MANIFEST-2 trial is providing longer follow-up to date for a JAK inhibitor–naive myelofibrosis (MF) combination regimen, and 96-week data suggest that adding the BET inhibitor pelabresib to ruxolitinib leads to deeper and more durable disease control than ruxolitinib alone, with a comparable safety profile.
Why myelofibrosis still has a major unmet need
JAK inhibitor (JAKi) monotherapy, most commonly ruxolitinib, is the current standard of care for symptomatic MF. While it can shrink spleen size and improve symptoms, its ability to control disease long-term is limited, and many patients experience loss of response, persistent cytopenias, or progression to acute leukemia. There is a clear need for well-tolerated approaches that deepen spleen and symptom responses and potentially modify the underlying disease biology.
Pelabresib is an oral, small-molecule BET (bromodomain and extra-terminal domain) inhibitor designed to be used in combination with ruxolitinib, a JAK1/2 inhibitor. BET proteins regulate expression of genes involved in inflammation and MF progression; by targeting BET and JAK/STAT signaling together, pelabresib plus ruxolitinib aims to achieve deeper responses and disease modification than JAK inhibition alone.
MANIFEST-2 trial design
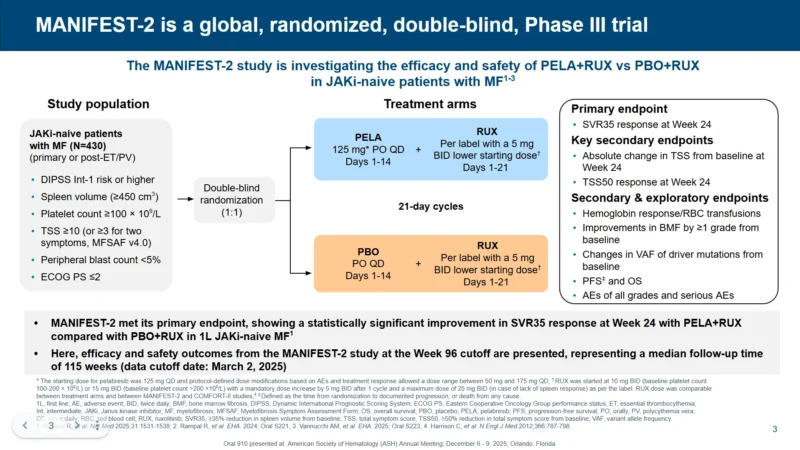
MANIFEST-2 is a global, randomized, double-blind phase 3 study evaluating pelabresib plus ruxolitinib (PELA+RUX) versus placebo plus ruxolitinib (PBO+RUX) in JAKi-naive patients with MF.
Source: AHS Annual Meeting , December 2025
The MANIFEST-2 study enrolled 430 patients with primary or post–ET/PV myelofibrosis who met key eligibility criteria reflecting clinically significant disease: DIPSS intermediate-1 risk or higher, spleen volume ≥450 cm³, platelet count ≥100 × 10⁹/L, and a total symptom score (TSS) of at least 10 (or ≥3 for two individual symptoms using MSAF v4.0). Patients also required peripheral blasts <5% and ECOG performance status ≤2, ensuring inclusion of individuals with symptomatic, measurable myelofibrosis appropriate for frontline systemic therapy.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to:
- PELA+RUX arm: pelabresib 125 mg orally once daily on days 1–14 of each 21-day cycle, plus ruxolitinib per label (with a 5-mg twice-daily lower starting dose option) on days 1–21
- Control arm: placebo once daily on days 1–14 plus ruxolitinib on days 1–21
Ruxolitinib dosing was individualized according to platelet count and label guidance.
Key endpoints
- Primary endpoint (EP): SVR35 response
Key secondary EPs:
- Absolute change in TSS from baseline
- Proportion of patients achieving TSS50
- Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS)
- Safety: All-grade and serious adverse events (AEs)
Initial 24-week data showed superiority of PELA+RUX versus PBO+RUX for spleen and symptom responses. The 96-week analysis presented at ASH 2025 focused on the durability of these benefits and longer-term safety.
