
Top GU Immunotherapy Trials to Watch at ESMO 2025
The upcoming ESMO 2025 Congress promises a wave of impactful data across oncology, particularly in the rapidly evolving field of genitourinary (GU) immunotherapy. From biomarker-guided treatment strategies to novel immunologic targets and ADC combinations, a handful of carefully designed clinical trials are set to influence future practice.
Here, we highlight five immunotherapy-focused studies in renal and urothelial cancer that may drive the next era of precision and personalized oncology.
OPTIC RCC Trial Results: Efficacy of Cabozantinib and Nivolumab in Cluster 1/2 Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract: 2591MO
Presenter: Scott M. Haake
Trial Type: Phase II
Session: Mini Oral – GU Tumours (Renal & Urothelial)
OPTIC RCC is among the first clinical trials to integrate RNAseq-defined molecular clusters into therapeutic stratification in metastatic clear cell RCC. This phase II trial evaluates the efficacy of cabozantinib and nivolumab in patients classified as Cluster 1 or 2, based on transcriptomic signatures.
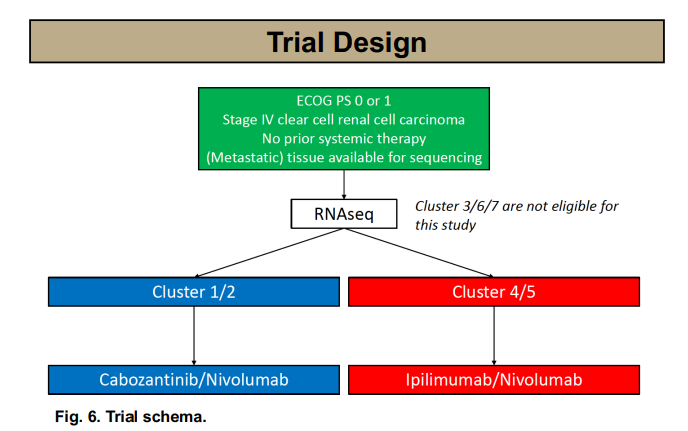
Source: kidneycan.org
Early translational work has suggested that these clusters may carry distinct immune and angiogenic profiles. By aligning targeted therapy with these subtypes, the OPTIC study could define a new standard in molecularly guided first-line treatment.
Why It Matters?
RNA-based classification may surpass traditional IMDC criteria, offering precision IO-TKI combinations.
CheckMate 274: 5-Year Update on Adjuvant Nivolumab in High-Risk MIBC
Abstract: 3068O
Presenter: Matthew D. Galsky
Trial Type: Phase III
Session: Proffered Paper – GU Tumours (Renal & Urothelial)
The long-anticipated 5-year efficacy and ctDNA data from the CheckMate 274 study are a central highlight of ESMO 2025. This trial randomized patients with high-risk muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) post-radical surgery to receive adjuvant nivolumab or placebo.
Source: Adjuvant Nivolumab in High-Risk Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma: Expanded Efficacy From CheckMate 274, Published in JCO 2024
Initial results had already supported FDA and EMA approvals; now, long-term follow-up may solidify OS benefit and validate ctDNA as a dynamic marker of minimal residual disease and recurrence risk.
Why It Matters?
May reinforce adjuvant IO as a new standard and support ctDNA for future risk-adapted surveillance strategies.
DISTINCT-I Trial: Disitamab Vedotin plus Tislelizumab as Nephron-Sparing Therapy for High-Risk Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
Abstract: 3071MO
Presenter: Jiwei Huang
Trial Type: Phase II
Session: Mini Oral – GU Tumours (Renal & Urothelial)
Upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) presents unique challenges due to the risk of renal loss with standard radical surgery. The DISTINCT-I trial explores a nephron-sparing immunotherapy strategy using Tislelizumab (PD-1 inhibitor) combined with Disitamab Vedotin, an anti-HER2 antibody-drug conjugate.
