Published in Cancer Control, Sage Journals in August 9, 2024.
Authors: Kosuke Hamai, Ryo Katsura, Shinya Miyake, Suguru Fujita, Shinpei Tada, Tetsu Hirakawa, Sayaka Ueno, Takuya Tanimoto and Nobuhisa Ishikawa.

Introduction
Docetaxel plus ramucirumab (DTX + RAM) therapy is a standard treatment for previously treated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, this combination often leads to significant adverse events, including fluid retention. This study aimed to investigate whether the concomitant use of oral dexamethasone (DEX) could minimise side effects and improve therapeutic outcomes in patients with recurrent lung cancer undergoing DTX + RAM therapy.
Design and Methods
This retrospective study included 40 patients with relapsed NSCLC who underwent DTX + RAM therapy between January 2017 and December 2021. Patients were divided into two groups based on the concomitant use of oral DEX:
- DEX group: Received 6.6 mg intravenous DEX on day 1 (treatment day) and 8 mg oral DEX on days 2 and 3.
- Non-DEX group: Received only 6.6 mg intravenous DEX on day 1.
The study compared therapeutic effects (disease control rate, objective response rate, progression-free survival, and overall survival) and toxicities between the two groups. Statistical analyses were performed using Fisher’s exact test for response rates and the log-rank test for survival outcomes.
What We Learned:
Efficacy
- Objective response rate (ORR) was significantly higher in the DEX group (31.6% vs 0%, P = 0.0203).
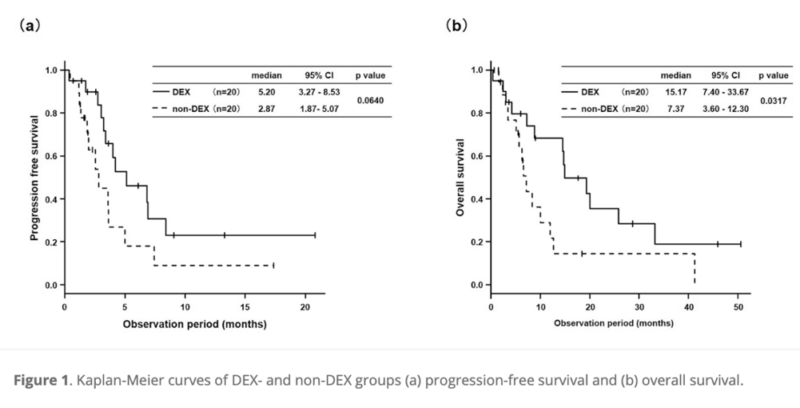
- Median progression-free survival (PFS) showed a positive trend in the DEX group (5.20 months vs 2.87 months, P = 0.0640).
- Median overall survival (OS) was significantly longer in the DEX group (15.17 months vs 7.37 months, P = 0.0317).
Toxicity
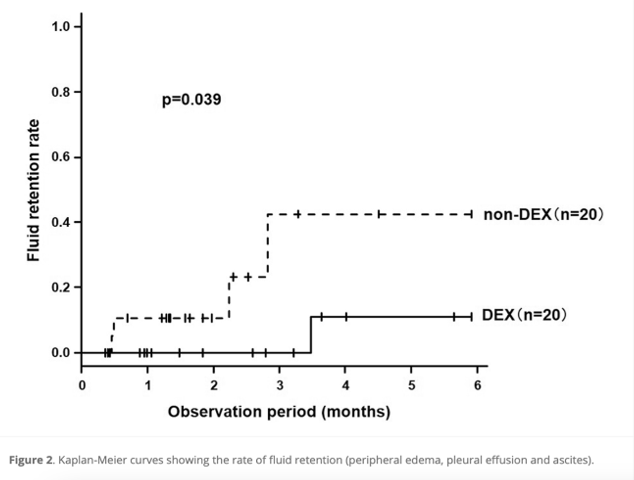
- Fluid retention within six months of treatment was significantly lower in the DEX group (10.0% vs 42.5%, P = 0.0390).
- Leukopenia, neutropenia, and febrile neutropenia were more common in the DEX group, likely due to less frequent use of pegfilgrastim.
Patient Characteristics
The non-DEX group had significantly higher use of pegfilgrastim (90% vs 45%, P = 0.0057).
More patients in the non-DEX group received immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) before DTX + RAM therapy (85% vs 35%, P = 0.0031).
Key Highlights
- Concomitant use of oral DEX significantly improved the objective response rate in previously treated NSCLC patients receiving DTX + RAM therapy.
- Overall survival was significantly prolonged in the DEX group, despite lower pretreatment utilization of pegfilgrastim and ICIs.
- The frequency of fluid retention, a common side effect of DTX + RAM therapy, was significantly reduced with oral DEX administration.
- The DEX group showed improved outcomes despite potentially unfavorable baseline characteristics (less prior ICI use and pegfilgrastim administration).
Key Takeaway Messages
- Oral dexamethasone may enhance the efficacy of DTX + RAM therapy in previously treated NSCLC patients.
- The addition of oral DEX to DTX + RAM therapy could significantly reduce the incidence of fluid retention, potentially allowing for longer treatment duration.
- The benefits of oral DEX were observed even in patients with less favorable baseline characteristics, suggesting a robust effect.
- While myelosuppression-related adverse events were more common in the DEX group, this may be attributed to less frequent use of pegfilgrastim rather than a direct effect of DEX.
- The significant improvement in overall survival with oral DEX administration warrants further investigation in larger, prospective studies.
Limitations and Future Directions
This study had several limitations, including its single-center retrospective design and small sample size. The difference in patient backgrounds, particularly in pegfilgrastim use and prior ICI treatment, may have influenced the results.
Future research should focus on
- Conducting multicenter prospective studies with larger sample sizes and matched patient backgrounds.
- Investigating the impact of oral DEX on quality of life measures, which were not assessed in this study.
- Examining the duration of side effects with and without DEX administration.
- Exploring the potential synergistic effects of oral DEX, pegfilgrastim, and prior ICI treatment on DTX + RAM therapy outcomes.
In conclusion, this retrospective analysis suggests that the concomitant use of oral dexamethasone with docetaxel-ramucirumab therapy may improve treatment outcomes and reduce fluid retention in previously treated non-small cell lung cancer patients. These findings provide a foundation for further research into optimizing treatment strategies for this patient population.