GSK5764227, also known as HS-20093, is an investigational antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) currently being studied in patients with advanced solid tumors. Unlike several established ADC therapies that target HER2, HS-20093 is designed to target a different tumor-associated protein known as B7-H3 (CD276), an emerging biomarker in oncology and immunotherapy research.
This therapy is in early clinical development and has not yet been approved for clinical use. Ongoing studies are evaluating its safety, pharmacologic properties, and potential anti-tumor activity across multiple cancer types.

Why B7-H3 Is Important in Cancer
B7-H3 is a cell-surface protein belonging to the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules. While its exact physiologic role remains under investigation, B7-H3 is frequently overexpressed in a wide range of malignancies, including:
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Gastric cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Head and neck cancers
- Several other solid tumors
Elevated B7-H3 expression has been associated with tumor progression, immune evasion, metastasis, and poor clinical outcomes in several tumor types. Because of its high tumor expression and relatively limited distribution in normal tissues, B7-H3 has become a promising therapeutic target.
How GSK5764227 Works
GSK5764227 belongs to the class of antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs), which are designed to deliver cytotoxic therapy directly to cancer cells while minimizing exposure to healthy tissues.
This treatment consists of three key components:
Targeting Antibody
The antibody portion of GSK5764227 specifically recognizes and binds to B7-H3 proteins expressed on tumor cells.
Linker Technology
A specialized molecular linker connects the antibody to the cytotoxic payload and helps maintain stability while circulating in the bloodstream.
Cytotoxic Payload
Once the ADC binds to B7-H3 on cancer cells, the drug complex is internalized. Inside the cell, the payload typically a topoisomerase I inhibitor, is released, causing DNA damage and tumor cell death.
This targeted delivery approach aims to improve treatment precision and reduce systemic toxicity compared with conventional chemotherapy.
The ARTEMIS-001 Clinical Trial
GSK5764227 is currently being evaluated in the ARTEMIS-001 study, a Phase I clinical trial investigating the drug in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors.
The primary goals of ARTEMIS-001 include:
- Evaluating safety and tolerability
- Determining appropriate dosing levels
- Characterizing pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
- Assessing preliminary anti-tumor activity
Patients enrolled in early-phase trials typically have advanced disease that has progressed after standard therapies. Because this is a first-in-human study, demonstrating safety and defining dosing are the primary objectives, while signals of clinical activity are considered exploratory.
Early Observations From Clinical Development
Data from early clinical development remain limited as enrollment and follow-up continue. Preliminary observations suggest that:
- The safety profile appears generally manageable
- Observed toxicities are consistent with ADC class effects
- Early signals of anti-tumor activity have been reported in selected tumor types
Further data from ongoing dose-expansion cohorts will be necessary to better define clinical efficacy.
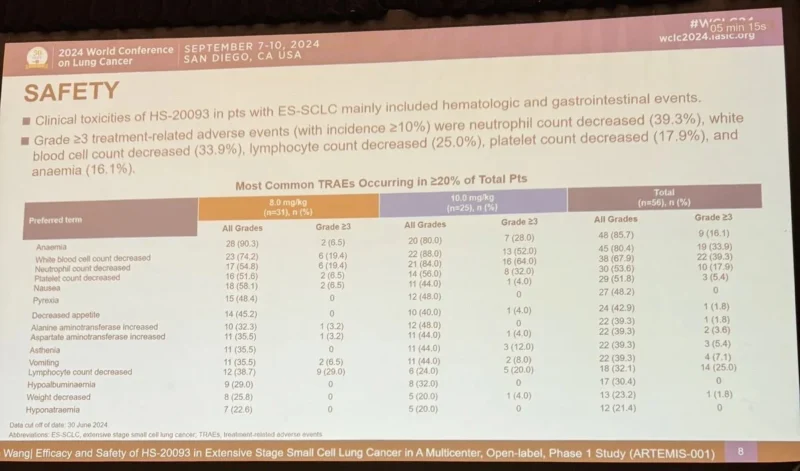
Safety Considerations
As with other ADC therapies, GSK5764227 may cause treatment-related side effects. Patients participating in clinical trials are closely monitored for potential toxicities, which may include:
- Fatigue
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Hematologic changes
- Pulmonary symptoms, including potential interstitial lung disease
Management strategies typically involve dose adjustments, treatment delays, or supportive care interventions. Patient safety remains the highest priority during early-phase drug development.
Potential Clinical Impact
B7-H3 targeted therapies represent an expanding area of oncology research. If clinical trials demonstrate meaningful efficacy and acceptable safety, GSK5764227 could become a future therapeutic option for patients with tumors expressing B7-H3, including those who have progressed after standard therapies.
In addition, continued research may clarify how B7-H3 targeted therapies interact with existing treatment strategies such as immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or combination ADC approaches.
What This Means for Patients
GSK5764227 remains an investigational therapy available only through clinical trials. Participation in clinical research offers patients access to emerging treatments and contributes to the advancement of cancer care. Patients interested in novel therapies targeting B7-H3 should discuss clinical trial eligibility with their oncology care team.
Key Takeaway
GSK5764227 (HS-20093) is an investigational antibody–drug conjugate that targets the B7-H3 protein, a promising tumor-associated antigen expressed in multiple solid cancers. While still in early clinical development, this therapy represents a new direction in precision oncology aimed at improving targeted drug delivery and expanding treatment options for patients with advanced malignancie


