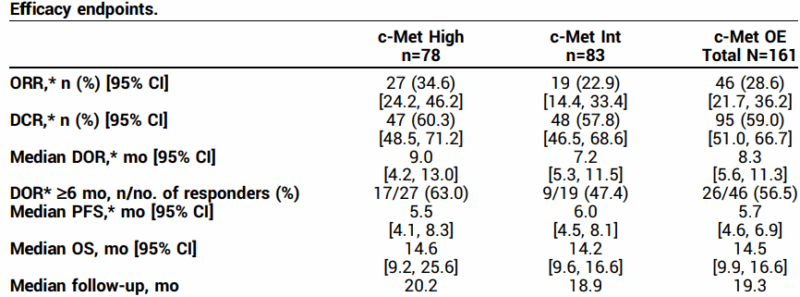
The LUMINOSITY trial found that Telisotuzumab Vedotin produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 34.6% in patients with c-Met high overexpression, and 22.9% in those with c-Met intermediate overexpression. The overall ORR across all patients was 28.6%. Patients in the c-Met high group had a median duration of response (DOR) of 9.0 months, while those in the c-Met intermediate group had a median DOR of 7.2 months. The overall median DOR was 8.3 months.
The study also measured progression-free survival (PFS), with the c-Met high group experiencing a median PFS of 5.5 months, compared to 6.0 months for the c-Met intermediate group. The median overall survival (OS) for all patients was 14.5 months, with 14.6 months for the c-Met high group and 14.2 months for the c-Met intermediate group.
Safety Profile and Adverse Events of Telisotuzumab Vedotin
The safety profile of Telisotuzumab Vedotin was consistent with prior findings, with peripheral sensory neuropathy (30%), peripheral edema (16%), and fatigue (14%) being the most common treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs). Serious side effects included grade 5 TRAEs, with one case of interstitial lung disease and another involving respiratory failure.
In conclusion, the results from the LUMINOSITY trial underscore the potential of Telisotuzumab Vedotin as a promising treatment for patients with c-Met overexpressing, EGFR wild-type advanced NSCLC, especially those with high c-Met expression. The therapy demonstrated durable responses and a manageable safety profile, making it a significant addition to the treatment options available for patients who have exhausted prior therapies. The FDA’s accelerated approval of Telisotuzumab Vedotin offers new hope to patients with this challenging form of advanced NSCLC, and ongoing clinical studies will further clarify its role in the treatment landscape.
Here you can read about trials results.
What is Telisotuzumab Vedotin?
Telisotuzumab Vedotin is an investigational ADC composed of:
- A monoclonal antibody that binds to the c-Met receptor
- A cleavable linker
- The cytotoxic agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), a microtubule inhibitor
After binding to c-Met on the tumor surface, Telisotuzumab Vedotin is internalized, and MMAE is released intracellularly to induce cell death.
How Telisotuzumab Vedotin Works?
Telisotuzumab Vedotin leverages a targeted approach by binding to c-Met on tumor cells. After internalization, the cytotoxic payload MMAE disrupts microtubules, leading to apoptosis. This targeted delivery enhances tumor specificity and limits damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
What is Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) makes up about 85% of lung cancer cases and includes adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. Compared to small cell lung cancer, NSCLC grows slower and has a better prognosis if detected early.
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type, especially in non-smokers, often with mutations like EGFR, ALK, and KRAS that make targeted therapies effective. Squamous cell carcinoma, linked to smoking, usually appears in the central lungs, and large cell carcinoma is aggressive and poorly differentiated, often diagnosed at advanced stages.
NSCLC can also have rare subtypes, such as adenosquamous carcinoma, sarcomatoid carcinoma, and pleomorphic carcinoma, which have poor prognoses. Molecular profiling has revolutionized treatment by identifying driver mutations. Key mutations include EGFR, ALK, ROS1, BRAF, KRAS, MET, and RET, with targeted therapies improving patient outcomes, especially in younger, non-smoking patients. High PD-L1 expression or tumor mutational burden (TMB) may indicate benefits from immunotherapy.
