HARMONi-6 (NCT05840016), a pivotal phase 3 trial presented by Prof. Shun Lu (Shanghai, China) at the ESMO Congress 2025, evaluated ivonescimab plus chemotherapy versus tislelizumab plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced or metastatic squamous non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), irrespective of PD-L1 expression. The trial demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) with ivonescimab, marking a major step forward in the management of squamous NSCLC.
Background
While PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy have significantly improved the management of advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), progress has been more limited in squamous histology. Ivonescimab represents a novel therapeutic strategy. It is a first-in-class bispecific antibody that simultaneously targets programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)—two key pathways that tumors exploit to evade immune destruction and sustain growth.
By blocking PD-1, ivonescimab restores antitumor T-cell activity, while inhibition of VEGF leads to normalization of the tumor vasculature, reduction of hypoxia, and enhanced immune cell infiltration. This dual mechanism creates a more favorable immune microenvironment, potentially amplifying the efficacy of immunotherapy even in tumors with low PD-L1 expression. Building on the encouraging results from earlier studies—where ivonescimab monotherapy demonstrated a significant progression-free survival (PFS) advantage over pembrolizumab in patients with PD-L1 tumor proportion score ≥1% NSCLC—the HARMONi-6 trial was designed to test whether combining ivonescimab with standard chemotherapy could further extend this benefit.
