Durvalumab is a human immunoglobulin G1 kappa (IgG1κ) monoclonal antibody that targets the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) protein. By inhibiting PD-L1, durvalumab enhances the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells.
On March 28, 2025, durvalumab was approved in combination with chemotherapy as a neoadjuvant treatment, followed by adjuvant durvalumab monotherapy after surgery for muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). This approval highlighted its evolving role across different stages of bladder cancer.
Which company produced Durvalumab?
Durvalumab, marketed under the brand name Imfinzi, is produced by AstraZeneca, a global biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Cambridge, UK. Founded in 1999 through the merger of Astra AB (Sweden) and Zeneca Group (UK), AstraZeneca focuses on developing innovative medicines in oncology, cardiovascular, respiratory, and rare diseases. The company is a major force in cancer research, with a strong portfolio that includes drugs like Tagrisso, Lynparza, and Enhertu. AstraZeneca operates in over 100 countries and is known for its commitment to scientific advancement and global patient access.
How does Durvalumab work?
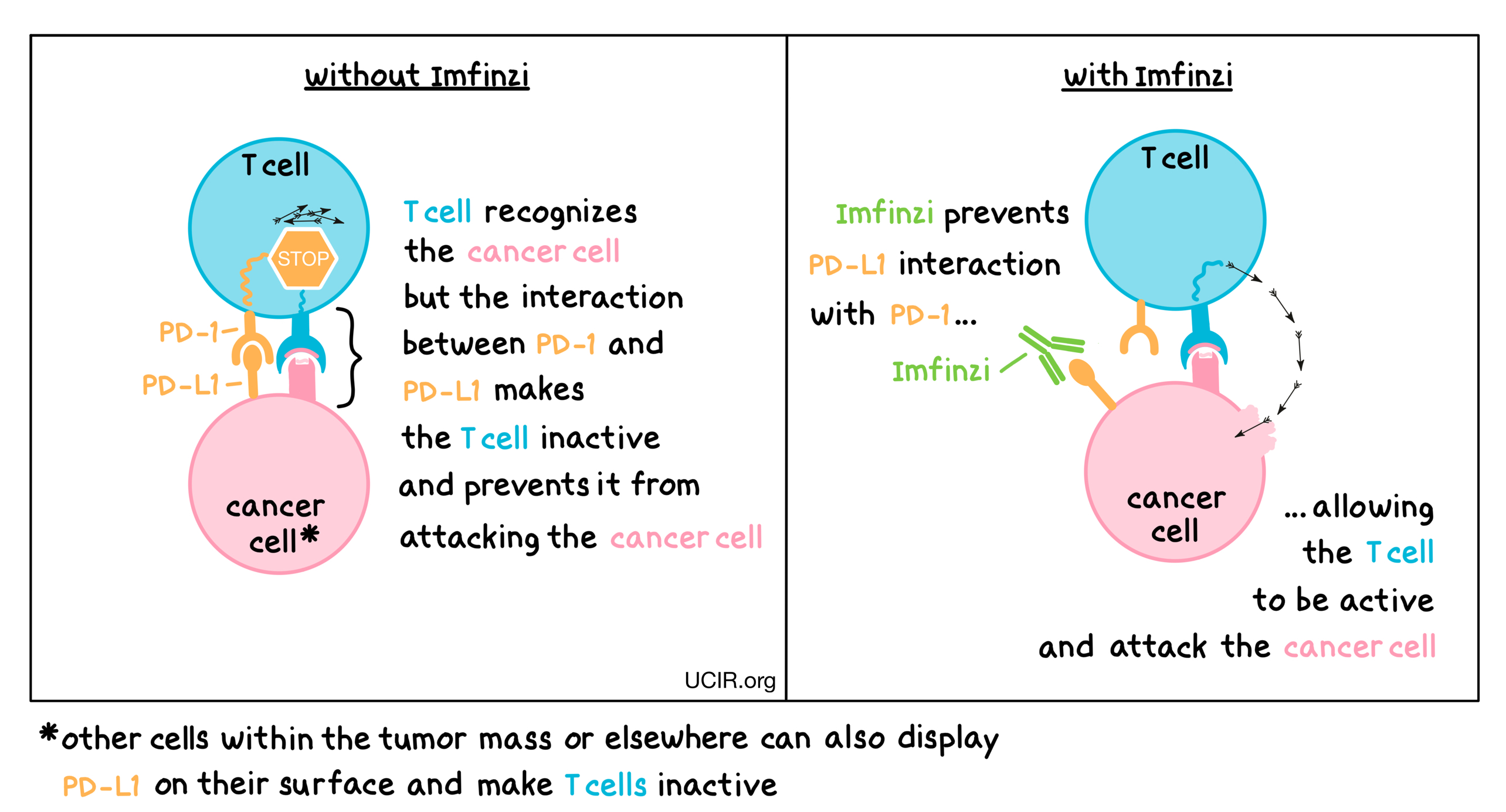
Durvalumab is an immune checkpoint inhibitor that works by blocking a protein called PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1), which is found on the surface of some cancer cells.
