Talha Badar, Hematology/Oncology Specialist at Mayo Clinic, shared a post on X:
“Brief thread on clonal hematopoiesis.
- CH associated with germline predisposition syndrome
- CH associated with genotoxic stressors
- CH in solid malignancies
CH arises with HSCs acquiring somatic mt that confers a competitive advantage, enabling its progeny to disproportionately populate blood cells
- Germline variants lower the threshold for clonal expansion.
- Genotoxic or inflammatory stressors promote the selection of a mutant clone.
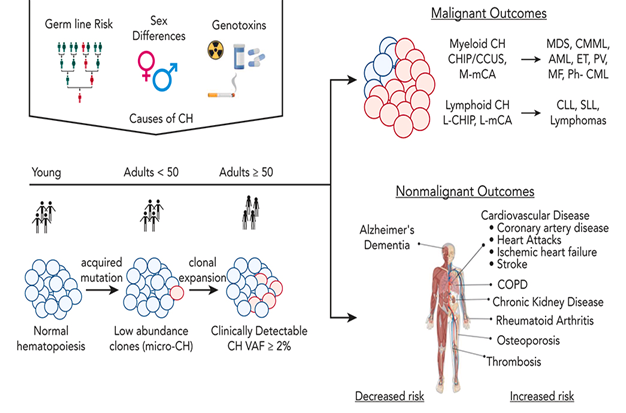
- Approx. 20 genes are recurrently mutated in CH.
- DNMT3A and TET2 confer the advantage of self-renewal (low differentiation).
- PPM1D and TP53 get a survival advantage from genotoxins (chemo, XRT, smoking).
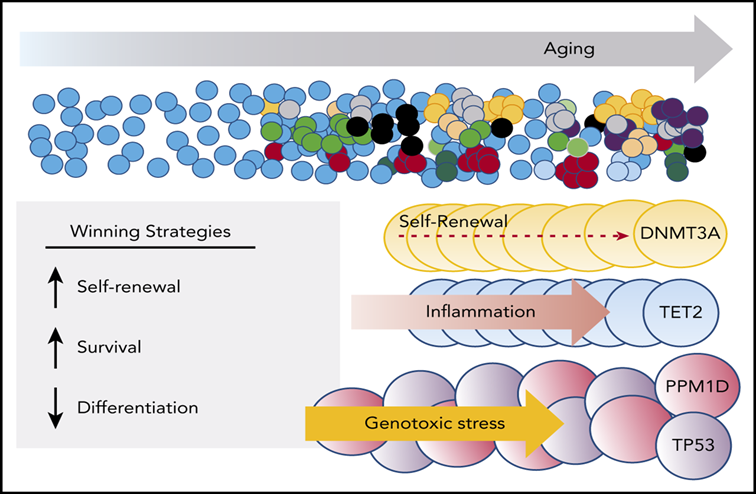
CH and aging
- CH and aging: common with aging, 10-20% over 70 years.
- Often assoc. DNMT3A, TET2, AXSL1 (TP53, PPM1D).
- CH biology conserved across mammals; however, animals such elephants, in spite long lifespan, have low cancer incidence (Peto’s paradox); 20 copies of TP53 compared to 1 in humans.
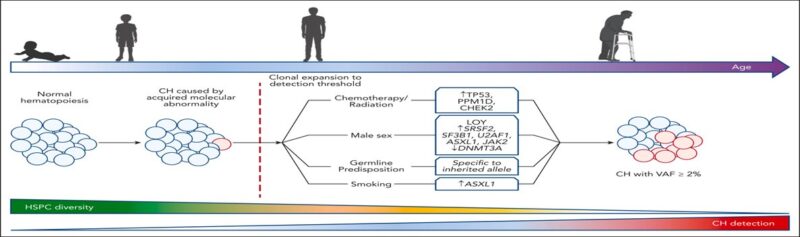
CH in hematological malignancies: risk factors for transformation
- Type of MT; DNMT3A low risk, TP53, IDH1, IDH2 and RUNX1 high risk.
