Elisabetta Bonzano, Radiation Oncologist at IRCCS San Matteo Polyclinic Foundation, shared an article by Dario Trapani, et al. on X:
“Optimizing Postneoadjuvant Treatment of Residual Breast Cancer With Adjuvant Bevacizumab Alone, With Metronomic or Standard-Dose Chemotherapy: A Combined Analysis of DFCI 05-055 and DFCI 09-134/TBCRC 012/ABCDE Clinical Trial.
Among patients with stage I-III breast cancer with residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the 36-month recurrence-free survival (RFS) was 58.0% with adjuvant bevacizumab monotherapy, 62.3% with bevacizumab plus metronomic cyclophosphamide and methotrexate, 72.7% with bevacizumab and flat-dosed capecitabine, and 75.0% with bevacizumab and body surface area (BSA)-dosed capecitabine.
Grade 3-4 adverse events were most frequent among patients who received bevacizumab with flat-dosed capecitabine (72.5%) or bevacizumab with BSA-dosed capecitabine (71.4%).
Treatment with capecitabine was independently associated with improved RFS in patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) (HR: 0.47; 95% CI, 0.23-0.96).
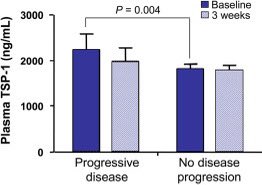
Optimizing Postneoadjuvant Treatment of Residual Breast Cancer With Adjuvant Bevacizumab Alone, With Metronomic or Standard-Dose Chemotherapy: A Combined Analysis of DFCI 05-055 and DFCI 09-134/TBCRC 012/ABCDE Clinical Trials.
Authors: Dario Trapani, et al.