Fresh from the ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, updated data were presented from INCB161734-101 (NCT06179160), a phase 1 study evaluating INCB161734, a novel oral KRAS G12D inhibitor, as monotherapy and in combination with standard-of-care chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Background
KRAS G12D mutations represent one of the most prevalent oncogenic drivers in PDAC and are also observed in colorectal cancer and non–small cell lung cancer. Despite their high frequency, KRAS G12D has historically been considered difficult to target therapeutically. INCB161734 is a selective, oral ON/OFF KRAS G12D inhibitor designed to bind both the active and inactive states of the mutant protein. Preclinical studies demonstrated more than 80-fold selectivity over wild-type KRAS, robust single-agent antitumor activity, and enhanced tumor growth inhibition when combined with chemotherapy in KRAS G12D xenograft and syngeneic models.
Study Design and Methods
This multicenter, first-in-human dose-escalation and expansion study (NCT06179160) is enrolling adults with advanced or metastatic solid tumors harboring a KRAS G12D mutation. The study is evaluating INCB161734 as monotherapy, including a PDAC-specific expansion cohort, as well as INCB161734-based combination regimens, including modified FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel, in patients with PDAC who have received ≤1 prior line of systemic therapy in the metastatic setting.
Dose escalation evaluated once-daily oral doses ranging from 200 mg to 1600 mg. Dose expansion cohorts explored INCB161734 at 600 mg or 1200 mg once daily, including PDAC-specific cohorts. Additional cohorts evaluated INCB161734 in combination with standard-of-care chemotherapy regimens, including gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel (GEMNabP) and modified FOLFIRINOX (mFOLFIRINOX).
The primary endpoint was safety and tolerability. Secondary endpoints included objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), duration of response (DOR), and pharmacokinetics.
Results
As of November 11, 2025, 61 patients with PDAC had received INCB161734 1200 mg once daily as monotherapy. Treatment was ongoing in 42 patients (69%), and the most common reason for discontinuation was disease progression (23%). In the combination cohorts, 28 patients received INCB161734 with GEMNabP and 16 patients received INCB161734 with mFOLFIRINOX.
Safety and Tolerability
INCB161734 monotherapy at 1200 mg once daily demonstrated a manageable safety profile in patients with KRAS G12D mutated PDAC. Treatment discontinuation due to treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) occurred in 2 patients (3%). Dose reductions due to TRAEs were reported in 6 patients (10%), with fatigue being the most common event leading to dose reduction. Dose interruptions due to TRAEs occurred in 13 patients (21%).
Gastrointestinal TRAEs were predominantly grade 1, were manageable with supportive care, and generally improved after cycle 1. Vomiting was mainly limited to the first cycle of treatment. Among patients receiving INCB161734 1200 mg daily monotherapy, any-grade TRAEs were reported in 90.2% of patients, with grade ≥3 TRAEs observed in 19.7%.
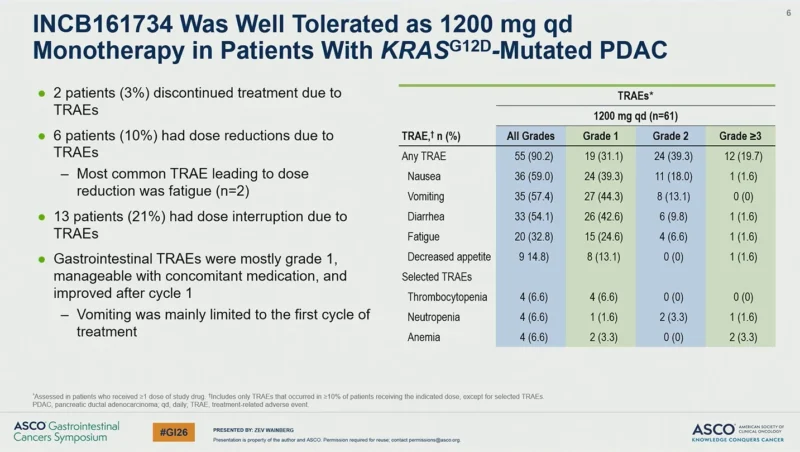
When administered in combination with chemotherapy, INCB161734 was well tolerated without compromising chemotherapy dose intensity. In the GEMNabP cohorts, the median relative dose intensity was 74% for both gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel. In the mFOLFIRINOX cohorts, median relative dose intensities were 76% for fluorouracil, 67% for irinotecan, and 67% for oxaliplatin, consistent with historical data for these regimens.
Antitumor Activity
Antitumor activity was observed with INCB161734 monotherapy in heavily pretreated patients with PDAC. Among evaluable patients treated with INCB161734 1200 mg daily (n=41), the disease control rate was 78% (32 patients), and the objective response rate was 37% (15 patients). Tumor shrinkage was observed in multiple patients, with several responses ongoing at the time of data cutoff.
Swimmer plot analyses demonstrated durable clinical benefit in a subset of patients, with prolonged treatment durations extending beyond one year in some cases.
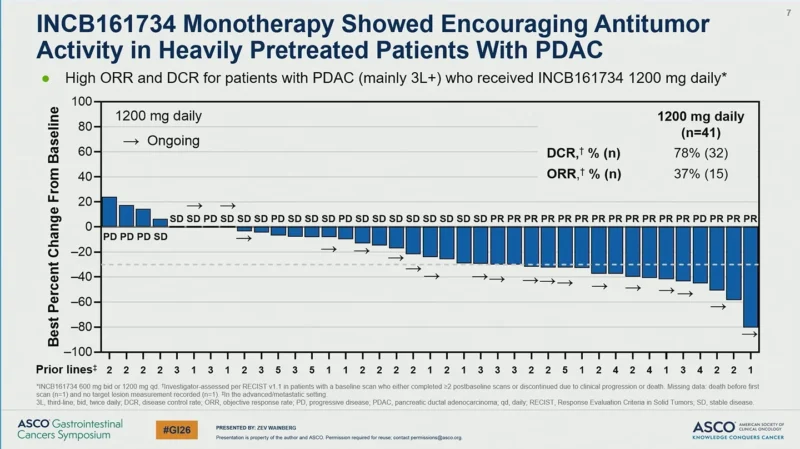
Antitumor activity was also observed when INCB161734 was combined with standard-of-care chemotherapy in the first-line setting, supporting continued evaluation of combination strategies in KRAS G12D mutated PDAC.
Conclusion
Data presented at ASCO GI 2026 indicate that INCB161734 demonstrates a manageable safety profile as monotherapy and in combination with chemotherapy, without compromising chemotherapy dose intensity. Evidence of antitumor activity was observed in heavily pretreated patients with KRAS G12D-mutated PDAC, including durable disease control. Ongoing enrollment and follow-up will further characterize the clinical profile of INCB161734 across treatment settings.
For more information, click here.


