
FDA Authorizes ImmunityBio to Provide Recombinant BCG as Alternative to TICE BCG Shortage for Bladder Cancer
On February 19, ImmunityBio, Inc. announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has authorized an expanded access program (EAP) to introduce recombinant BCG (rBCG) as an alternative to TICE BCG, addressing a critical supply shortage impacting bladder cancer patients in the U.S.
BCG remains a standard-of-care therapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), but ongoing shortages of TICE® BCG have created significant barriers to treatment. A Sermo survey of 100 U.S. urologists found that 57% were unable to treat patients in the past year due to the lack of access.
The alternative rBCG was developed by the Serum Institute of India, the world’s largest vaccine manufacturer by volume. European clinical trials have demonstrated its strong immunogenicity, activating CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, and suggest an improved safety profile compared to earlier BCG formulations.
Dr. Patrick Soon-Shiong, Founder, Executive Chairman, and Global Chief Scientific and Medical Officer of ImmunityBio, emphasized the importance of securing a consistent supply of essential oncology therapeutics:
“With the increasing threat of supply shortages of essential medicines, the biopharmaceutical industry must innovate and secure new means of ensuring uninterrupted access to vital therapeutics. Our collaboration with the FDA and Serum Institute to ensure a reliable supply of this critical drug for bladder cancer patients underscores ImmunityBio’s commitment to addressing access issues that affect so many patients.”
This FDA authorization represents a significant step in ensuring continued access to BCG therapy, mitigating treatment disruptions for bladder cancer patients.
About BCG and rBCG
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) is a live attenuated vaccine derived from Mycobacterium bovis, primarily used to prevent tuberculosis (TB) and other mycobacterial infections. Developed by Calmette and Guerin in 1921, it remains one of the most widely used vaccines and is part of routine newborn immunization schedules. In addition to TB, BCG offers protection against conditions like leprosy and Buruli ulcer. It is also utilized in the treatment of superficial bladder cancer
BCG in Bladder Cancer Treatment
In bladder cancer, a single intravesical dose of BCG shows significant therapeutic benefits, particularly for non-invasive forms. It helps delay progression and prevent recurrence of the malignancy.
Recombinant BCG (rBCG) has undergone two genetic modifications to enhance its immunogenicity and safety compared to earlier strains. Clinical trials in Europe, including Phase 1/2 studies, have shown that rBCG is well-tolerated with a safety profile similar to placebo, and it reduces adverse events seen with traditional BCG formulations.
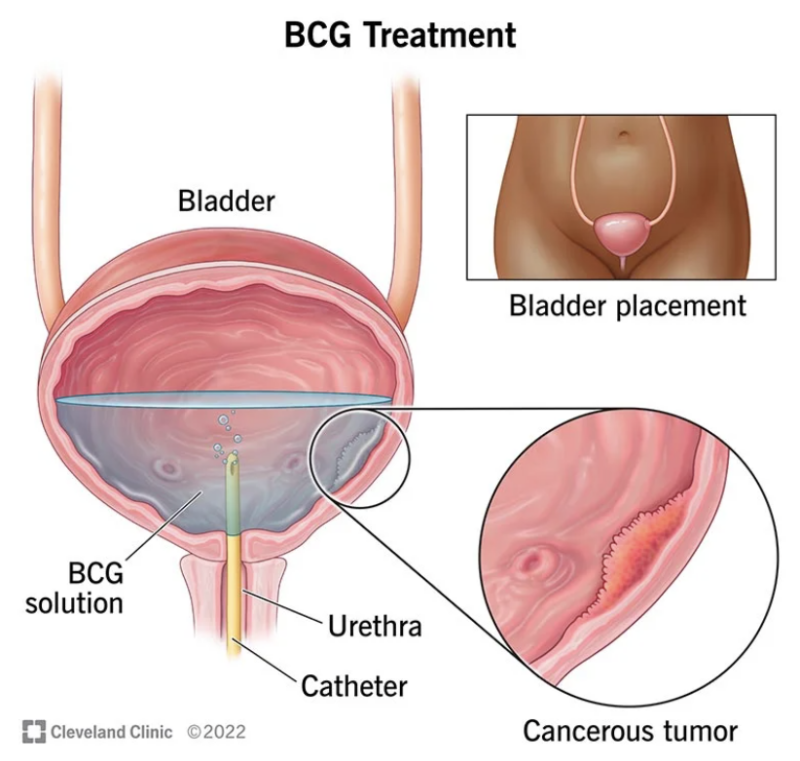
Source: Cleveland Clinic
rBCG Clinical Trials and Applications
Clinical data for rBCG as a TB vaccine are available from four trials, including studies on healthy adults, newborns, and BCG-naïve infants exposed to HIV. Trials have also examined its effects on TB recurrence and respiratory diseases during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
While BCG is widely used globally, its production is more complex than many other vaccines due to its biological nature. The Serum Institute of India is the largest BCG manufacturer, while Merck & Co. produces TICE BCG in the U.S.
You can also read Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer by OncoDaily.
-
Challenging the Status Quo in Colorectal Cancer 2024
December 6-8, 2024
-
ESMO 2024 Congress
September 13-17, 2024
-
ASCO Annual Meeting
May 30 - June 4, 2024
-
Yvonne Award 2024
May 31, 2024
-
OncoThon 2024, Online
Feb. 15, 2024
-
Global Summit on War & Cancer 2023, Online
Dec. 14-16, 2023