96-week efficacy: deeper and more durable benefit
At week 96, PELA+RUX continued to demonstrate clinically meaningful improvements across key MF endpoints.Durable SVR35 responses-PELA+RUX maintained substantially higher rates of spleen volume response:
SVR35 at week 96:
- PELA+RUX: 91.5%
- PBO+RUX: 57.6%
Kaplan–Meier curves for duration of spleen response showed an early separation between arms that remained throughout the 96-week follow-up. In the intent-to-treat population:
Median duration of spleen response was not reached with PELA+RUX versus 138.3 weeks with PBO+RUX.
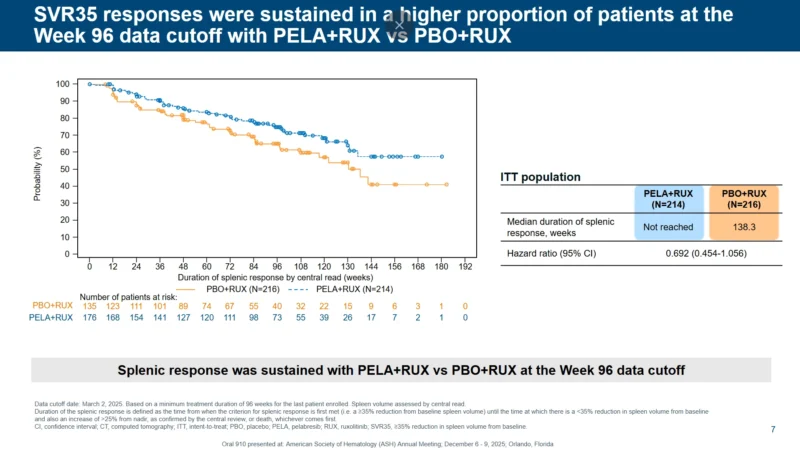
Hazard ratio for loss of spleen response was 0.692 (95% CI 0.454–1.056), favoring the combination.
Sustained symptom improvement
Symptom control was also better sustained with the combination.Mean change in TSS at week 96 (ITT population, least-squares mean):
- PELA+RUX: –15.07
- PBO+RUX: –12.48
- Difference: –2.59 (95% CI –5.23 to 0.05)
Waterfall plots showed a larger proportion of patients in the PELA+RUX arm achieving substantial reductions in symptom burden. Importantly, twice as many patients achieved both SVR35 and TSS50 with PELA+RUX compared with PBO+RUX (31.8% vs 15.7%), indicating combined spleen and symptom benefit in a higher fraction of patients.
These findings support the hypothesis that dual BET and JAK/STAT inhibition may impact underlying MF biology, beyond symptomatic and spleen responses alone.
Safety and leukemic transformation
Longer-term safety was generally consistent with earlier readouts and with the known profile of ruxolitinib.Overall AE rates and serious AEs were comparable between PELA+RUX and PBO+RUX and no new safety signals emerged with extended treatment.
An early analysis had raised concern about a numerical imbalance in leukemic transformation (progression to acute myeloid leukemia) between arms. With additional follow-up, this imbalance diminished that the updated leukemic transformation rate in the PELA+RUX arm is now within the range typically observed in MF populations.This supports a favorable benefit–risk profile for the combination over nearly two years of therapy.
What MANIFEST-2 means for the MF treatment landscape
For patients with intermediate- or high-risk MF starting systemic therapy, JAK inhibitors have long been the backbone of care, yet many patients do not achieve deep or durable responses, and disease progression remains common.
Taken together, the MANIFEST-2 96-week results reinforce pelabresib plus ruxolitinib as a promising potential new standard for JAK inhibitor–naive patients with MF and support ongoing development of BET/JAK combination strategies aimed at altering the natural history of this challenging disease.
For more information click here.


