“I’ve got breast cancer. But it’s early. That’s the key word — early.”
Jessie J, the British singer, publicly revealed her diagnosis of early-stage breast cancer on June 4 2025. She shared the news in an Instagram video, emphasizing the word “early” to convey a positive outlook despite the diagnosis. Jessie J explained that she had been undergoing private tests for about nine weeks and planned to have surgery shortly after performing at the Capital’s Summertime Ball music festival in London on June 15, 2025.

Photo: Depositphotos
What Is Jessie J’s Breast Cancer Prognosis?
Jessie J’s prognosis for her early-stage breast cancer is generally favorable. She emphasized the word “early” in her diagnosis, which is significant because early-stage breast cancer typically has a high survival rate. According to the National Breast Cancer Foundation, the five-year survival rate for patients diagnosed at an early stage is very good, often exceeding 90% with appropriate treatment. Jessie J is scheduled to undergo surgery soon, which is a standard and effective treatment for early breast cancer
Why Did Jessie J Decide to Share Her Diagnosis Publicly?
She expressed mixed emotions about going public, noting concerns that the media might sensationalize her diagnosis. However, she felt compelled to share the news with her fans and loved ones, acknowledging that openness has helped her receive support in the past.
“I’m so grateful for the love and support I’ve already received. It means the world to me.”
Overall, Jessie J’s early-stage breast cancer diagnosis highlights the importance of early detection and treatment. She remains optimistic about her prognosis while preparing for surgery and recovery.
How Is Jessie J Coping with the Diagnosis?
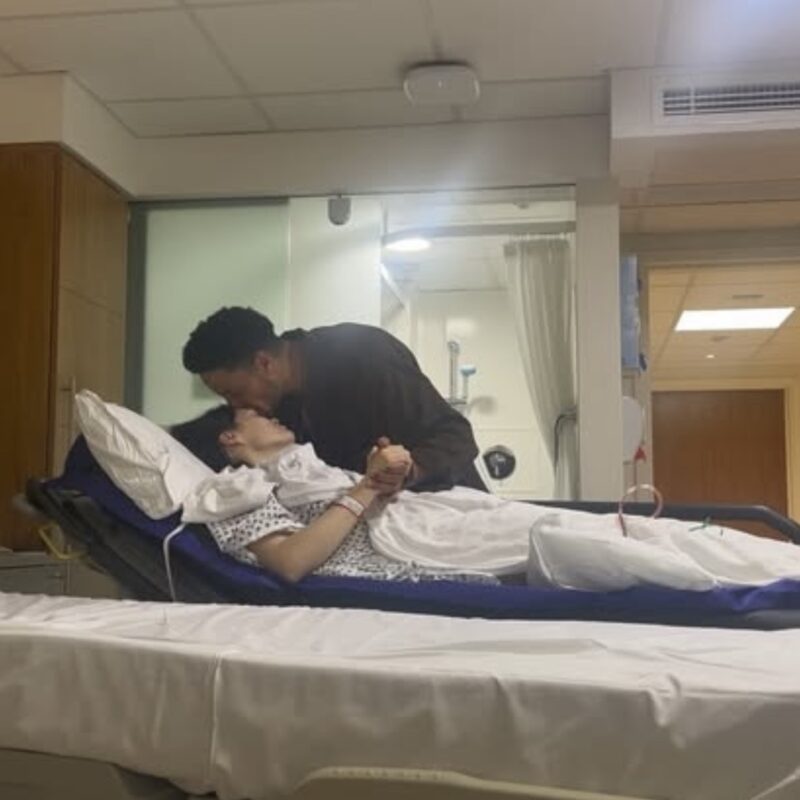
Despite the diagnosis, she maintained a hopeful and humorous tone, joking about her upcoming surgery as “a very dramatic way to get a boob job” and promising to return with “massive tits and more music.” She also reassured fans that she would keep her nipples, addressing concerns about the surgery.
How Does This Diagnosis Affect Her Music Career?
Jessie J’s diagnosis came just before the release of her single “No Secrets,” adding an ironic twist to her music career timeline. She plans to take a break from public appearances to focus on treatment but intends to return to music afterward.
What Has Been the Public Response?
Her announcement received an outpouring of support from fans and fellow artists, including messages from Rita Ora and Katy Perry. Jessie J has previously been open about her health, including a diagnosis of Ménière’s disease affecting her hearing.
