Agenus Inc. (Nasdaq: AGEN) is a U.S.-based biotechnology company specializing in immuno-oncology, focused on discovering and developing checkpoint inhibitors, cell therapies, and immune modulators to treat cancer. Known for its investigational drugs balstilimab (BOT) and balstilimab (BAL), Agenus is targeting some of the most treatment-resistant tumors in oncology today—including microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer (MSS CRC), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), sarcomas, and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Zydus Lifesciences Ltd., headquartered in India, is a multinational pharmaceutical company with over 27,000 employees and operations across 55 countries. As one of India’s largest life sciences companies, Zydus has deep experience in generics, biologics, and vaccine development, and is expanding its global presence in contract development and manufacturing (CDMO) for biologics.
Agenus Secures Strategic Capital and U.S. Manufacturing in Zydus Partnership
Agenus Inc. (Nasdaq: AGEN), today announced the closing of its previously disclosed strategic collaboration with Zydus Lifesciences Ltd. The agreement is intended to accelerate global development and potential commercialization of Agenus’ botensilimab and balstilimab (BOT+BAL) immunotherapy combination program.
The collaboration provides Agenus with strategic capital and committed, long-term biologics manufacturing capacity in the United States to support BOT+BAL clinical development, authorized early access pathways, and commercial supply preparation.
“Closing this collaboration with Zydus strengthens our balance sheet and, critically, secures dedicated U.S. manufacturing capacity at a pivotal moment for Agenus,”
said Dr. Garo Armen, PhD, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Agenus.
As part of the collaboration, Agenus has granted Zydus exclusive rights to develop and commercialize botensilimab and balstilimab in India and Sri Lanka, with Agenus eligible to receive royalties on net sales in those territories.
The collaboration, first announced on June 3, 2025, included the following key financial terms: an upfront consideration of $75 million in cash to Agenus for the transfer of biologics manufacturing facilities in Emeryville and Berkeley, California; a $16 million equity investment through Zydus’ purchase of approximately 2.1 million shares of Agenus common stock at $7.50 per share; contingent milestone payments of up to $50 million payable to Agenus, triggered by BOT+BAL production orders; and an exclusive license granting Zydus rights in India and Sri Lanka, with Agenus eligible to receive a 5% royalty on net sales in those territories.
In 2025, the BOT+BAL combination demonstrated a two-year overall survival rate of 42% and a now-mature median overall survival of 21 months in an expanded cohort of 123 patients with third-line or later microsatellite-stable (MSS) metastatic colorectal cancer without active liver metastases. Building on these results, Agenus, in collaboration with the Canadian Cancer Trials Group (CCTG), has initiated the global BATTMAN Phase 3 trial, with sites activated and prepared to enroll patients.
Following the closing, the Emeryville and Berkeley, California biologics manufacturing facilities will be transferred to Zydus and housed under a newly formed subsidiary named Zylidac Bio LLC. Agenus has secured committed manufacturing capacity at these U.S. sites to support BOT+BAL supply needs for clinical trials, global access programs, and future commercialization. “With this deal, Zylidac Bio LLC will now provide biologics manufacturing sites offering CDMO services to biopharmaceutical companies globally,” said Dr. Sharvil P. Patel, Managing Director of Zydus Lifesciences Limited.
The transaction further positions Agenus to execute its near- and long-term strategy as interest in BOT+BAL continues to grow globally.
“This supports the evolving landscape of biological product manufacturing in the U.S., which prioritizes secure, domestic, and high-quality supply chains for advanced therapies,”
Dr. Patel added.
What drugs are Botensilimab (BOT) and Balstilimab (BAL)?
BOT is a novel Fc-enhanced CTLA-4 inhibitor engineered to engage both innate and adaptive immunity, particularly in so-called “cold” tumors that are typically less responsive to standard immunotherapies. It supports T-cell priming and activation, reduces intratumoral regulatory T cells, activates myeloid cells, and may promote durable immune memory.
BAL, Agenus’s PD-1 inhibitor, blocks PD-1 interactions with its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, thereby strengthening T-cell activity and immune-mediated tumor killing. Together, the BOT/BAL combination has shown strong and durable anti-tumor activity in multiple hard-to-treat cancers, including colorectal cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
What Does the Latest Data Reveal?
In early 2025, Agenus presented notable results from multiple studies at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting. Among them, the NEOASIS trial reported meaningful pathologic responses in both microsatellite-stable (MSS) and microsatellite-instability–high (MSI-H) solid tumors, including historically treatment-resistant triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
- NEOASIS trial: Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates reached 70% in MSI-H tumors and 20% in MSS tumors, suggesting BOT/BAL activity beyond patient groups that typically respond to immunotherapy.
- HCC cohort: In hepatocellular carcinoma patients whose disease progressed after prior immunotherapies, BOT/BAL achieved a 17% overall response rate and a 72% disease control rate, with a median overall survival of 12.3 months.
- Metastatic CRC data: In a randomized Phase 2 study in MSS colorectal cancer previously resistant to standard therapies, BOT/BAL produced a 19% overall response rate, compared with 0% for standard-of-care treatment.
NEOASIS Study (Neoadjuvant Pan-Cancer Setting)
Led by Myriam Chalabi, MD PhD, this investigator-initiated study assessed BOT/BAL efficacy in early-stage solid tumors, both MMR-proficient (pMMR) and MMR-deficient (dMMR).
Safety: At both 25mg and 50mg botensilimab doses, no significant delays or serious dose-limiting toxicities occurred. Mild and manageable immune-related adverse events were observed.