Normally, PD-L1 binds to the PD-1 receptor on T cells (a type of immune cell), sending a “stop” signal that prevents the immune system from attacking the cancer. This is a natural mechanism that prevents overactivation of the immune response, but cancer cells can exploit it to avoid being destroyed.
Imfinzi binds to PD-L1 and prevents it from interacting with PD-1 and CD80, effectively releasing the “brakes” on the immune system. This allows T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
It doesn’t directly kill cancer cells—instead, it empowers the patient’s own immune system to fight the tumor more aggressively.
Durvalumab FDA Approvals: A Comprehensive Timeline of Indications
Over the years, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved durvalumab for multiple cancer types, solidifying its importance in modern oncology.
🗓 May 1, 2017
Indication: Locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma
Details: Approved for patients whose disease progressed during or after platinum-based chemotherapy, or within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment.
🗓 February 16, 2018
Indication: Unresectable Stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Details: Approved for patients who have not progressed after concurrent chemoradiotherapy. A key advancement in lung cancer maintenance therapy.
🗓 March 27, 2020
Indication: Extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC)
Details: Approved in combination with etoposide and either carboplatin or cisplatin as first-line treatment.
🗓 September 2, 2022
Indication: Locally advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer
Details: Approved with gemcitabine and cisplatin, offering a new standard of care for a difficult-to-treat cancer.
🗓 June 14, 2024
Indication: Primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer (dMMR)
Details: Approved in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, followed by durvalumab monotherapy for mismatch repair deficient tumors.
🗓 August 15, 2024
Indication: Resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Details: Approved as neoadjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy plus durvalumab, followed by adjuvant durvalumab monotherapy post-surgery.
🗓 December 4, 2024
Indication: Limited-stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC)
Details: Approved for patients with LS-SCLC whose disease has not progressed after concurrent chemotherapy and radiation.
🗓 March 28, 2025
Indication: Muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC)
Details: Approved with gemcitabine and cisplatin as neoadjuvant therapy, followed by adjuvant durvalumab after radical cystectomy.
With each FDA approval, durvalumab has expanded its reach across a wide range of solid tumors, making it a cornerstone of immunotherapy in oncology. From lung and bladder cancer to gynecologic and biliary tract malignancies, durvalumab continues to redefine the treatment landscape with durable responses and improved patient outcomes.
Read more about Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer: Types, Success Rate, Side Effects on OncoDaily.
What research is behind the approval?
Imfinzi’s approval journey spans from 2017 to 2025, supported by a series of pivotal clinical trials. In this section, we’ll explore the key studies behind each approval, highlighting how evidence from research shaped its expanding indications.
Durvalumab for NSCLC
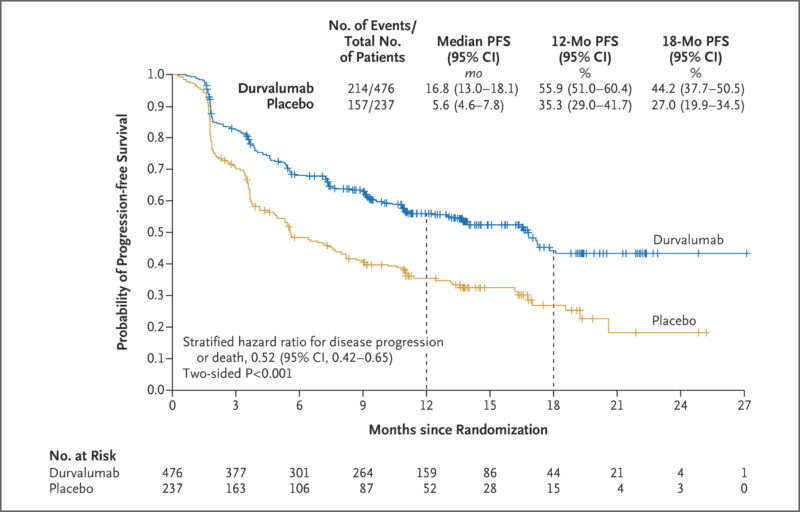
In 2017, a PACIFIC Phase III trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that Imfinzi significantly improved progression-free survival in patients with locally advanced, unresectable stage III NSCLC who had not progressed after chemoradiotherapy. The median progression-free survival with durvalumab was 16.8 months, compared to 5.6 months with placebo. Durvalumab also showed higher response rates and longer duration of response. The safety profile was similar between both groups. These results led to durvalumab’s approval as consolidation therapy in this setting.