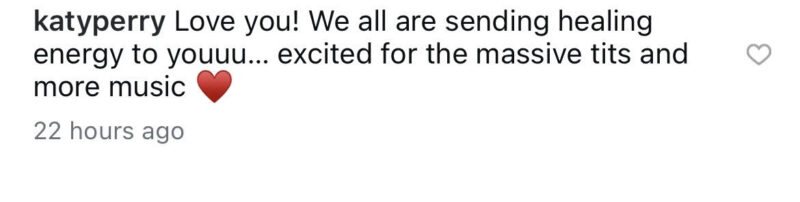
Jessie J, 37, underwent surgery to remove breast cancer on June 23, 2025. She shared an honest Instagram post describing the “lows and highs” of the last 48 hours surrounding her surgery and recovery. Prior to surgery, Jessie performed at Wembley Stadium on June 16, 2025, calling it her “last show before I go to beat breast cancer.” She vowed to fight the disease and expressed gratitude for her life, career, and family. She expressed deep gratitude to her doctor, surgeon, nurses, family, and friends for their support. Her boyfriend, Chanan Safir Colman, and their 2-year-old son Sky were by her side during the hospital stay.
You Can Also Read Olivia Munn and Breast Cancer: How She Went Against, How She Survived, and More by Oncodaily

What Causes Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental risk factors.
Genetic and Hormonal Factors
Genetic mutations, particularly in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, significantly increase breast cancer risk. Women with a BRCA1 mutation have a 55-65% chance of developing breast cancer by age 70, while those with a BRCA2 mutation have a 45% risk (National Cancer Institute, 2021). Family history is also important; having a first-degree relative with breast cancer can double a woman’s risk (American Cancer Society, 2022).Hormones, especially estrogen, play a critical role in breast cancer development. Prolonged estrogen exposure, such as starting menstruation before age 12 or entering menopause after age 55, can elevate risk (World Health Organization, 2019). Additionally, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may increase breast cancer risk by 26% (JAMA Oncology, 2019).
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Diets high in saturated fats and low in fruits and vegetables increase the risk of breast cancer, while obesity, particularly after menopause, is also linked to a higher risk (American Cancer Society, 2022). Regular alcohol consumption further raises this risk, with women who drink more than one alcoholic beverage daily having a 20-25% higher chance of developing breast cancer (National Cancer Institute, 2021).
Additionally, a lack of physical activity contributes to obesity and hormonal imbalances, further increasing risk, while regular exercise provides protective benefits. Environmental pollutants, such as pesticides, have also been associated with a heightened breast cancer risk (Environmental Health Perspectives, 2019). Radiation exposure, especially to the chest area during youth, is another well-established risk factor (World Health Organization, 2019). Together, these factors highlight the importance of lifestyle choices and environmental awareness in breast cancer prevention.
How Can Breast Cancer Be Prevented?
Regular mammograms and other screening methods are vital for the early detection of breast cancer, significantly improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.In addition to regular screenings, specific lifestyle changes can significantly lower the risk of developing breast cancer.
Regular Screenings and Early Detection
BRCA mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes significantly raise the risk of breast and ovarian cancers, with women facing up to an 85% lifetime risk for breast cancer and 40-60% for ovarian cancer. Preventive options include increased screening, risk-reducing surgeries like prophylactic mastectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy, medications, lifestyle changes, and genetic counseling.
Many individuals opt for surgeries to lower their cancer risk, and the National Cancer Institute outlines the benefits of these options. Additionally, some may choose chemoprevention with medications such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors, which can reduce breast cancer risk, as noted by the Mayo Clinic.