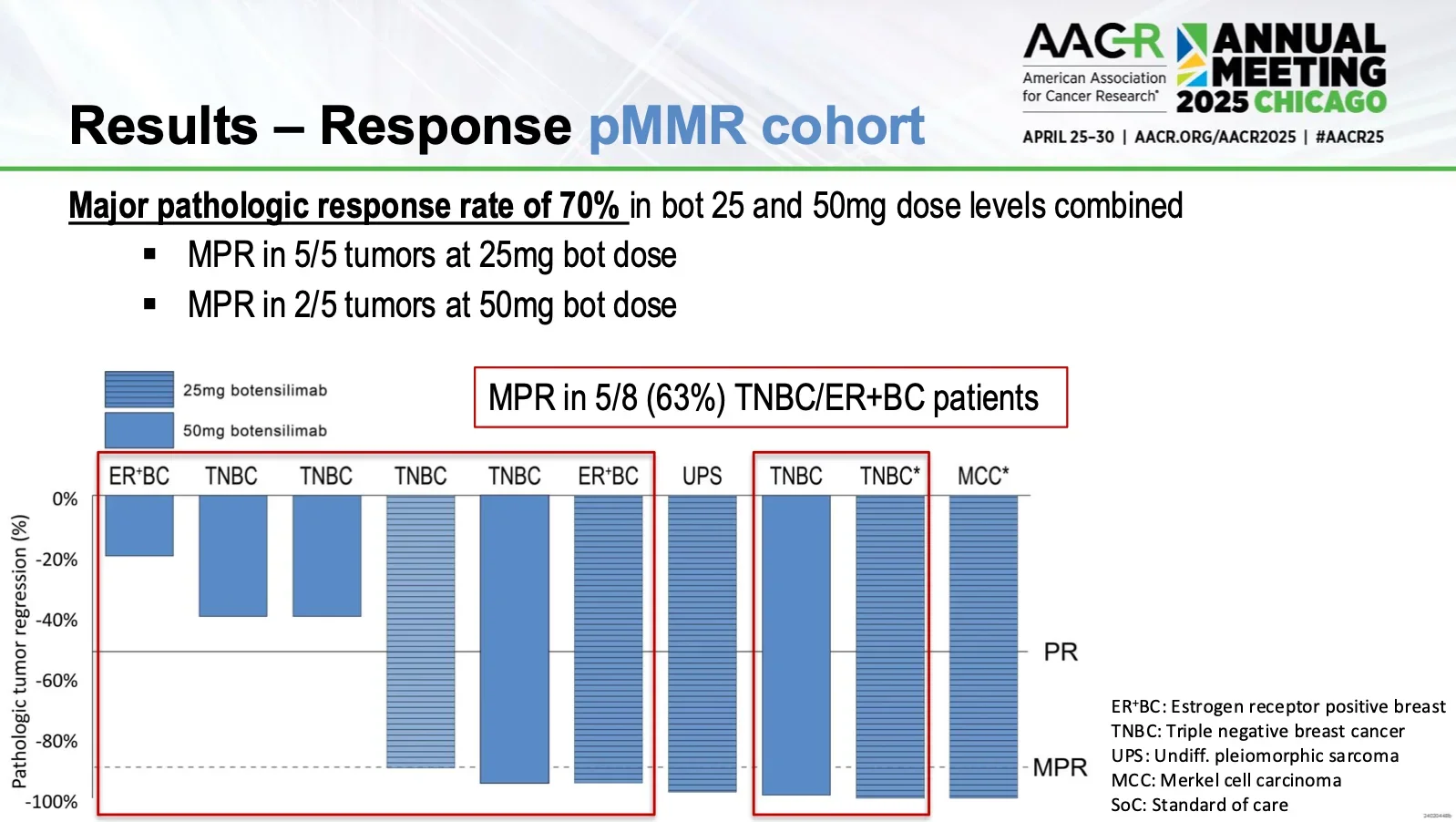
Efficacy (pMMR cohort)
- Major pathological response (MPR): 70%
- Triple-negative breast cancer subset showed 63% MPR.
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clear macroscopic regression with complete pathological response.
Efficacy (dMMR cohort)
- 80% MPR, with 70% achieving pathological complete response (pCR)
- 100% pCR at the 50mg BOT dose.
Chalabi concluded that BOT/BAL effectively induces responses in traditionally immune-cold tumors, potentially broadening immunotherapy application.
Phase 1 BOT/BAL in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Dr. Anthony El-Khoueiry reported promising results for patients with advanced HCC previously unresponsive to first-line immunotherapies:
- Overall Response Rate (ORR): 17%
- Disease Control Rate (DCR): 72%
- Median Progression-Free Survival (PFS): 4.4 months
- Median Overall Survival (OS): 12.3 months
Safety profiles were consistent and manageable, encouraging further exploration in larger studies.
Phase 1 BOT/BAL in Relapsed/Refractory MSS CRC
This study evaluated BOT/BAL in heavily pretreated patients with relapsed or refractory MSS metastatic CRC. Results showed that patients without active liver metastases (a major driver of immunotherapy resistance) derived notable benefit, helping shape the design of Agenus’s ongoing Phase 2 trials.
- Overall response rate (ORR): 17%
- Disease control rate (DCR): 61%
- 12-month overall survival (OS): 69% in patients with non-liver metastases (n=77) and 30% in those with active liver metastases (n=24)
- Non-liver metastases subgroup: ORR: 22% and DCR: 73%
These findings helped refine the MSS CRC population most likely to benefit from BOT/BAL, setting the stage for the randomized Phase 2 trial that followed.
Overall, these data suggest BOT/BAL may extend meaningful clinical benefit to patients with historically immunotherapy-resistant cancers. Ongoing and planned late-stage studies will be essential to confirm durability, define the patients most likely to benefit, and clarify how best to integrate this regimen into standard practice.