Durvalumab for ES-SCLC
In 2019, the CASPIAN trial results were published in The Lancet, showing that Imfinzi combined with platinum–etoposide significantly improved overall survival in treatment-naive patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). The phase 3, randomized trial involved 537 patients across 23 countries, comparing durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide to platinum–etoposide alone. Patients in the durvalumab group had a median overall survival of 13.0 months compared to 10.3 months in the control group, with 34% of patients alive at 18 months versus 25%.
Safety profiles were consistent with expectations, and the combination therapy was well-tolerated. These results led to durvalumab’s approval for use in ES-SCLC as a first-line treatment.
Durvalumab for Biliary Tract Cancer
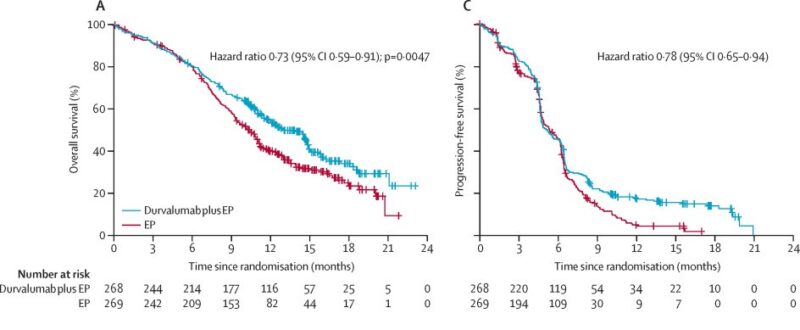
Published in NEJM 2022, the TOPAZ-1 trial assessed durvalumab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced biliary tract cancer, where the standard treatment had remained unchanged for over 10 years. In this phase 3 study, 685 patients received either durvalumab or placebo with gemcitabine and cisplatin. The results showed a 24-month overall survival rate of 24.9% with durvalumab versus 10.4% with placebo (hazard ratio 0.80, P=0.021). Durvalumab also improved progression-free survival and objective response rates, with similar adverse event rates in both groups.

Durvalumab for Endometrial Cancer
The Phase III DUO-E trial, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology in 2023, evaluated the addition of durvalumab—with or without olaparib—to standard chemotherapy in patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. The study showed that both combinations significantly improved progression-free survival, especially in mismatch repair–deficient and PD-L1–positive subgroups. The combination of durvalumab and olaparib offered the greatest benefit, supporting a potential new frontline option for this patient population.

Durvalumab for LS-SCLC
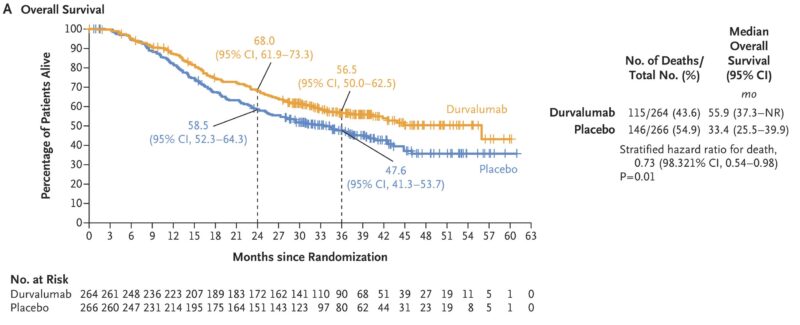
In 2024, results from the ADRIATIC Phase 3 trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine, showing that durvalumab significantly improved overall survival and progression-free survival in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) who had no disease progression after standard chemoradiotherapy. Patients receiving durvalumab (1500 mg every 4 weeks) had a median overall survival of 55.9 months, compared to 33.4 months with placebo. Additionally, durvalumab showed a median progression-free survival of 16.6 months, versus 9.2 months for placebo.