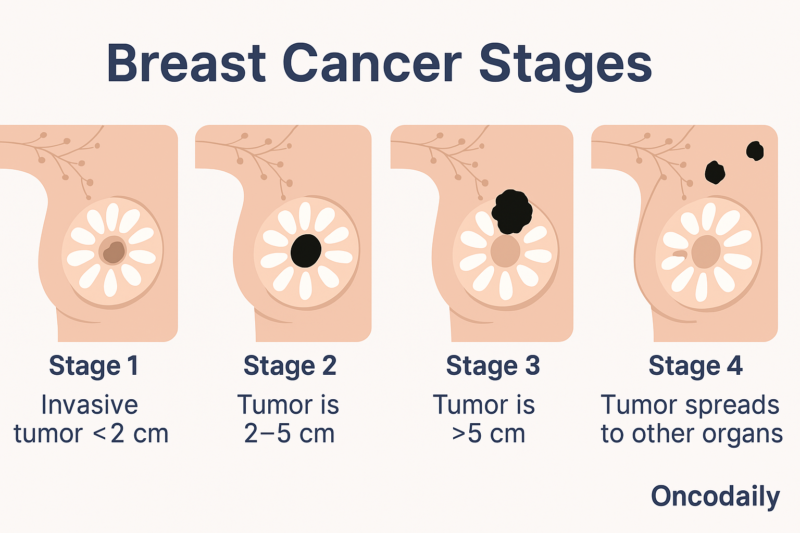
Women aged 40 and older should have annual mammograms, as early detection through mammography can identify breast cancer before symptoms develop, leading to less invasive treatments. The American Cancer Society reports a 5-year survival rate of 99% for localized breast cancer, compared to just 29% if diagnosed at a later stage (American Cancer Society, 2021). Regular mammography can reduce breast cancer mortality by approximately 15-30% among women aged 40-74 (U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, 2016). Prioritizing screenings allows women to catch breast cancer early, resulting in more effective treatments and better outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes
A healthy diet is vital for reducing breast cancer risk, focusing on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Research indicates that women with a diet high in fruits and vegetables have a 20% lower risk of breast cancer (American Institute for Cancer Research, 2018). Regular exercise is also important; at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly can reduce breast cancer risk by about 25% (National Cancer Institute, 2020).
Limiting alcohol intake is crucial, with recommendations of no more than one drink per day. Consuming two to three drinks daily increases the risk of breast cancer by 20-30% (American Cancer Society, 2021). Maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as obesity raises the risk by 30-60% in postmenopausal women (World Health Organization, 2020). Lastly, avoiding tobacco is key; women who smoke are 25% more likely to develop breast cancer compared to non-smokers (Cancer Research UK, 2019).
Global Key Statistics of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide and a major public health concern. In 2022, approximately 2.3 million new cases of female breast cancer were diagnosed globally, making it the leading cancer type in women and the second most common overall (International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2025). On average, about 1 in 20 women worldwide will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lifetime (BreastCancer.org, 2025). Unfortunately, breast cancer also causes significant mortality, with around 670,000 deaths reported globally in 2022. This translates to about 1 in 70 women dying from breast cancer in their lifetime (Nature Medicine, 2025).
Incidence and mortality rates vary widely by region. The highest incidence rates are observed in Australia/New Zealand, Northern America, and Northern Europe, with about 100 new cases per 100,000 women. In contrast, South-Central Asia and parts of Africa report much lower incidence rates, around 27 per 100,000. Mortality rates are highest in Melanesia, Polynesia, and Western Africa, and lowest in Eastern Asia, Central America, and Northern America. These disparities reflect differences in healthcare access, early detection, and treatment quality. In countries with very high Human Development Index (HDI), about 17% of women diagnosed with breast cancer die from the disease, while in low-HDI countries, mortality can exceed 56% (The Lancet Oncology, 2025).
In the United States, breast cancer remains a leading cancer diagnosis and cause of cancer death among women. For 2025, it is estimated that approximately 316,950 new invasive breast cancer cases and 59,080 cases of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) will be diagnosed in women. Breast cancer deaths are projected to reach about 42,170 among women and 510 among men. The incidence of invasive breast cancer has been increasing by about 1% per year overall since the mid-2000s, with a higher increase in women under 50 years old. Advances in early detection and treatment have improved survival rates, yet breast cancer continues to pose a significant health burden (American Cancer Society, 2025).
Looking ahead, breast cancer cases are expected to rise substantially. By 2050, global new cases are projected to increase by 38% to approximately 3.2 million annually, and deaths may increase by 68% to around 1.1 million per year. This rise will disproportionately affect low- and middle-income countries, underscoring the urgent need for improved access to screening, diagnosis, and effective treatment worldwide (Nature Medicine, 2025).
In summary, breast cancer remains a critical health challenge globally, with significant variation in incidence and mortality across regions. Early detection and equitable access to quality care are essential to reduce the disease burden and improve outcomes for women everywhere (International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2025; American Cancer Society, 2025).
You Can Also Read Immunotherapy for Breast Cancer: Types, Success Rate, Side Effects & More by Oncodaily

Written by Aharon Tsaturyan MD


