POTOMAC Trial evaluated durvalumab plus BCG in BCG-naïve, high-risk non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), a disease with high recurrence and progression risk despite standard TURBT followed by intravesical BCG.
Preclinical and clinical evidence implicates PD-1/PD-L1–mediated immune suppression in BCG resistance. Durvalumab, a selective PD-L1–blocking antibody, demonstrated efficacy across urothelial cancer settings, and in POTOMAC, its addition to BCG significantly reduced recurrence or death risk by 32%, establishing a new benchmark for bladder-sparing immunotherapy in early-stage disease.
Study Design and Methods
POTOMAC (NCT03528694; EudraCT 2017-002979-26) was a randomized, open-label, global phase 3 study conducted at 116 sites across 12 countries. Eligible patients (≥18 years) had histologically confirmed, high-risk NMIBC confined to the mucosa or submucosa, had undergone complete TURBT within four months before randomization, and had no prior BCG exposure within three years. Participants were stratified by the presence of carcinoma in situ (CIS) and higher-risk papillary disease, then randomly assigned (1 : 1 : 1) to one of three arms:
- Durvalumab + BCG induction + BCG maintenance (I + M),
- Durvalumab + BCG induction only, or
- BCG induction + maintenance (control).
Durvalumab (1500 mg IV) was administered every four weeks for 13 cycles (1 year). BCG induction consisted of weekly intravesical instillations for six weeks, and maintenance included three weekly doses at months 3, 6, 12, 18, and 24. The primary endpoint was investigator-assessed disease-free survival (DFS) comparing durvalumab + BCG I + M versus BCG I + M in the intention-to-treat population.
Results
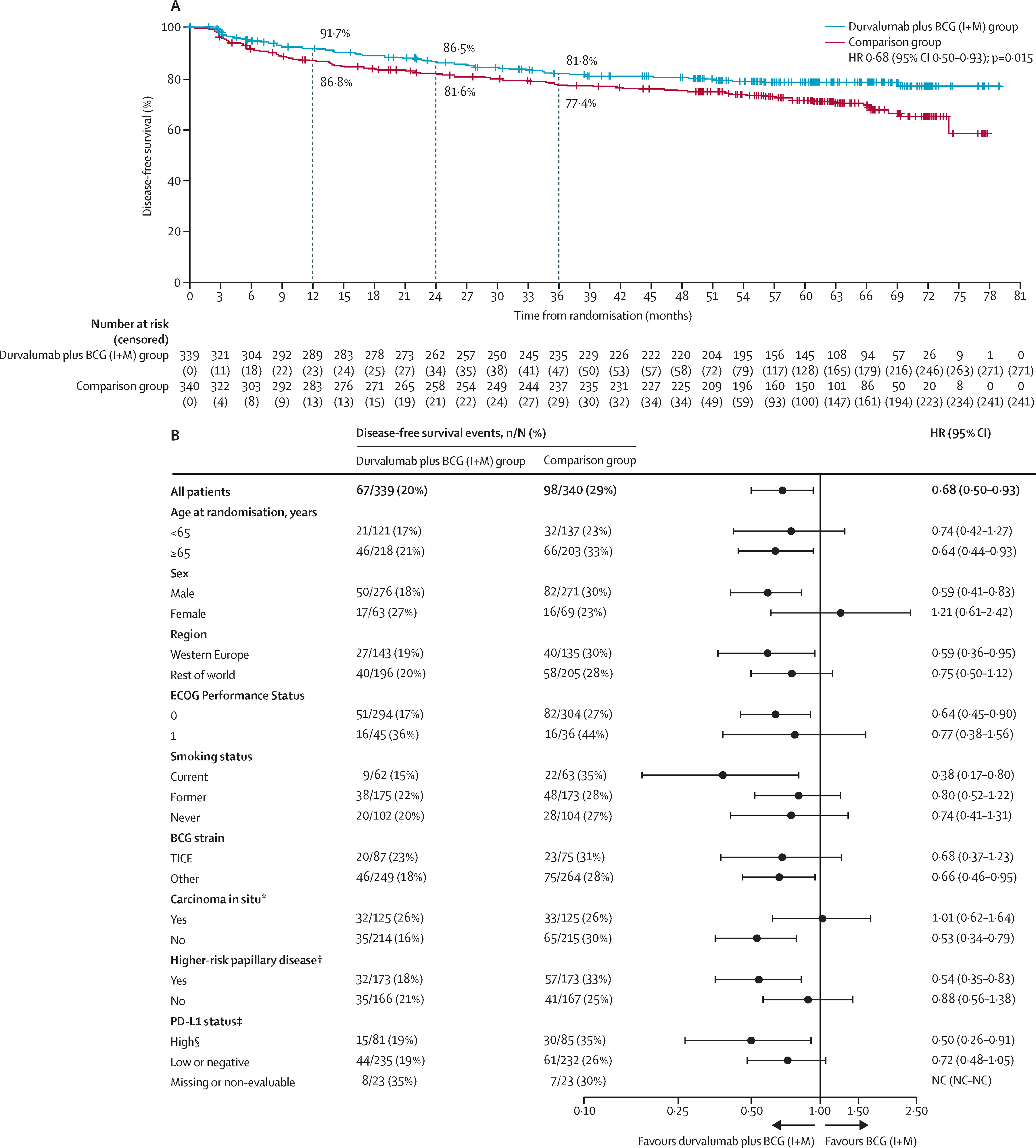
A total of 1 018 patients were randomized: 339 to durvalumab + BCG I + M, 339 to durvalumab + BCG induction only, and 340 to the comparison arm. Baseline characteristics were well balanced across groups (median age 68 years; 81 % male; 37 % CIS). At a median follow-up of 60.7 months, the addition of durvalumab to BCG induction and maintenance produced a 32 % reduction in the risk of recurrence or death (HR 0.68, 95 % CI 0.50–0.93; p = 0.015). The 24-month DFS rate was 86.5 % versus 81.6 % for the control group. Benefit was consistent across prespecified subgroups, including patients with papillary-only disease (HR 0.56, p = 0.0046).