This dual approach aims to preserve renal function without compromising oncologic control—especially relevant in HER2-expressing or high-risk localized tumors.
Why It Matters?
A practice-changing concept if effective, potentially sparing patients from radical nephroureterectomy.
IO Triplet: Ipilimumab + Nivolumab + Ciforadenant in First-Line RCC
Abstract: 2596MO
Presenter: Kathryn Beckermann
Trial Type: Phase 1b/2
Session: Mini Oral – GU Tumours (Renal & Urothelial)
Checkpoint blockade alone fails in a significant subset of RCC patients. This trial investigates a triplet regimen adding Ciforadenant, an adenosine A2a receptor antagonist, to standard IPI/NIVO in advanced RCC.
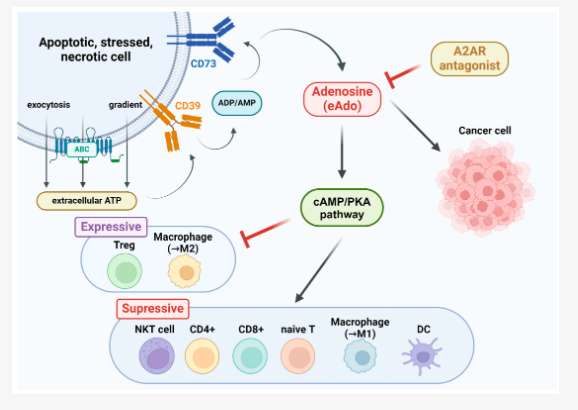
Figure 1. An illustration of the activation of adenosine A2AR and its influences on tumor growth. The occurrence of cell injuries, necrosis, or apoptosis triggers the release of extracellular ATP. CD39, a vascular ATP diphosphohydrolase, then converts the extracellular ATP into ADP/AMP, while CD37, which is similar to CD39, then converts ADP/AMP into extracellular adenosine (eADO). Excessive eADO stimulates the adenosine A2A and A2B receptors and activates the downstream cAMP/PKA pathway. Source: Targeting the Adenosine A2A Receptor as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Mechanisms and Clinical Trial Review
Adenosine signaling is known to mediate immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment, particularly via T cell inhibition. By blocking this axis, the trial targets IO resistance mechanisms at the metabolic level.
Why It Matters?