By directly comparing ivonescimab plus chemotherapy with tislelizumab plus chemotherapy, the trial sought to determine whether dual blockade of PD-1 and VEGF provides superior efficacy across all PD-L1 subgroups in patients with advanced or metastatic squamous NSCLC, where new treatment options are critically needed.
Methods
A total of 532 patients with previously untreated stage IIIB–IV squamous NSCLC were randomized (1:1) to receive either:
- Ivonescimab 20 mg/kg Q3W plus paclitaxel (175 mg/m²) and carboplatin (AUC 5) × 4 cycles, followed by ivonescimab maintenance, or
- Tislelizumab 200 mg Q3W plus the same chemotherapy backbone, followed by tislelizumab maintenance.
Randomization was stratified by disease stage (IIIB/IIIC vs IV) and PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) (≥1% vs <1%).
The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) by independent radiographic review (RECIST v1.1). The key secondary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
Results
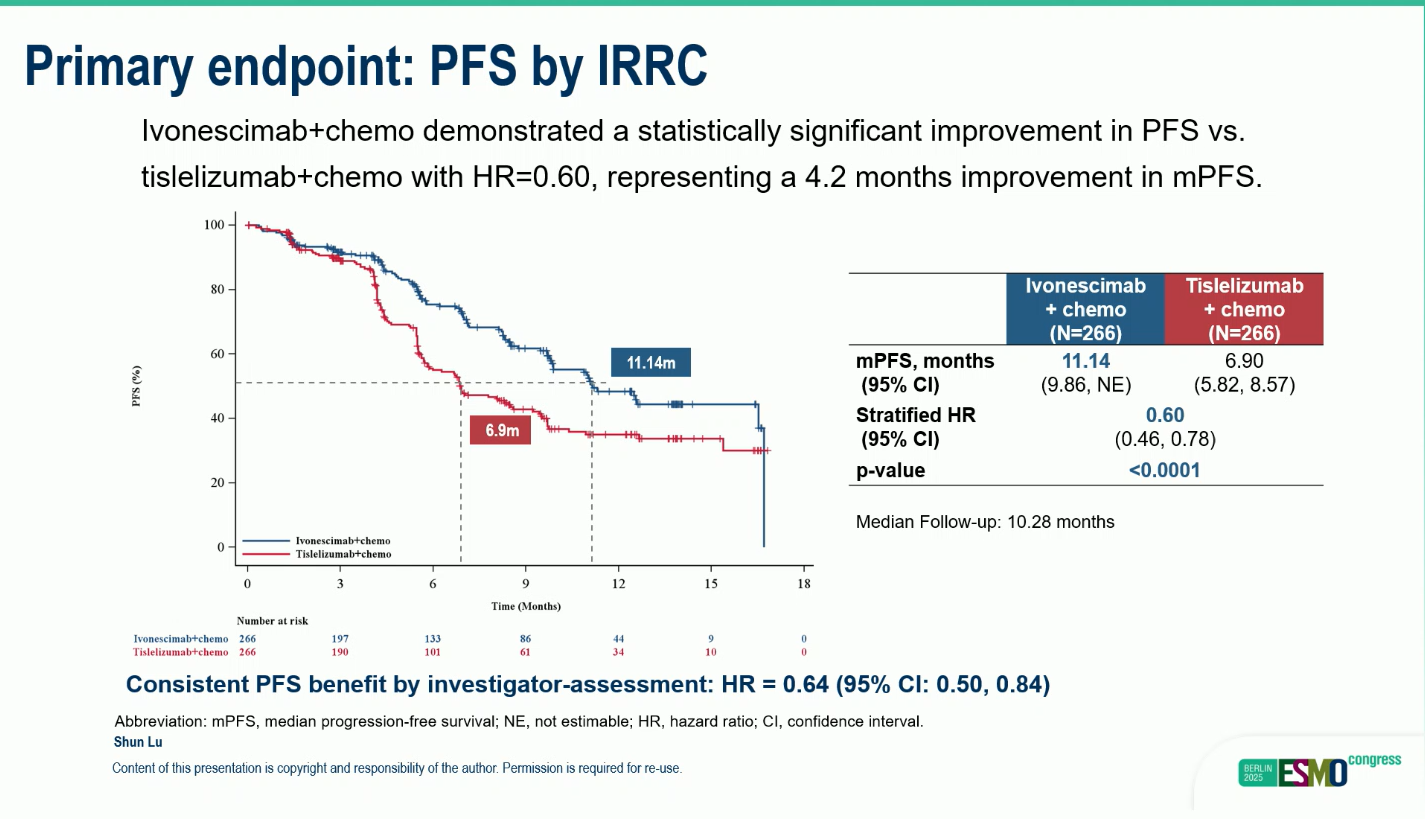
At the time of analysis, HARMONi-6 met its primary endpoint, showing a significant and clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) with ivonescimab plus chemotherapy compared with tislelizumab plus chemotherapy. The benefit was consistent across all key patient subgroups, regardless of PD-L1 expression.
- Baseline characteristics were well balanced between groups. Over 63% of patients had centrally located tumors, 8.8% had cavitation, and 17.5% showed vascular encasement.