- Clonal size (VAF %).
- Number of mol. abn
Germline predisposition to CH
- Common germline mutations; DDX41, GATA2, RUNX1, CEBPA, and SAMD9/9L.
- IBMF have impaired baseline global fitness compared to HSPCs; somatic transformation occurs thru loss of fitness/bypass of tumor suppressor pathway
- Clinical and genomics data from germ-line RUNX1, GATA2, and DDX41 variant carriers were collected from the RUNX1 database.
- CH is the least common in the most prevalent DDX41m myeloid neoplasm
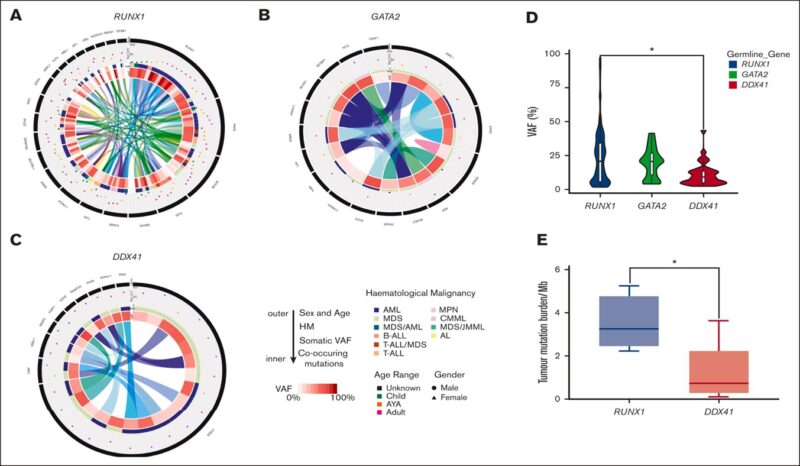
CH and DDX41 mt germline predisposition syndrome
We conducted an observational study to analyzed frequency of CH associated with DDX41m precursor disease states (CHIP/CCUS), MN
- Most common somatic mutation was DDX41 (R525H;55%).
- Incidence of ARCH was lower compared to other GPS and de novo MDS/AML.
- Further evaluation is needed to understand leukemogenesis in DDX41m MN.
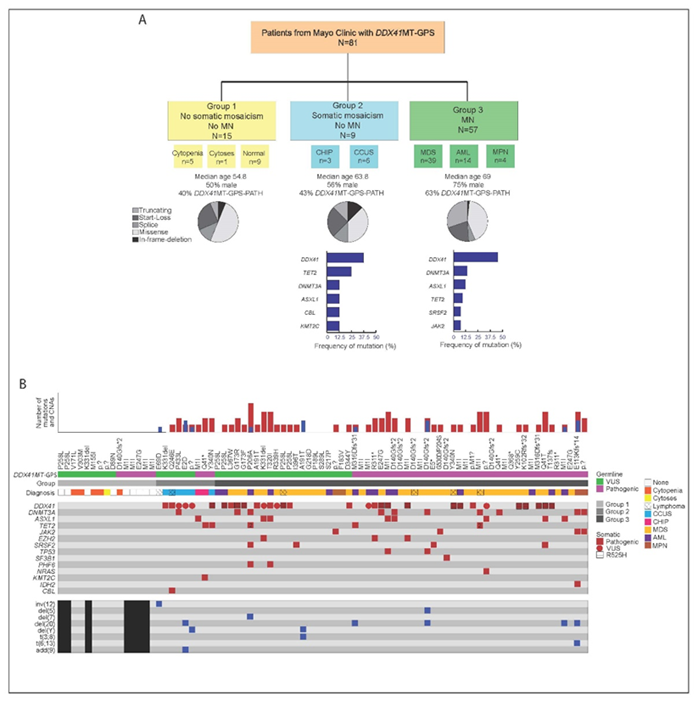
CH secondary to genotoxic stress
- Initial Hit: HSPCs acquire somatic mutations in genes related (DDR: TP53, PPM1D and CHEK2).
