The Role of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Understanding Tumor Microenvironment and Drug Resistance Mechanisms
Authors: Ali Tavakoli Pirzaman, Ali Alishah, Bahareh Babajani, Pouyan Ebrahimi, Seyyed Ali Sheikhi, Farhad Moosaei, Amirhossein Salarfar, Shahrbanoo Doostmohamadian, and Sohrab Kazemi.
Introduction:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a primary liver cancer, is the sixth most prevalent cancer globally and ranks fourth in cancer-related mortality. Accounting for approximately 80% of liver cancer cases, HCC poses a significant challenge due to its rapid acquisition of resistance to available chemotherapeutic treatments. This narrative explores the crucial role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the tumour microenvironment (TME) and drug resistance mechanisms of HCC.
Design/Methods:
This is a comprehensive narrative review, synthesizing findings from various studies exploring the intricate interplay between miRNAs, the TME, and drug resistance in HCC. The review encompasses the mechanisms of HCC initiation, the impact of miRNAs on the TME components, and the role of miRNAs in mediating resistance to chemotherapeutic agents.
What We Learned:
- Tumor Microenvironment:
- miRNAs play a pivotal role in shaping the HCC microenvironment by influencing immune phenotypes, hypoxic conditions, acidification, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix (ECM) composition.
- Altered miRNA expression can modulate the recruitment and differentiation of immune cells, including macrophages, regulatory T cells (Tregs), natural killer (NK) cells, and tumour-associated neutrophils (TANs), creating an immunosuppressive TME.
- Hypoxia and acidic conditions, common in HCC, can induce the expression of specific miRNAs, such as miR-377-5p, miR-576-3p, and miR-100-5p, promoting tumor growth and metastasis.
- miRNAs like miR-140, miR-26a, miR-195, and miR-503 regulate angiogenesis by modulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and other pro-angiogenic factors.
- The ECM in HCC tumors is influenced by miRNAs, such as miR-26a/b-5p and miR-29, which can affect cell adherence and the formation of metastatic niches.
- Drug Resistance:
- miRNAs contribute to drug resistance in HCC through various mechanisms, including autophagy, membrane transporter activity, and disruption of apoptosis.
- Overexpression of miRNAs like miR-27b, miR-146b-5p, miR-181a/d, and miR-146a can induce multidrug resistance (MDR) against chemotherapeutic agents such as doxorubicin, carboplatin, cisplatin, mitomycin C, and vincristine.
- Upregulation of miRNAs like miR-32-5p and miR-181a, or downregulation of miRNAs like miR-491-3p, miR-122, and miR-223, can modulate the activity of membrane transporters (e.g., ABCB1, ABCC1), leading to drug resistance.
- miRNAs can influence autophagy-related genes (ATGs), impacting autophagic processes and contributing to resistance to drugs like sorafenib, doxorubicin, and cisplatin.
- Disruption of apoptosis through miRNA-mediated regulation of genes like PTEN, Bcl-2, and Mcl-1 can confer resistance to chemotherapeutic agents, including sorafenib, 5-fluorouracil, and cisplatin.
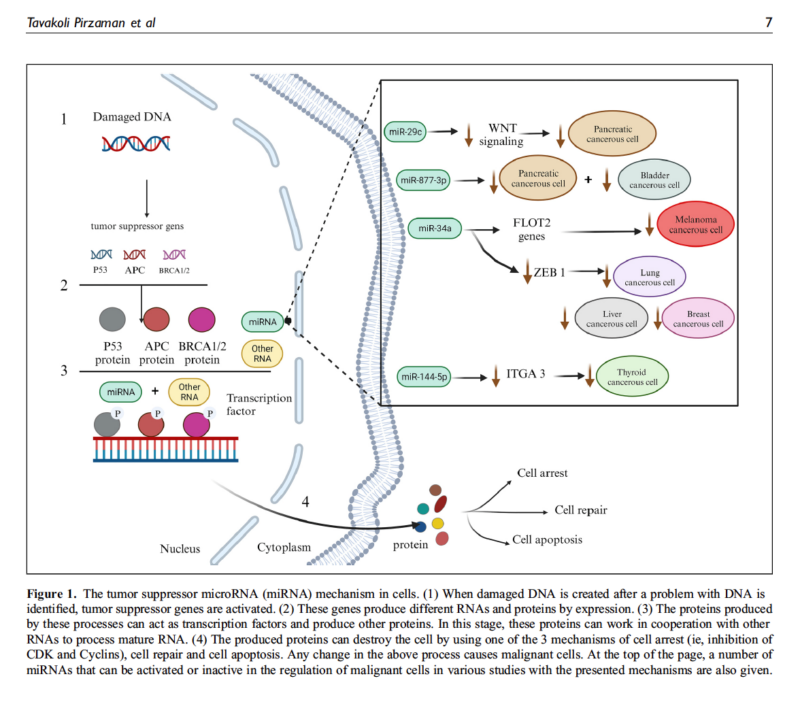
Key Highlights:
- The review emphasizes the intricate interplay between miRNAs, the TME, and drug resistance mechanisms in HCC, highlighting the potential of miRNA-based therapies for improved treatment outcomes.
- Specific miRNAs are identified as key regulators of various components of the TME, including immune cell recruitment, angiogenesis, and ECM remodelling, contributing to tumour growth and metastasis.
- miRNA-mediated modulation of cellular processes, such as autophagy, apoptosis, and membrane transporter activity, plays a crucial role in the development of drug resistance in HCC.
- The identification of miRNAs involved in HCC pathogenesis and drug resistance opens up avenues for miRNA-targeted therapies and the development of miRNA-based biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
Key Takeaway Messages:
- miRNAs are crucial players in shaping the TME and mediating drug resistance in HCC, making them attractive therapeutic targets and potential biomarkers.
- Understanding the intricate interplay between miRNAs, the TME, and drug resistance mechanisms is essential for developing effective strategies to overcome treatment resistance and improve patient outcomes.
- miRNA-based therapies hold promise for personalized and targeted approaches in HCC management, potentially enhancing treatment efficacy and reducing adverse effects.
- Further research is needed to address the challenges associated with miRNA-based diagnostics and therapeutics, such as standardization, normalization, and cost-effective sample collection methods.
Summary by Amalya Sargsyan, MD