- Ivonescimab plus chemotherapy achieved a median PFS of 11.4 months compared with 6.9 months for tislelizumab plus chemotherapy (HR 0.60; 95% CI 0.46–0.78; p < 0.0001).
- This represents a 40% reduction in the risk of disease progression or 3death.
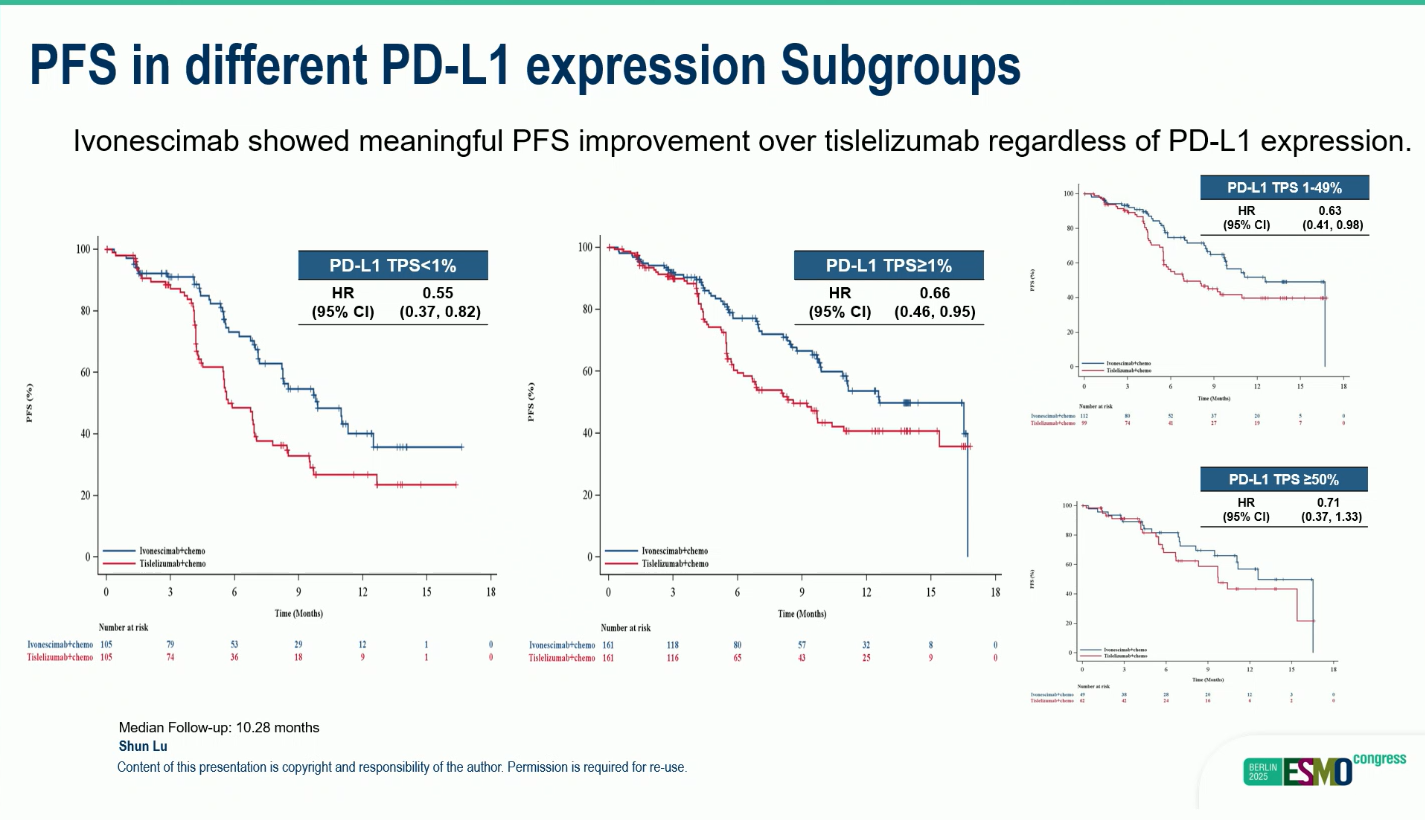
Subgroup Analysis:
- The PFS benefit was consistent across PD-L1 subgroups.
- PD-L1 <1%: 9.9 vs 5.7 months (HR 0.55; 95% CI 0.37–0.82)
- PD-L1 ≥1%: 12.6 vs 8.6 months (HR 0.66; 95% CI 0.46–0.95)
- These results demonstrate robust efficacy independent of PD-L1 expression.
Safety: The overall safety profile was manageable and comparable between arms.Treatment-related serious adverse events (SAEs) occurred in 32.3% with ivonescimab and 30.2% with tislelizumab.Grade ≥3 hemorrhagic events were rare (1.9% vs 0.8%), and no new safety signals were reported. Common adverse events included anemia, fatigue, and rash, consistent with prior findings.
Conclusions
The HARMONi-6 trial met its primary endpoint, demonstrating a clinically and statistically significant PFS improvement with ivonescimab plus chemotherapy compared with tislelizumab plus chemotherapy in first-line advanced squamous NSCLC. The consistent benefit across PD-L1 subgroups suggests broad applicability. The safety profile remained acceptable, aligning with prior studies of ivonescimab. These findings position ivonescimab plus chemotherapy as a potential new standard of care for patients with advanced or metastatic squamous NSCLC, offering enhanced efficacy without compromising tolerability
You can read the full abstract here.