The safety profile was similar between the groups, with 24.4% of patients on durvalumab experiencing severe adverse events. These findings suggest that durvalumab may be an effective adjuvant therapy for this patient population, leading to its potential use in clinical practice.
Durvalumab for Bladder Cancer
In 2024, the NIAGARA Phase 3 trial results were published in The New England Journal of Medicine, demonstrating that perioperative durvalumab combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy improved outcomes for cisplatin-eligible patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Patients who received durvalumab plus chemotherapy had a 24-month event-free survival rate of 67.8%, compared to 59.8% in the chemotherapy-only group. Additionally, the overall survival at 24 months was 82.2% in the durvalumab group, versus 75.2% in the control group.
The addition of durvalumab resulted in better survival outcomes with similar safety profiles between the groups. These findings suggest that adding perioperative immunotherapy to the standard treatment regimen can significantly improve survival in this patient population.

Read more about this approval on OncoDaily.
Durvalumab side effects and its management
Durvalumab, an immunotherapy drug used in treating cancers like non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and bladder cancer, can lead to a range of side effects. These effects vary from mild to severe, and it’s essential for patients to be aware of them so they can receive appropriate management if needed.
Common side effects
Among the most common side effects of Imfinzi are respiratory issues. These can include cough, shortness of breath, and in more serious cases, inflammation of the lungs, known as pneumonitis. This type of lung inflammation can cause discomfort and, if left untreated, can become serious. Gastrointestinal symptoms are also frequent and can include nausea, constipation, abdominal pain, and a general decrease in appetite. Patients may notice these symptoms soon after starting treatment, and they can impact their quality of life.
Another commonly reported side effect is fatigue. Many patients feel general weakness, which can hinder daily activities and make it harder for them to manage their usual routines. Skin reactions are also common, such as rashes, itching, or dryness, which can cause discomfort and may require topical treatments to alleviate the symptoms.
Less Common Side Effects
While rarer, some patients may experience more severe side effects. Durvalumab can trigger immune-mediated conditions, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. These include hepatitis (inflammation of the liver), colitis (inflammation of the colon), and nephritis (inflammation of the kidneys). Symptoms like yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), abdominal pain, or persistent diarrhea should be addressed immediately.
Endocrine disorders are another potential concern.
Imfinzi can affect the thyroid, leading to hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone levels), which can result in symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold. These symptoms can worsen if not properly managed. In rare cases, patients may also experience neurological issues, such as numbness, tingling, or weakness, which could indicate nerve damage or complications.
Serious Side Effects
The most serious side effects of durvalumab are allergic reactions. These can manifest as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or rashes. If a patient experiences these symptoms, immediate medical attention is required. In rare instances, patients may also develop pneumonitis or other severe lung issues that could interfere with breathing and require treatment.
In cases of significant immune-related side effects, doctors may recommend the use of immunosuppressive drugs, such as corticosteroids, to manage inflammation and prevent further complications. Some patients may need to discontinue Imfinzi treatment if these severe side effects occur, especially if they don’t respond to supportive measure.

Mangement of side effects
Managing these side effects typically involves monitoring for any changes in thyroid function, liver enzymes, and kidney function, with regular check-ups. For milder symptoms, symptom management such as anti-nausea medications, pain relievers, or antihistamines can help alleviate discomfort. In cases of more severe immune-related side effects, immune suppression with corticosteroids or other medications may be necessary. If serious adverse effects occur, healthcare providers may recommend treatment modification, which could include adjusting the dosage or even discontinuing the therapy.
What is the Recommended Dosage of Durvalumab?
Durvalumab is available as an injectable solution, with a strength of 50mg/mL in 2.4-mL or 10-mL single-dose vials. It’s used to treat several cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC), and bladder cancer. For patients with stage III NSCLC or limited-stage SCLC, durvalumab is given after chemotherapy and radiation, with doses based on weight: 10 mg/kg IV every 2 weeks for those ≥30 kg, or 1500 mg IV every 4 weeks.
In combination with chemotherapy, Imfinzi is used as neoadjuvant therapy for NSCLC, followed by adjuvant therapy post-surgery. The treatment regimen varies based on weight, with dosages of 1500 mg IV every 3 weeks for those ≥30 kg in neoadjuvant therapy, and continuing with 1500 mg IV every 4 weeks post-surgery.