Offers a window into next-generation IO combinations aimed at overcoming immune escape.
LAG3 Expression as a Predictor of Immunotherapy Response in RCC
Abstract: 2593MO
Presenter: Rana R. McKay
Session: Mini Oral – GU Tumours (Renal & Urothelial)
The role of LAG3 as an immunotherapy target is gaining traction across multiple tumor types. In this translational study, LAG3 expression in metastatic RCC was analyzed in relation to treatment outcomes with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
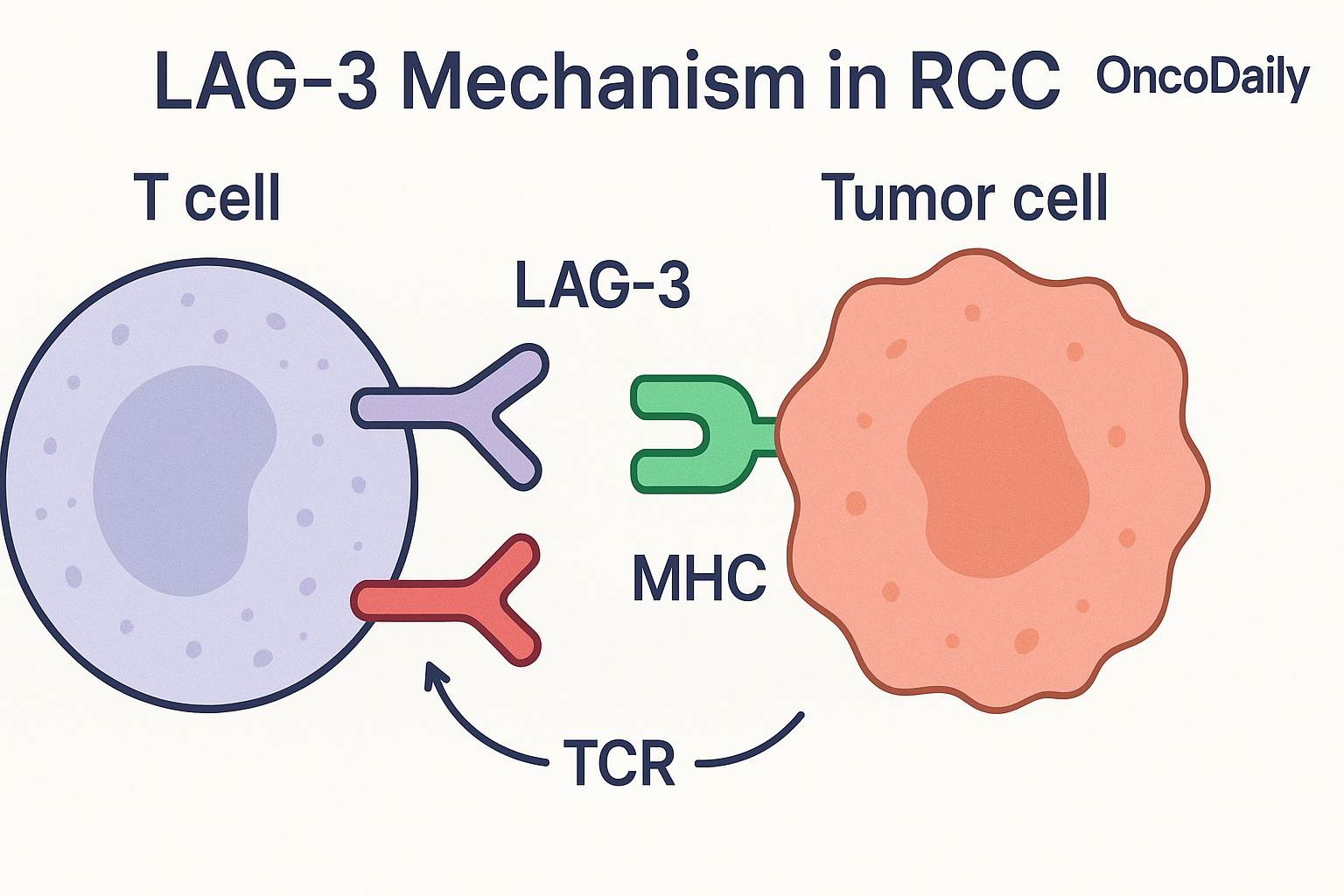
Preliminary findings suggest that high LAG3 expression may correlate with response or resistance patterns, potentially offering biomarker-driven rationale for future dual checkpoint trials (e.g., PD-1 + LAG3 inhibition).
Why It Matters?
Enhances checkpoint biology understanding and supports rational design of future combination regimens.
As the field continues to move beyond “one-size-fits-all” IO, these studies signal a more tailored, mechanistically informed era for genitourinary oncology. Late Braking Abstracts Will be Released Later. ESMO 2025 will be held in Berlin from October 17-21, will showcase groundbreaking discoveries, cutting-edge treatments, and a collaborative approach to shaping the future of cancer care.
You can Read More About ESMO 2025 on OncoDaily

-
Challenging the Status Quo in Colorectal Cancer 2024
December 6-8, 2024
-
ESMO 2024 Congress
September 13-17, 2024
-
ASCO Annual Meeting
May 30 - June 4, 2024
-
Yvonne Award 2024
May 31, 2024
-
OncoThon 2024, Online
Feb. 15, 2024
-
Global Summit on War & Cancer 2023, Online
Dec. 14-16, 2023