- Genotoxic Exposure: Chemo, radiation, or other insults kill off most HSPCs.
- Selective Advantage: Mutant HSPCs with resistance to apoptosis and expand disproportionately.
- Clonal Expansion: Resistant clones dominate hematopoiesis; additional mutations may drive malignancy.
Spectrum, prevalence and clinical correlates of PPM1DMT in patients with t-CH/t-CCUS
We studied the clinical and molecular landscape of t-CH/t-CCUS patients with the following four genotypes: PPM1D MT/TP53 WT, PPM1D MT/TP53 MT, PPM1D WT/TP53 MT and PPM1D WT/ TP53 WT.
- PPM1D MT/ TP53 WT and PPM1D MT/TP53 MT genotypes, were significantly enriched in the therapy-related sub-gp (39%).
- Median time interval from last genotoxic therapy exposure to diagnosis of t-CH/t-CCUS was shorter (≤ 6 months) in the PPM1D MT/ TP53 WT and PPM1D MT/ TP53 MT gps.
- The therapy-related PPM1DMT CH group, with or without TP53MT had significantly higher exposures to PARP inhibitors (30%) and radioligand therapies (50%).
CH in solid malignancies
- CH ≥ in patients with solid tumors compared to the general population, esp after chemo/XRT.
- Impact: High risk CVD, impaired immune response and high risk of tumor progression.
- Relevance: can inform risk of t-MNs or guide treatment selection, particularly in older or heavily pretreated patients.
Tumor-infiltrating clonal hematopoiesis (TI-CH)
- CHIP and TI-CH was compared in 421 NSCL Ca patients.
- 42% of CHIP patients have TI-CH; predicting high risk or recurrence vs without CHIP (HR=1.80, 95% CI 1.23-2.63)
Pich et al. NEJM 2025
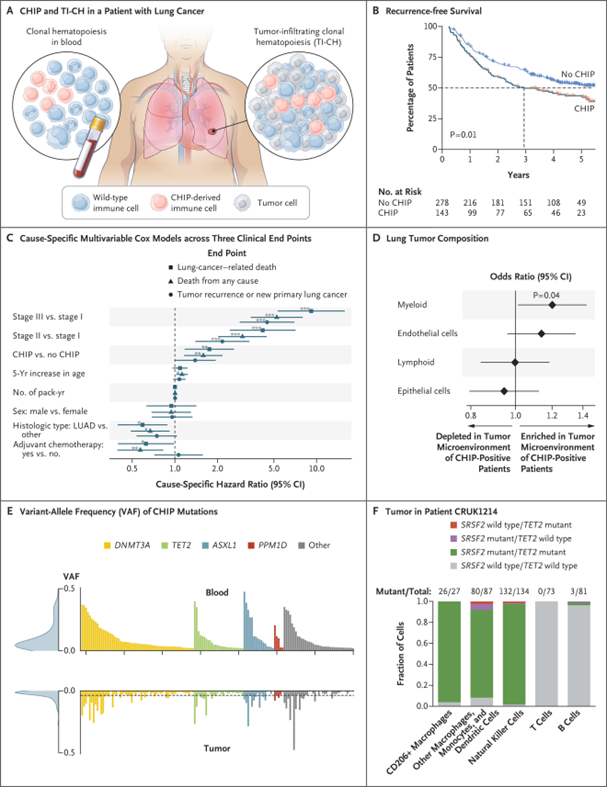
Clonal hematopoiesis Summary:
- CH is a common, age-related phenomenon that can signal increased risk for diverse diseases.
- It is influenced by both inherited predisposition and acquired stressors.
- CH can precede or accompany, hem or solid malignancies and well non-malignant conditions.
- Early detection may guide surveillance, risk stratification, and treatment decisions.”
More posts featuring Talha Badar.