How is Durvalumab administered?
Durvalumab is administered intravenously, and the solution should be visually inspected for clarity and color before use. It should appear clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow, and free of visible particles. If the solution is cloudy or discolored, discard it. Prepare the dose by withdrawing the required volume from the vial and transferring it to an IV bag with 0.9% NaCl or D5W. Gently invert to mix; do not shake. The final concentration should be between 1-15 mg/mL. The solution must be infused over 1 hour through an IV line with a sterile 0.2- or 0.22-micron filter.
For combination therapy, infuse each drug separately using different infusion bags and filters. The order of infusions varies: with Tremelimumab, infuse it first, followed by durvalumab. With chemotherapy, infuse durvalumab first, then the chemotherapy.
Store unopened vials in the refrigerator at 2-8°C (36-46°F), protected from light. Once prepared, infuse immediately or store the solution for a maximum of 24 hours in the refrigerator or 4 hours at room temperature.
What to Avoid During Durvalumab Treatment?
During Imfinzi treatment, patients should avoid live vaccines, as they may not be effective due to the treatment’s impact on the immune system. It is advised not to mix Imfinzi with other medications in the same IV line and not to stop the treatment without consulting a doctor. If infections or symptoms like fever occur, patients should contact their healthcare provider immediately. Overuse of steroids may interfere with the treatment, so caution is recommended. Smoking is also discouraged, as it may reduce the effectiveness of the treatment. Following the doctor’s instructions is essential for a safe treatment experience.
Durvalumab’s effectiveness over time
Durvalumab has proven effective not only in lung cancer but also in several other cancers, including bladder, endometrial, and urothelial cancers. In bladder cancer, when combined with chemotherapy as a neoadjuvant treatment, it has led to improved event-free survival and overall survival after surgery. In endometrial cancer, Imfinzi has demonstrated significant benefits in patients with mismatch repair-deficient tumors when combined with chemotherapy, followed by single-agent durvalumab. Similarly, in urothelial carcinoma, Imfinzi has shown effectiveness, particularly in combination with chemotherapy, leading to better outcomes in patients with locally advanced or metastatic disease.
Its effectiveness across these cancers highlights Imfinzi’s potential in a variety of malignancies, offering promising survival benefits when used in combination with chemotherapy or as a single-agent adjuvant therapy. However, as with all treatments, its long-term efficacy depends on individual patient factors and disease progression, with treatment typically continued until disease progression or unacceptable side effects occur.
Ongoing trials with Durvalumab
The Phase 2 HAIC-quad trial (NCT06859684) investigates hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) combined with durvalumab and lenvatinib as first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. This approach aims to improve outcomes by enhancing local drug delivery and reducing systemic toxicity compared to standard therapy.
The Phase I/IIa trial (NCT06911255) evaluates the safety and efficacy of combining tremelimumab and durvalumab with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. The study aims to improve progression-free survival, with secondary outcomes including overall survival, response rate, time to progression, and safety.
The Phase 1b trial (NCT06898957) investigates the safety and tolerability of tarlatamab combined with YL201, with or without anti-PD-L1, in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.
Read more about Immunotherapy vs Chemotherapy: Success Rates, Side Effects, Costs Compared on OncoDaily.
Written by Mariam Khachatryan, MD
FAQ
What is Imfinzi used for?
Imfinzi treats several cancers, including lung, bladder, biliary tract, and endometrial cancers. It's often used with chemotherapy or after radiation.
Is Durvalumab a form of chemotherapy?
No, durvalumab is an immunotherapy drug. It helps your immune system fight cancer but is sometimes combined with chemotherapy.
How is durvalumab different from pembrolizumab?
Both are immune checkpoint inhibitors, but Imfinzi targets PD-L1, while pembrolizumab targets PD-1. They are used for different cancers and in different settings.
How long do you take durvalumab?
Treatment usually continues until disease progression or unacceptable side effects—often up to 12 months or more, depending on cancer type.
What are the most common side effects?
Fatigue, cough, skin rash, and nausea are common. More serious effects can include pneumonitis or thyroid issues.
Does Imfinzi weaken the immune system?
It modifies the immune system to fight cancer. It may cause immune-related side effects but doesn’t typically cause immune suppression like chemotherapy.