Screening, especially with low-dose CT for high-risk groups like long-term smokers, helps in early detection, significantly improving survival rates. Risk factors include smoking, secondhand smoke, exposure to carcinogens like asbestos and radon, and genetic susceptibility.
Lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, reducing environmental carcinogen exposure, and maintaining a healthy diet and weight can lower risk. Early screening further supports better outcomes. The prognosis for NSCLC varies with stage, molecular subtype, and treatment response, with early-stage cases having a higher survival rate, especially with targeted and immunotherapies.
In this context, identifying actionable targets such as c-Met overexpression becomes essential. c-Met dysregulation has been associated with resistance to existing therapies, aggressive tumor biology, and poor outcomes. As such, therapies targeting this pathway hold significant clinical value.
Learn more about Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Latest 2025 Advances in Targeted and Immunotherapy on OncoDaily.
What Are People Saying About Telisotuzumab Vedotin on Social Media?
Dr. Rahul Gosain, MD, MBA, a medical oncologist and co-host of the Oncology Brothers podcast, shared key results from the Phase II LUMINOSITY trial on his LinkedIn page. He highlighted Telisotuzumab Vedotin’s FDA approval for previously treated, c-Met overexpressing metastatic NSCLC, with promising response rates and median overall survival.
Dr. Aakash Desai, MD, MPH, FASCO, a medical oncologist specializing in thoracic oncology and early-phase drug development, shared his insights on the FDA approval of Telisotuzumab Vedotin (Emrelis) in a recent LinkedIn post. He wrote:
“Another ADC lands in #lung cancer! On May 14, 2025, the FDA granted accelerated approval to telisotuzumab vedotin (Emrelis) for adults with previously treated, advanced non-squamous NSCLC harboring high c-Met protein overexpression (≥50% 3+ IHC). Approved alongside the VENTANA MET (SP44) RxDx Assay as the companion diagnostic. Based on LUMINOSITY trial (N=84):
• ORR: 35%
• Median DOR: 7.2 months
Notable AEs: peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, ↓ appetite, edema
Dose: 1.9 mg/kg IV q2wThis adds another option for EGFR-wt, c-Met high NSCLC—especially where targeted options remain limited. The field of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) continues to grow rapidly. Read more: https://lnkd.in/eDa9agCi”
His commentary reflects growing enthusiasm among oncologists for this new ADCeor, especially in areas with limited targeted therapies.
Dr. Steven V Liu, Director of Thoracic Oncology & Developmental Therapeutics in Georgetown University, shared thoughts on latest FDA accelerated approval on X.
Results from phase II LUMINOSITY trial of telisotuzumab vedotin (#MET ADC) in NSCLC now @JCO_ASCO. In cMET high, RR 34.6%, DOR 9m, OS 14.6m. In cMET intermediate, RR 22.9%, DOR 7.2m, OS 14.2m. AEs include neuropathy (30% with 7% G3+), edema, fatigue.
Treatment Landscape and Future Outlook
Currently, treatment for advanced EGFR wild-type NSCLC after progression on chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Telisotuzumab Vedotin offers a targeted approach with durable responses, especially in the c-Met high population, and may redefine the therapeutic strategy for this group.
Further confirmatory trials are warranted to evaluate its role in earlier lines of therapy and potentially support regulatory approval.
-
Challenging the Status Quo in Colorectal Cancer 2024
December 6-8, 2024
-
ESMO 2024 Congress
September 13-17, 2024
-
ASCO Annual Meeting
May 30 - June 4, 2024
-
Yvonne Award 2024
May 31, 2024
-
OncoThon 2024, Online
Feb. 15, 2024
-
Global Summit on War & Cancer 2023, Online
Dec. 14-16, 2023
