B7-H3 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target across a wide range of solid tumors, reflecting growing interest in tumor-associated immune regulatory proteins as drivers of cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. While HER2 remains one of the most clinically validated oncogenic targets in oncology, emerging data highlight B7-H3 as a distinct and complementary target with broad tumor expression and potential applicability across multiple malignancies.
GSK5764227, also known as HS-20093, is an investigational antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) directed against B7-H3 (CD276) and is being developed through a collaboration between GSK and Hansoh Pharma. The program reflects the expanding strategic focus on next-generation ADCs engineered to improve tumor selectivity, optimize payload delivery, and enhance therapeutic index.
Although still in early clinical development, GSK5764227 represents a novel B7-H3–targeted ADC platform designed to address unmet needs across several advanced solid tumors.

Molecular Design and Mechanism of Action
GSK5764227 incorporates three core elements characteristic of modern ADC design:
Targeting Antibody
The monoclonal antibody component of HS-20093 specifically binds to B7-H3, a cell-surface protein frequently overexpressed in malignant tissues. B7-H3 has been implicated in tumor immune evasion, invasion, metastatic progression, and adverse clinical outcomes in several cancer types.
Cleavable Linker
The antibody is connected to a cytotoxic payload via a cleavable linker engineered to maintain stability in systemic circulation while enabling selective payload release following tumor cell internalization.
Cytotoxic Payload
After binding B7-H3 on tumor cells, the ADC undergoes receptor-mediated endocytosis. Intracellular processing releases the payload commonly a topoisomerase I inhibitor resulting in DNA damage and tumor cell death. The payload design may allow a controlled bystander effect, potentially improving activity in tumors with heterogeneous B7-H3 expression.
Biological Rationale for Targeting B7-H3
B7-H3 belongs to the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules and is expressed at relatively low levels in most normal tissues but frequently upregulated in multiple malignancies, including:
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Gastric cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Head and neck cancer
- Gynecologic malignancies
High B7-H3 expression has been associated with immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment, aggressive tumor biology, and treatment resistance. These characteristics support B7-H3 as an attractive therapeutic target for ADC development.
Rationale for Clinical Development
Despite advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapy, resistance and tumor heterogeneity remain major challenges across advanced solid tumors. B7-H3 targeting provides a complementary therapeutic strategy, particularly in tumors that may not be driven by classical oncogenic receptor pathways.
GSK5764227 has been engineered to optimize:
- Drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR)
- Linker stability
- Tumor-selective payload release
- Controlled systemic toxicity
These design features reflect evolving ADC engineering approaches aimed at maximizing efficacy while minimizing off-target effects.
Early Clinical Development Program
GSK5764227 is currently being evaluated in early-phase clinical studies enrolling patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors. These trials are designed to characterize safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and preliminary antitumor activity across multiple tumor types expressing B7-H3.
Dose-escalation cohorts follow traditional phase I trial objectives, including identification of dose-limiting toxicities and determination of recommended expansion doses. Subsequent expansion cohorts aim to evaluate activity across selected tumor indications.
ARTEMIS Study: First-in-Human Clinical Evaluation
The clinical development of GSK5764227 is anchored by the ARTEMIS clinical trial, a first-in-human, multicenter Phase I study evaluating HS-20093 in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors.
Study Design and Objectives
ARTEMIS follows a dose-escalation and dose-expansion framework. The primary objectives include:
- Evaluation of safety and tolerability
- Identification of dose-limiting toxicities
- Determination of recommended phase II dosing
Secondary and exploratory endpoints include pharmacokinetic analysis, biomarker evaluation including B7-H3 expression, and preliminary assessment of clinical activity. Patients enrolled in ARTEMIS typically have advanced malignancies that have progressed following standard therapy.
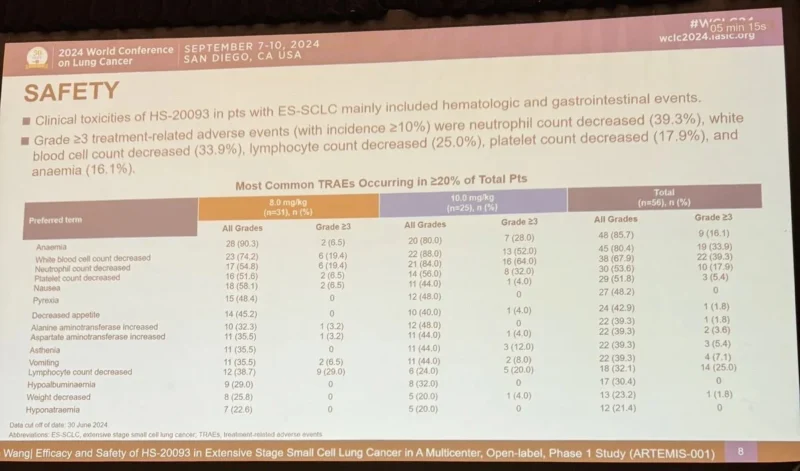
Early Clinical Signals from ARTEMIS
Clinical data from ARTEMIS remain preliminary. Early observations suggest:
- Manageable safety profile consistent with ADC class effects
- Evidence of biological activity across selected solid tumor types
- Pharmacokinetic profiles supporting predictable systemic exposure
Formal efficacy outcomes, including objective response rates and durability of response, remain under investigation as patient follow-up continues. Ongoing translational studies aim to clarify the relationship between B7-H3 expression levels, ADC exposure, and clinical outcomes.
Safety Considerations and Class Effects
As with other ADCs, safety monitoring remains critical. Potential adverse effects associated with GSK5764227 may include:
- Hematologic toxicity
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Fatigue
- Pulmonary toxicity including possible interstitial lung disease
Preclinical optimization of linker stability and payload release kinetics is intended to improve tolerability. However, long-term safety data will be essential to fully define the therapeutic window of the agent.
Positioning Within the Evolving ADC Landscape
B7-H3–directed ADCs represent an expanding therapeutic class. The clinical differentiation of GSK5764227 will depend on demonstrating:
- Meaningful clinical activity across B7-H3 expressing tumors
- Activity in treatment-resistant disease settings
- Favorable safety and tolerability profile
- Potential synergy with immunotherapy or targeted treatment combinations
The collaboration between GSK and Hansoh Pharma highlights increasing global investment in next-generation biologic oncology platforms.
Future Directions
Ongoing clinical trials will help define the role of GSK5764227 in the management of advanced solid tumors. Key research questions include:
- Predictive value of B7-H3 expression as a biomarker
- Activity in tumors with co-expression of other therapeutic targets
- Optimal sequencing relative to immunotherapy and targeted therapies
- Potential utility in earlier treatment settings or combination regimens
As clinical development progresses, HS-20093 may contribute to expanding precision oncology strategies beyond traditional oncogenic receptor targets.
Key Takeaway
GSK5764227 (HS-20093) is an investigational antibody-drug conjugate targeting B7-H3, a tumor-associated immune regulatory protein expressed across multiple solid tumors. While still in early clinical development, this agent represents a promising addition to the next generation of precision ADC therapies.