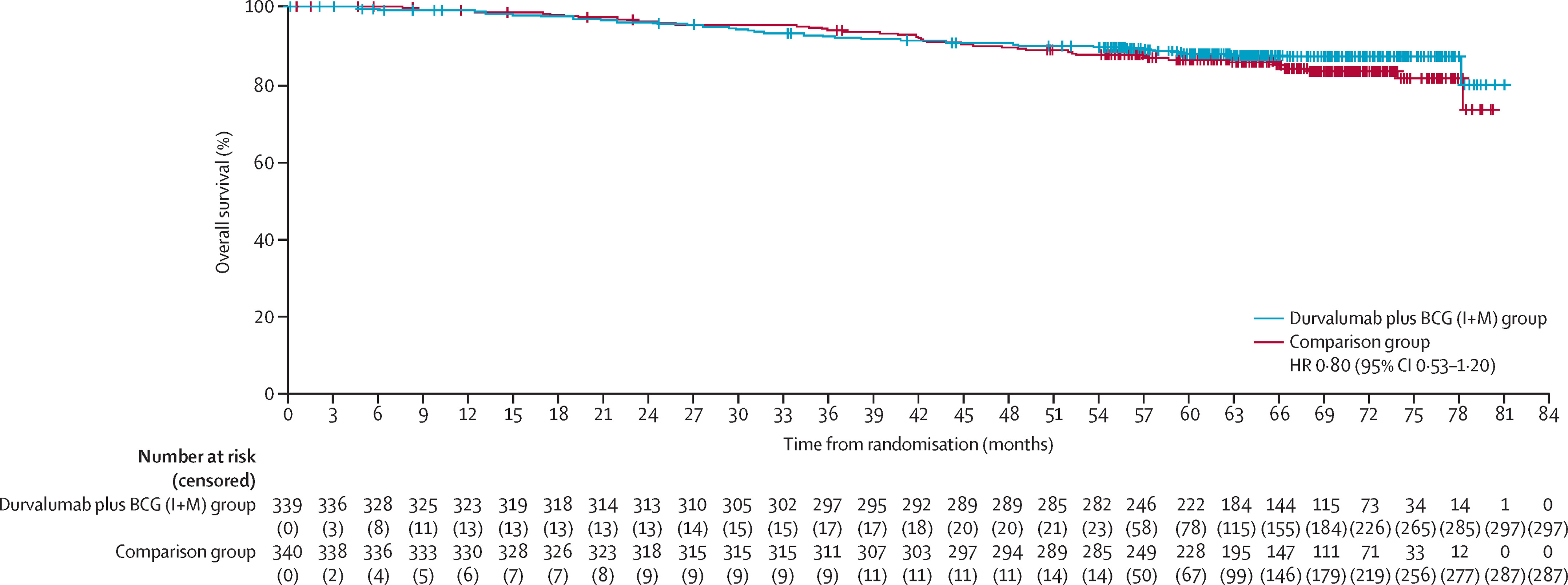
In contrast, the durvalumab + BCG induction-only arm did not show a statistically significant improvement versus BCG I + M (HR 1.14, p = 0.35), emphasizing the necessity of the maintenance phase. In the CIS subgroup, 6-month complete-response rates were 93 % for durvalumab + BCG I + M and 93 % for BCG I + M. Overall survival was immature but showed no detriment with durvalumab (HR 0.80, 95 % CI 0.53–1.20); median OS was not reached in any arm.
Safety
Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) occurred in 89 % of patients in the durvalumab + BCG I + M arm versus 72 % with BCG alone. Grade 3–4 TRAEs were reported in 21 %, 15 %, and 4 % of patients in the durvalumab + BCG I + M, durvalumab + BCG induction-only, and control arms, respectively. The most common TRAEs were dysuria, haematuria, pollakiuria, and cystitis. Immune-mediated AEs—most frequently hypothyroidism and rash—occurred in 27 % of durvalumab + BCG I + M patients, were mostly grade 1–2, and resolved in nearly half. No treatment-related deaths occurred, and quality-of-life scores (EORTC QLQ-C30) remained stable across treatment groups.
Conclusions
The final analysis of POTOMAC demonstrates that one year of durvalumab in combination with BCG induction and maintenance significantly improves disease-free survival in patients with BCG-naïve, high-risk NMIBC, reducing recurrence or death risk by nearly one-third compared with standard BCG therapy alone.
The combination exhibited a manageable safety profile, consistent with the known effects of each agent. These findings, together with results from the CREST trial evaluating subcutaneous sasanlimab + BCG, reinforce the therapeutic value of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade combined with BCG in early-stage bladder cancer and establish durvalumab + BCG induction and maintenance as a potential new standard for this population.
You Can Read All Article Here


